Difference between revisions of "Battery Electric Vehicle Platforms"
| Line 149: | Line 149: | ||
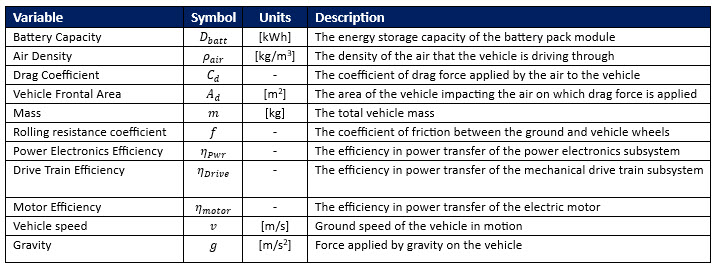
[[File:BEV Variables.jpg]] | [[File:BEV Variables.jpg]] | ||
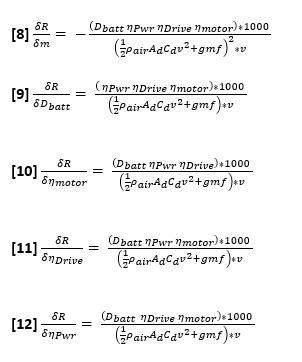
The variables in the range equation above can be adjusted to impact the range as shown in the derivatives below. Changes to the range are limiated to variables, which are not fixed / constant. Those that cannot be varied include constants such as air density, gravity, drag coefficient, the rolling resistance coefficient, and the vehicle speed (which is controlled by the driver, not directly by design). By varying the mass of the platform, the efficiency of the motor, power electronics, and drive train, and by adjusting the battery capacity (based on pack size), the range of the BEV platform ma in turn be adjusted. | |||
[[File:BEV Derive.jpg]] | |||
To examine the impact of these indivdual variables, derivatives above were normalized and the values of such were plotted in the tornado chart below. From this it can be seen that ... | |||
==Financial Model== | ==Financial Model== | ||
Revision as of 14:46, 1 November 2023
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
- 2BEV - Battery Electric Vehicle Platforms
The Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) platform, a level 2 roadmap, represents the critical product/system of the Battery Electric Platform that is integrated within a broader electrified vehicle. The level 1 system above the BEV is the electrified vehicle market segment, which includes other types of electrified vehicles (e.g., FCEV's, PHEV's, etc.) as well as the other vital systems that comprise electrified vehicles (e.g., steer-by-wire systems). Level 3 roadmaps represent critical subsystems within a BEV platform-based electrified vehicle, and level 4 roadmaps would indicate an individual component technology roadmap.
Roadmap Overview
Electrified vehicles (PHEV, BEV, FCV, etc.) are vehicles that utilize electric power (from a variety of different sources, such as batteries or fuel cells) to power an electric motor-based propulsion system. Electrified vehicles are an increasingly popular alternative to traditional gas-powered vehicles that generate propulsion through internal combustion engines. Electrified vehicles are one part of a broader ecosystem of solutions being used to combat the evolving problem/challenge of climate change. Electric vehicles help to solve this problem by providing humanity with an alternate mode of transportation that does not produce harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
This roadmap will focus specifically on the battery electric vehicle (BEV) platform. BEV platforms are becoming increasingly popular as consumers seek different options within the electric vehicle market, and manufacturers look for ways to meet this customer demand through the use of modular architectures that multiple different vehicle variants may be built upon. Modular architectures / platforms for battery electric vehicles are typically comprised of a battery pack, on board charging module, integrated power electronics, drive units, and a chassis will a wheel base. Multiple different vehicle bodies and accompanying features may then be built upon these platforms. Below are two examples BEV platforms being produced today (one by Tesla Motors, and one by General Motors).
