Difference between revisions of "Satellite Communications 5G NTN D2D"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==DSM Allocation== | ==DSM Allocation== | ||
<gallery heights="400" widths =" | <gallery heights="400" widths ="500"> | ||
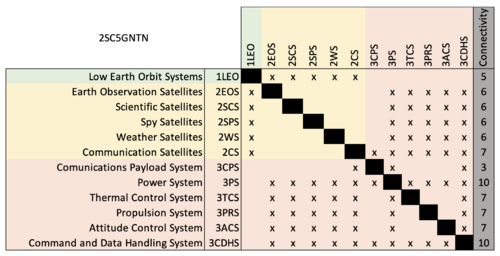
File:SC DSM Updated.png|Connectivity DSM | File:SC DSM Updated.png|Connectivity DSM | ||
File:SatComms Tree.jpg|Tree | File:SatComms Tree.jpg|2SC5GNTND2D Tree | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 19:17, 9 October 2024
Roadmap Overview
Communication satellites play a critical role in enabling global telecommunications. These artificial satellites ensure connectivity even in the world's most remote regions. There are various uses for satellite communications technology, including TV broadcasting, telephone services, internet access, navigation, military tactical communications, and others. Recently, with 3GPP release 17 and the standardization of non-terrestrial 5G networks (5G NTN), a new frontier for satellite communications has been defined -- direct-to-device communications. This advancement has resulted in significant interest and investment from both new and established market players, all competing for the largest market share. Additionally, mobile device manufacturers are now developing compatible user equipment, creating a dynamic, double-sided market that is about to experience a significant expansion.
This roadmap focuses on Low Earth Orbit (LEO) communication satellites used in 5G Non-Terrestrial Networks (NTN) for direct-to-device communications. LEO satellites, operating at altitudes ranging from 180 to 2,000 kilometers, constitute the primary choice for non-terrestrial 5G applications. These satellites have attracted considerable attention because of their advantages, including lower latency and increased communication speeds, which are beneficial for real-time applications such as high-speed internet. By being in an LEO orbit, the coverage of a single satellite is reduced; however, deploying a satellite constellation working in tandem can enhance throughput and coverage. LEO satellites are also cheaper to build, and due to their size, they can often be sent to space as a secondary payload. This reduced cost and direct-to-device potential have led to new entrants to the satellite communications market, such as Lynk Global, AST SpaceMobile, and Amazon Kuiper, with the big existing player Starlink.
DSM Allocation
- SatComms Tree.jpg
2SC5GNTND2D Tree