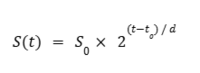Difference between revisions of "2ADS Autonomous Drone Swarms"
| (48 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Autonomous Drone Swarms= | =Autonomous Drone Swarms= | ||
==Roadmap Overview== | ==Roadmap Overview== | ||
Autonomous drone swarms are a collection of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that collaborate to perform a task with minimal human intervention. These drones take some information from a ground control station to outline the task but mainly rely on their own autonomous decision making to perform that task and synchronize with other drones in the swarm. Swarms can range from a few to thousands of drones depending on the application and the maturity of the technology used in these drones. Drone | Autonomous drone swarms are a collection of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that collaborate to perform a task with minimal human intervention. These drones take some information from a ground control station to outline the task but mainly rely on their own autonomous decision making to perform that task and synchronize with other drones in the swarm. Swarms can range from a few to thousands of drones depending on the application and the maturity of the technology used in these drones. | ||
The '''2ADS - Autonomous Drone Swarms''' identifier represents a Level 2 technology roadmap that pertains to product-level aspects of Autonomous Drone Swarms. | |||
[[File:Drones.png|500px]] | [[File:Drones.png|500px]] | ||
Key features of autonomous drone swarms are as follows: | |||
* '''Collective behavior''': Drones in a swarm coordinate their actions, sharing data, relative locations (through GPS or other mechanisms in GPS-denied environments) and reacting to environmental stimuli in real-time. | |||
* '''Distributed sensing''': Swarms can cover vast areas simultaneously, gathering data from multiple sensors to enhance situational awareness and enable detailed mapping, environmental monitoring, and disaster assessment. | |||
* '''High reliability''': The failure of a single drone does not lead to an overall failure of the swarm due to redundancies, ensuring reliability in mission critical settings. | |||
* '''Adaptability''': Autonomous swarms can use artificial intelligence techniques to respond to new or unexpected situations. | |||
Due to the above features, autonomous drone swarms have extensive high-impact use-cases such as: | |||
* '''Military operations''': reconnaissance, electronic warfare, payload delivery | |||
* '''Disaster response''': search and rescue, wildfire fighting, damage assessments | |||
* '''Agriculture''': crop monitoring, harvesting, pollination | |||
* '''Entertainment''': aerial light shows replacing fireworks | |||
Autonomous drone swarms are disruptive innovation since they offer previously impossible capabilities such as large-scale coordinated aerial operations with minimal/no human control. Drone swarms have the potential to disrupt multiple markets simultaneously, from military operations to agriculture and entertainment. This is a broad impact across various sectors instead of focused improvements on existing markets. | |||
Thus, the focus of this research will be the technological advancements in edge compute, drone hardware and swarm algorithms that have enabled the development of drone swarms and a prediction of where this technology will go next. We will analyze all the developments within the military application space since it is the most rapidly maturing application of drone swarms. Ultimately, drone swarms will revolutionize how we approach distributed tasks and bring us closer to emulating the swarm behaviors we see in nature. | |||
==DSM Allocation== | ==DSM Allocation== | ||