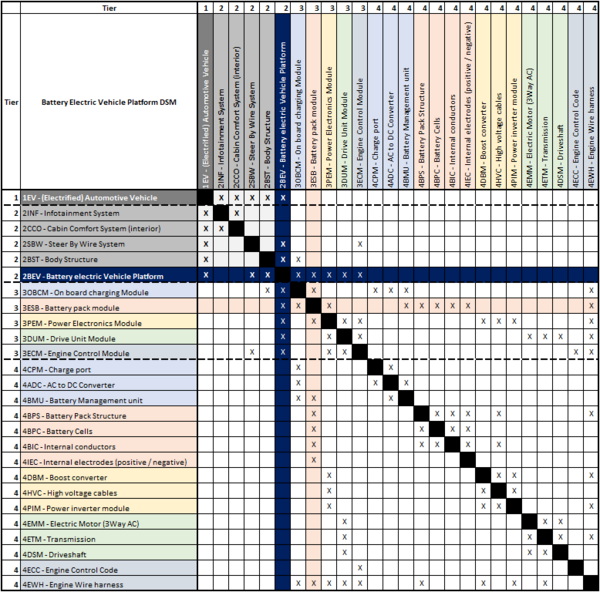
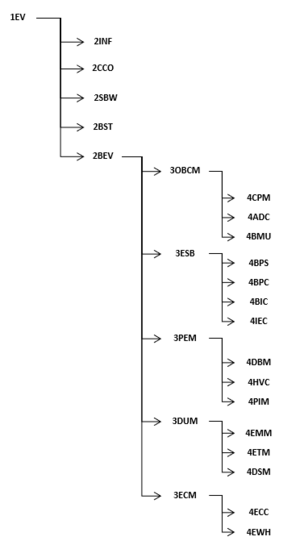
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
Our technology of interest, battery electric vehicle platforms, is identified in the DSM below with dark blue highlighting at level 2 (2BEV). Additionally, we also show a tree structure that decomposes into the systems, and subsystems that comprise our level 2 technology. The DSM shows how these critical systems and subsystems interact to comprise the battery electric vehicle platform. For example, we see that a critical subsystem is the level 3 battery pack module, which is color-coded to indicate that it has its own, existing technology roadmap (3ESB - Energy_Storage_via_Battery). The battery pack module (or Energy Storage Battery) is comprised of the battery cells, pack structure, and other subsystems. The battery cells break down into their individual components (anode, cathode, etc.) that generate electrons to conduct electricity. However, we also see the interdependency between the battery pack structure and the high voltage cables, which in turn have a connection to the power inverter module. All this is to say that the interconnected nature of subsystems within a BEV platform critically come together to create the emergence exhibited by a battery electric vehicle.
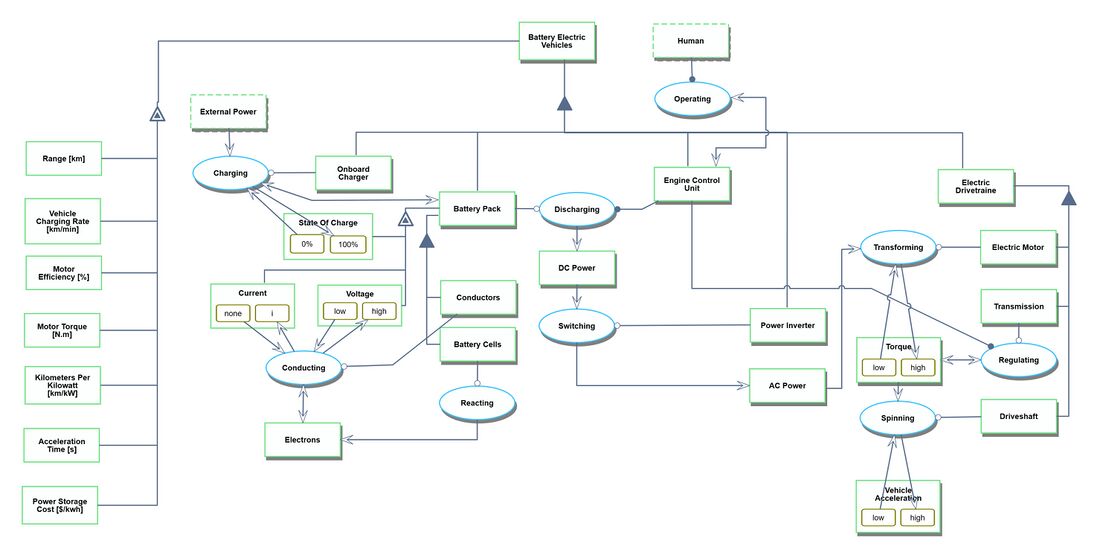
Roadmap Model using OPM
We provide an Object-Process-Diagram (OPD) of the Battery Electric Vehicle (BEV) Platform in the figure below. This diagrams captures the main object of the technology (Battery Electric Vehicle), the value-generating processes and different instruments associated with their characterization by Figures of Merit (FoM).
