Difference between revisions of "Electric Heat Pumps"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Heat pumps have versatile applications, spanning various power scales and temperature lifts. These range from residential and commercial to industrial settings. The current dominant technology is fossil-fuel-burning boilers which are not sustainable environmentally and not strategic from an energy security perspective. This roadmap will focus on domestic heat pumps for designed residential applications in cold climates. | Heat pumps have versatile applications, spanning various power scales and temperature lifts. These range from residential and commercial to industrial settings. The current dominant technology is fossil-fuel-burning boilers which are not sustainable environmentally and not strategic from an energy security perspective. This roadmap will focus on domestic heat pumps for designed residential applications in cold climates. | ||
[[File: | [[File:Picture4.png]] | ||
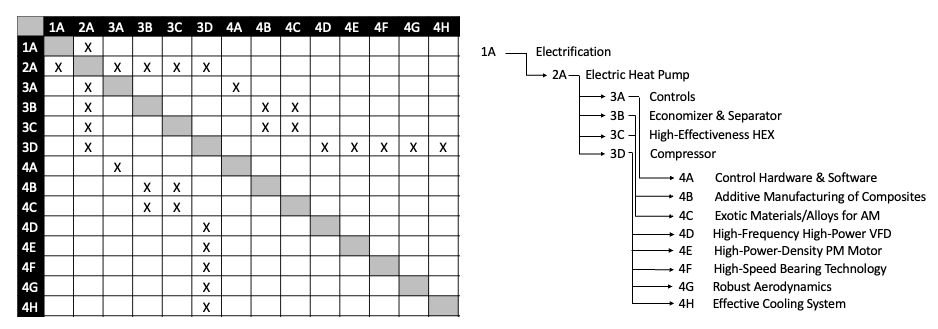
==Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation== | ==Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation== | ||
Revision as of 00:38, 12 October 2023
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
- 2EHP - Electric Heat Pumps
The Electric Heat Pumps (EHP) roadmap is a level 2 roadmap at the product level, which is part of the level 1 roadmap for Electrification (1ELE). Levels 3 and 4 roadmaps would be subsystem and component roadmaps for Electric Heat Pumps (EHP).
Roadmap Overview
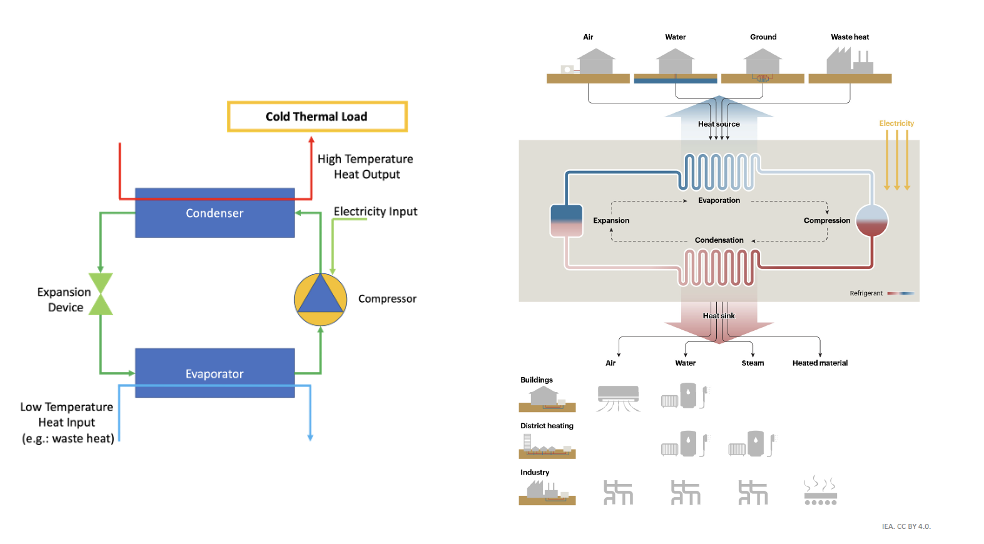
An electric heat pump spatially transfers heat from a low-temperature source to a high-temperature application. This process is based on the thermodynamics of the vapor compression refrigeration cycle, where the heat pump operates in a closed loop with a refrigerant fluid circulating within. In the "evaporator," the refrigerant fluid undergoes a phase change from liquid to vapor at a constant pressure, absorbing heat in the process. Following this, the "compressor" elevates both the pressure and temperature of the refrigerant, preparing it for the "condenser." Here, the refrigerant rejects the absorbed heat and transforms it back from a vapor to a liquid. Finally, an "expansion device" reduces the refrigerant's pressure and temperature back to the levels suitable for the "evaporator", completing the cycle and allowing it to commence anew.
Heat pumps have versatile applications, spanning various power scales and temperature lifts. These range from residential and commercial to industrial settings. The current dominant technology is fossil-fuel-burning boilers which are not sustainable environmentally and not strategic from an energy security perspective. This roadmap will focus on domestic heat pumps for designed residential applications in cold climates.
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
Roadmap Model using OPM
TBD
Figures of Merit
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
TBD
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
TBD
Technical Model
TBD
Financial Model
TBD
List of R&D Projects and Prototypes
TBD
Key Publications, Presentations and Patents
TBD
Technology Strategy Statement
TBD
References
TBD