Autonomous Drone Swarms can be broken down into the following technologies that have some inter-dependencies. | Autonomous Drone Swarms can be broken down into the following technologies that have some inter-dependencies. Autonomous Drone Swarms at the product level relies heavily on the product roadmap of drone technology since 2ADS is a composition of multiple units of 2D. 3FCS has many inter-dependencies with 3ES since the flight control system needs the components in the electrical system. | ||
The high levels of inter-dependencies show that while individual technologies can improve certain operating characteristics of a single drone, multiple technologies need to advance together to realize the full benefits of autonomous drone swarms. For example, better batteries, more efficient motors and advanced autonomy software can significantly improve the flight time FOM. | |||
'''DSM''' | |||
1SR Swarm Robotics | 1SR Swarm Robotics | ||
| Line 28: | Line 53: | ||
::: 4RTR Radio Transmitter & Receiver | ::: 4RTR Radio Transmitter & Receiver | ||
::: 4LIO Lithium Ion Batteries | ::: 4LIO Lithium Ion Batteries | ||
[[File:NewdroneDSM.PNG]] | [[File:NewdroneDSM.PNG]] | ||
==OPM | ==OPM== | ||
The main physical components of the drone swarm are individual drones and the control station. The drone swarm has a few key operations: | |||
* Commanding - manages the interactions between the drones in the swarm and the control station | |||
* Flying - translates the flight commands into physical motion of the drone | |||
* Decision Making - assess the environment and task instructions to generate flight commands | |||
* Charging - recharges the drone | |||
[[File:Drone_OPM.PNG]] | [[File:Drone_OPM.PNG]] | ||
| Line 40: | Line 71: | ||
==Figures of Merit (FOM)== | ==Figures of Merit (FOM)== | ||
There are a number of FOMs applicable to the 2ADS product roadmap. Swarm size and cost are FOMs attributed to the entire drone swarm system while the remaining FOMs are for an individual drone. The most important FOM for the drone swarm is the number of drones in the swarm while the most important FOM for an individual drone is endurance. Swarm size is analyzed in more detail below the table; endurance is analyzed in the technical model section. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 69: | Line 102: | ||
| [ms] | | [ms] | ||
| How quickly a drone can respond to commands from a control center or react to signals from other drones. Lower latency systems will be safer. | | How quickly a drone can respond to commands from a control center or react to signals from other drones. Lower latency systems will be safer. | ||
|- | |||
| Mass | |||
| [kg] | |||
| Overall mass of drone. Affects other FOMs such as endurance. | |||
|} | |} | ||
== | |||
===Deep Dive into Swarm Size FOM=== | |||
We can analyze the trends and factors affecting swarm size to attempt a quantitative model of improvement over time. The following factors affect UAV drone swarm size: | |||
*Algorithmic complexity: Primary limit on drone swarm size is the development of algorithms and systems to coordinate drones receiving increasingly complex information | |||
*Computing power: As computing power grows, the capacity to manage information exchanges between more drones increases | |||
*Energy density: Ongoing research in energy density increases payload capacity and flight endurance of unmanned platforms | |||
*Communication capabilities: Communication bandwidth and protocols are necessary for coordination among swarm members | |||
*Cost: As swarms become more sophisticated, production costs may increase, potentially limiting strategic value | |||
To quantitatively model the rate of improvement, we create a simple model based on Moore’s law, assuming that the key factors we have described above (particularly algorithmic complexity, computing power, communication capabilities and energy density) follow similar/comparable growth trajectories. | |||
Thus, we define our model as: | |||
[[File:Swarm-eq.PNG|200px]] | |||
Where: | |||
* S(t) is the swarm size at time t | |||
* S_0 is the initial swarm size at time t_0 | |||
* t is the current year | |||
* t_0 is the base year | |||