An Object-Process-Language (OPL) description of the roadmap scope is auto-generated and given in OPL_Battery_Electric_Vehicle. It reflects the same content as the previous figure, but in a formal natural language.
Figures of Merit
The table below summarizes the figures of merit used to evaluate battery electric vehicle platform technologies. Some of these figures of merit, such as range and acceleration, are very similar to the figures of merit used to evaluate traditional automotive vehicle. Other figures of merit, such as power storage cost and charge rate, are critical to evaluating the battery pack technology employed within the battery electric vehicle as well as the battery electric vehicle platform itself. Finally, FOM's such as carbon dioxide emissions and kilometers per kilowatt are very specific FOM's to battery electric vehicle platform technologies in totality.
| Figure of Merit (FOM) | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Range | [km] | The number of miles the vehicle can travel on a single full charge |
| Acceleration time | [s] | Time to accelerate to from 0 to 100 kmh (km per hour) |
| Motor Torque | [N.m] | Torque produced by the electric vehicle motor |
| Motor Efficiency | [%] | Percentage of energy discharged from the battery pack that is converted to mechanical energy |
| Kilometers per kilowatt | [km / kw] | The average distance the vehicle travels based upon the amount of energy used |
| Vehicle charge rate | [km/min] | The rate at which vehicle range (in km) is added to the BEV platform during charging |
| Power Storage Cost | [$/kWh] | Total cost of power storage within a BEV platform (at the battery pack level) in dollars per kilowatt |
| Carbon Dioxide Emissions | [g/km] | The total amount of carbon dioxide emissions generated by the vehicle platform per mile driven |
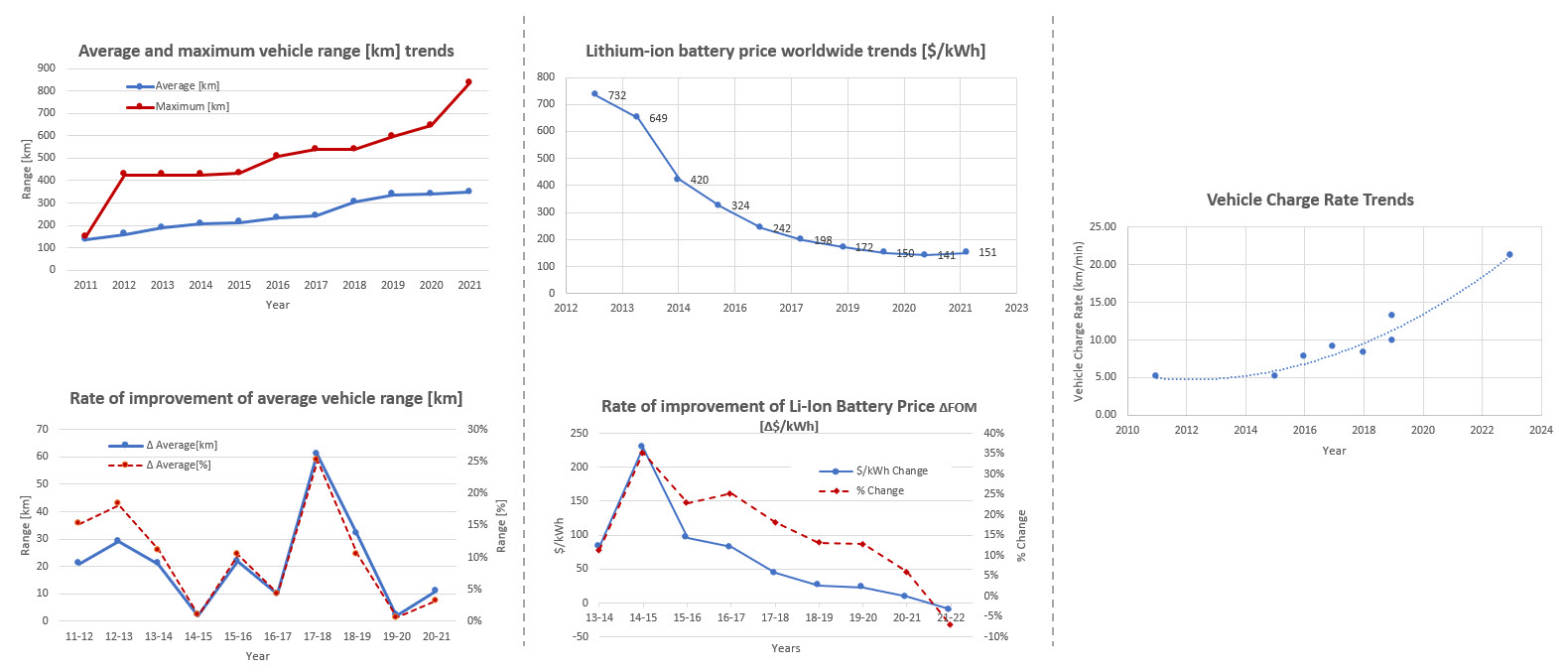
Below are some trends related to the figures of merit listed above. The charts show that the range of battery vehicles has been steadily increasing over the past decade, all while battery prices have rapidly declined. Both of these factors have contributed to increasing adoption of battery electric vehicle platforms, as the cost and performance of these systems continue to rise. Finally, charging trends are improving substantially, as new technology around superchargers enters the market (on both the BEV platform and charging station sides of the interface).
In addition to the figures of merit shown above, some of the key governing equations for battery electric vehicles are shown below.
| Input | Key Relationship or Governing Equation | Output |
|---|---|---|
|
ηm = P_out / P_in | ηm : motor efficiency (expressed as a %) |
|
T = (V_ac* I_ac * p_f ) / ((2π* N_rpm )/60) | T = motor torque |
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
The Automotive industry as a whole is in the midst of significant disruption. The market is shifting as new entrants such as Tesla, Rivian, and others bring advanced technology and supporting capabilities to a customer base wanting of change. As our organization prepares to remain competitive with the likes of Tesla, Rivians, and others, there are three key pillars to our response in the market. First is embracing the transportation transformation. This means that we must realize that our customer base has a desire for an entirely new propulsion option when choosing the vehicle that they purchase. Customers want a vehicle with low or no emissions, and as such we must be prepared to offer this to them. In our case, this will be via a battery electric vehicle. Second is modularity and commonization of key subsystems and components. A key success factor to our ability to deliver new BEV platforms will be ensuring that we have identified where we can modularize major sub-systems and components, so that they can be easily reused across current and future platforms. Our third pillar is interoperability and integration. As our vehicles go out into the market, they cannot operate on their own any longer. We need to ensure that we have a level of interoperability with new infrastructure being brought online (e.g., charging stations of any brand), and we also must ensure that our products are integrated in a way that allows us to track the performance of vehicles in the field, deliver insights and diagnostics, and provide new features and updates to our customers.
Listed below are the strategic drivers for the company, and the alignment targets of our roadmap with these drivers:
| Number | Strategic Drivers | Alignment targets |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | To develop a set of battery electric vehicle platforms that will be utilized across all future vehicle production, with optimization of market segment coverage kept in mind and with the ability to scale the platform as necessary to meet the different needs of specific customers. The design of these platforms should minimize CAPEX and OPEX expenditures by allowing for engineering and design focus on a set of modular subsystems across platforms as well as commonization across manufacturing lines used to produce the platforms (reducing the cost of specified equipment). | The 2BEV roadmap is aligned to this strategic driver. This roadmap will support this strategic driver by identifying where modularity can be employed across a platform to better enable optimization of platforms within market segments defined by the organization. |
| 2 | To develop a battery electric vehicle platform that has an appropriate range for customers seeking to replace their existing internal combustion engine vehicle with a battery powered electric vehicle. | The 2BEV roadmap is aligned to this strategic driver. The battery electric vehicle platform roadmap will target 1000 km as the desired maximum range of the BEV platform that is developd. This is benchmarked off of the top end range of internal combustion engine vehicles on the market today. |
| 3 | To support integration of battery electric vehicle platforms with critical external interfaces to better enable customer experience in areas such as charging, vehicle feature release, etc. | The 2BEV roadmap is aligned to this strategic driver. The battery electric vehicle platform roadmap will ensure compliance with the latest SAE charging protocols (e.g., charge port configuration), as well as other industry standards for key functions such as software development and deployment (e.g., AutoSar standards for OTA configuration). |
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
The images and table below show examples of other battery electric vehicle platforms available on the market today (or previously available on the market) along with representative data points for key figures of merit that BEV platforms are evaluated upon.
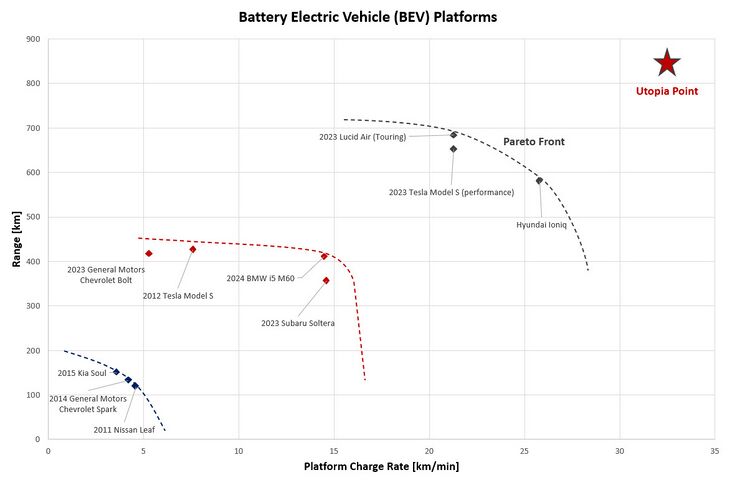
| Manufacturer | Model | Model Year | Range [km] | Battery Size [kwh] | Acceleration Time [s] | Vehicle Charge Rate [km/min] | Max Torque [N.m] | Electric Drive Configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| General Motors | Chevrolet Bolt | 2023 | 416 | 65 | 6.5 | 5.3 | 360 | Single Electric Motor (FWD) |
| Tesla | Model S (performance) | 2023 | 652 | 100 | 2.4 | 21.3 | 967 | Dual Electric Motors |
| Lucid | Air (Touring) | 2023 | 684 | 94 | 3.4 | 21.3 | 1200 | Dual Electric Motors |
| BMW | i5 M60 | 2024 | 411 | 84 | 3.7 | 14.5 | 795 | Dual Electric Motors |
| Subaru | Soltera | 2023 | 357 | 73 | 6.5 | 14.6 | 338 | Dual Electric Motors |
| Nissan | Leaf | 2011 | 118 | 24 | 9.9 | 4.6 | 280 | Single Electric Motor (FWD) |
| Kia | Soul | 2015 | 150 | 30.5 | 11.2 | 3.6 | 285 | Single Electric Motor (FWD) |
| Tesla | Model S | 2012 | 426.5 | 85 | 5.4 | 7.6 | 440 | Single Electric Motor (RWD) |
| General Motors | Chevrolet Spark | 2014 | 132 | 21.3 | 7.9 | 4.2 | 542 | Single Electric Motor (FWD) |
| Hyundai | IONIQ | 2023 | 581 | 77 | 5.1 | 25.8 | 350 | Dual Electric Motors |
Below is a graph of range [km] vs vehicle charging rate [km/min] for the BEV platforms listed in the table above. This chart illustrates how the pareto front of BEV platform performance has shifted over time as it relates to the key FOM's of range and charging rate. In the bottom left of the chart, there is a cluster of early mass-production BEV platforms such as the Nissan Leaf and the Chevy Spark. In the middle of the chart, we see current-day BEV platforms such as the Chevy Bolt and BMW i5 M60. Towards the upper right side of the chart, we see a high-performing group of current-day BEV platforms in the Tesla Model S (performance), the Lucid Air, and the Hyundai Ioniq. This group of high-performing current-day mass production BEV platforms form the pareto front for existing advancement in BEV platform technology.
This chart also shows how specific manufacturers have improved the performance of their technology over time, and what tradeoffs they have made in doing so. For example, General Motors (parent company of the brand Chevrolet) made significant improvements in vehicle range between their 2014 Chevy Spark and their 2023 Chevy Bolt. However, they made only marginal improvements in the performance of vehicle charging rate. On the other hand, Tesla made considerable improvements in both of these areas between their 2012 version of the Tesla Model S and their 2023 Tesla Model S (performance edition). It is also interesting to note that companies like Tesla truly appear to be pushing the Pareto front forward with their latest BEV platforms. They had the most advanced platform on the road when they introduced the model S in 2012, and the latest version of this BEV platform is also near the edge of the pareto front.
Technical Model
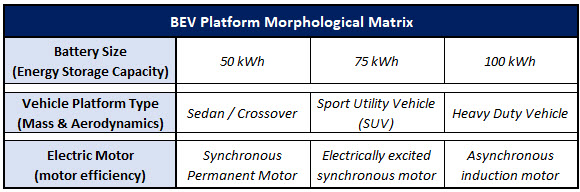
In order to assess the feasibility of the technical targets that we have set, at the level of the battery electric vehicle platform roadmap, we have developed a technical model. The purpose of this model is to evaluate the sensitivity of key FOM's (representing progress in technology development) to individual variables that can be adjusted through different architectural and design decisions. As a first step, we have compiled a morphological matrix that represents a set of options available in our future architectural decision-making process:
The morphological matrix for the battery electric vehicle technology represents decisions that can be made around several of the underlying technologies that comprise battery electric vehicle platforms. The selection of different options in these categories represents an impact to individual variables that describe the governing range equation associated with battery electric vehicle performance. Specifically, the variables impacted are those in the parametrized equation representing vehicle driving range. Below is the equation for battery electric vehicle range [equation 1], as well as the decomposition of battery electric vehicle range into underlying, foundational variable parameters [equation 7]. Adjustment to any of the variables shown below will impact the resultant range that a BEV platform may drive.
The variables in the range equation above can be adjusted to impact the range as shown in the derivatives below. Changes to the range are limiated to variables, which are not fixed / constant. Those that cannot be varied include constants such as air density, gravity, drag coefficient, the rolling resistance coefficient, and the vehicle speed (which is controlled by the driver, not directly by design). By varying the mass of the platform, the efficiency of the motor, power electronics, and drive train, and by adjusting the battery capacity (based on pack size), the range of the BEV platform ma in turn be adjusted.
To examine the impact of these indivdual variables, derivatives above were normalized and the values of such were plotted in the tornado chart below. From this it can be seen that ...
Financial Model
TBD
List of R&D Projects and Prototypes
TBD
Key Publications, Presentations and Patents
The following are a representative set of patents that have contributed to the overall development of Battery Electric Vehicle Platforms. Battery electric vehicle platforms fall under the umbrella CPC code of B60L - "Propulsion of electrically propelled vehicles". Many of the patents describing advances in subcomponent technology, control algorithms, etc. can be found beneath even more detailed CPC codes such as B60L 50/60 ("Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle using power supplied by batteries), B60L 50/51 ("electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle using propulsion power supplied by batteries or fuel cells characterized by AC-motors”), and B60L 15/20 ("methods for controlling the traction motor speed of electrically-propelled vehicles").
High Power Low Voltage Electrified Powertrain
- US Patent: 9484852 B2
- Assignee: FCA US LLC
- Inventors: Timmons, Adam, Anand Sathyan, and Marian Mirowski
- Year:2016
- Description: This patent represents a way in which 4 low voltage battery modules could be used to power an electric motor by providing 4 distinct DC voltages to a power inverter that then switches the DC power to AC power to drive an electric motor of 4 or more phases. This represents one potential approach to how a BEV platform could be configured.
Electrified Powertrain With Maximum Performance Mode Control Strategy Using Extended Inverter Limit
- US Patent: 2022/1069237
- Assignee: GM Global Technology Operations LLC
- Inventors: Hu, Yiran, Gagas Brent, Kee Kim, James Creehan, and Brian Welchko
- Year:2022
- Description: This patent describes the concept of electrified powertrain maximum performance mode control strategy using extended inverter limit.
System and Method of Controlling Power Distribution From Charging Source to Electric Vehicle
- US Patent: 2021/0031643 A1
- Assignee: GM Global Technology Operations LLC
- Inventors: Wang, Yue-Yun, J Brooks, Jun-Mo Kang, and Donald Grimm
- Year:2021
- Description: This patent describes the concept of controlling power distribution from a charging source to electric vehicle, including how the state of charge of the battery is controlled during the charging process.
In addition to the many patents published on concepts that comprise battery electric vehicle platforms, many articles have also been published to describe BEV's, their market progression, and example architectures. Some early examples of articles that reviewed the BEV technology readiness and BEV technology progress are below:
- Andwari, Amin, Apostolos Pesiridis, Srithar Rajoo, Ricardo Martinez-Botas, and Vahid Esfahanian. “A Review of Battery Electric Vehicle Technology and Readiness Levels.” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 78 (2017): 414–30.
- Sun, Xiaoli, Zhengguo Li, Xiaolin Wang, and Chengjiang Li. “Technology Development of Electric Vehicles: A Review.” Energies 13, no. 1 (2019): 90.
Technology Strategy Statement
TBD
References
[1] Szczesny, Joseph. “GM Targeting Bigger Share of Bev Market, CEO Barra Says.” WardsAuto, June 16, 2022. https://www.wardsauto.com/industry-news/gm-targeting-bigger-share-bev-market-ceo-barra-says.
[2] Seabaugh, Christian. “Beyond Plaid: A Quad-Motor Tesla Model S Is Possible.” MotorTrend, June 18, 2021. https://www.motortrend.com/news/tesla-model-s-quad-motor-report/.
[3] Ritchie, Hannah. “The End of Range Anxiety: How Has the Range of Electric Cars Changed over Time?” Sustainability by numbers, February 27, 2023. https://www.sustainabilitybynumbers.com/p/electric-car-range.
[4] 2023 Bloomberg Finance L.P. (2022, December 6). Lithium-ion battery pack prices rise for first time to an average of $151/kwh. BloombergNEF. https://about.bnef.com/blog/lithium-ion-battery-pack-prices-rise-for-first-time-to-an average-of-151-kwh/
[5] Cai, Wenlong, Yu-Xing Yao, Gao-Long Zhu, Chong Yan, Li-Li Jiang, Chuanxin He, Jia-Qi Huang, and Qiang Zhang. “A Review on Energy Chemistry of Fast-Charging Anodes.” Chemical Society Reviews 49, no. 12 (June 2020): 3806–33. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cs00728h.