* d is the doubling period in years | |||
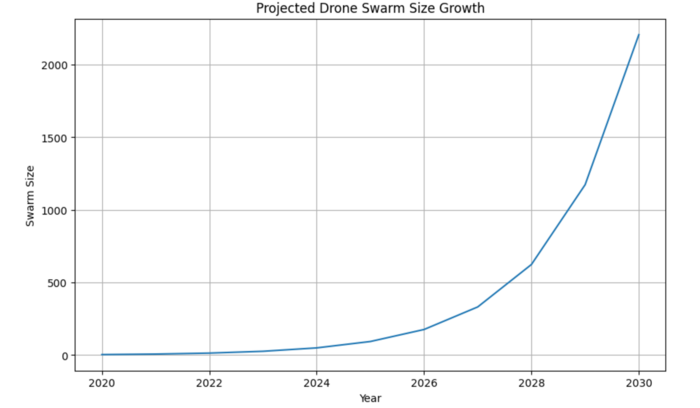
Based on known swarm sizes over time, we can plot the trajectory of growth of Swarm Size as follows: | |||
[[File:Swarm-growth.PNG|700px]] | |||
This model projects infinite exponential growth in swarm sizes over time. While there is no theoretical limit to swarm sizes, there are practical limitations which could lead to growth slowing down over time. Some of these practical considerations are as follows: | |||
* Cost: As swarm sizes increase, the total cost may become prohibitive for many applications. | |||
* Regulatory limits: Current regulations (including those imposed by the FAA) often restrict drone operations, which may limit practical swarm sizes in certain contexts | |||
We estimate that this technology is in the rapid progress phase of the S-curve. This is supported by the following details: | |||
* The technology has moved beyond the initial concept and early prototypes, and is thus past the Incubation phase. Successful demonstrations and tests with over 100 drones have been conducted. | |||
* Significant progress in drone swarm technology in recent years. For example, Airbus and Quantum Systems successfully tested AI-driven drone swarm technology for the German Armed Forces in September 2024 [ref, ref, ref]. | |||
* Increasing Capabilities: Recent tests have demonstrated advanced features such as AI-powered coordination of mixed UAS swarms, real-time merging of reconnaissance data, and | |||
autonomous mission execution in GPS-denied conditions | |||
While advancing rapidly, drone swarms have not reached widespread adoption or maturity. Many applications are still in theoretical, early or test phases. | |||
==Alignment with Company Drivers== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 99: | Line 175: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Company | ==Company Positioning vs. Competition== | ||
The following table summarizes the positioning of various drones manufactured by the top UAV companies. Individual drones are typically compared based on the FOMs of range and endurance. Comparing these FOMs to mass allows us to observe how these drones tradeoff between key FOMs and mass. The drones that do this most effectively will exist on the leading edge of the pareto front. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 137: | Line 215: | ||
| 11 | | 11 | ||
|} | |} | ||
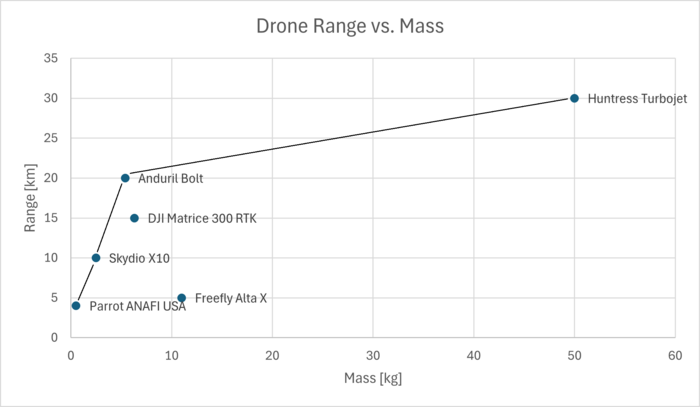
The Parrot ANAFI, Anduril Bolt and Huntress Turbojet are some products that exist on the pareto frontier of both range and endurance. These drones also exhibit differences in use cases that make sense at their positions of the pareto front. | |||
* Parrot ANAFI is light and ideal for short distances, hence it is used primarily for photography | |||
* Huntress Turbojet is heavy and built for long distance travel, hence it is used for payload transfer | |||
* Anduril Bolt has average mass and range, hence it is used for both reconnaissance and payload transfer | |||
[[File:ADSrange.png|700px]] | [[File:ADSrange.png|700px]] | ||
| Line 142: | Line 225: | ||
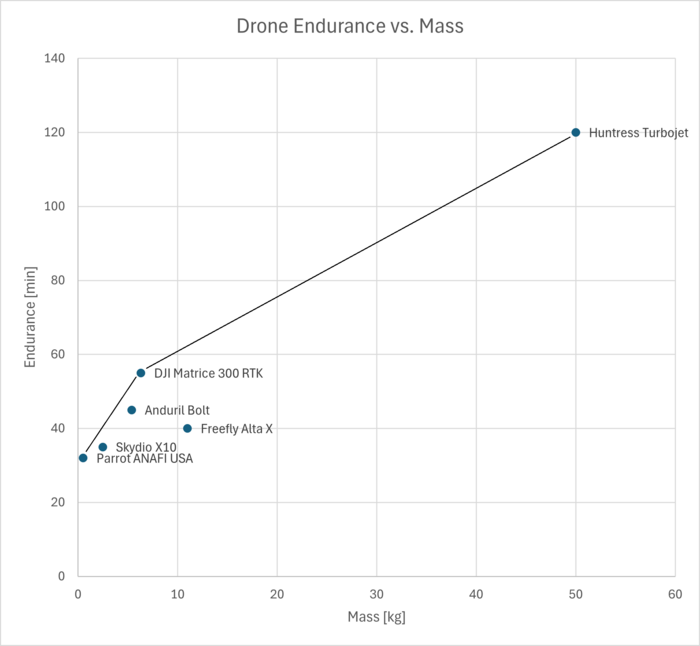
[[File:ADSendurance.png|700px]] | [[File:ADSendurance.png|700px]] | ||
In order to move the pareto front higher, technological improvements need to be made on battery capacity and efficiency of the overall drone system | In order to move the pareto front higher, technological improvements need to be made on battery capacity and efficiency of the overall drone system. Currently, the existing companies are trying to get to the existing pareto front taking on a fast follower strategy. A hypothetical company attempting to move this front would be an attacker in this space. A hypothetical company could also find a niche by providing the best-in-class drone for a specific application which could have a more nuanced pareto front. | ||
==Technical Model | ==Technical Model== | ||
===Morphological Matrix=== | |||
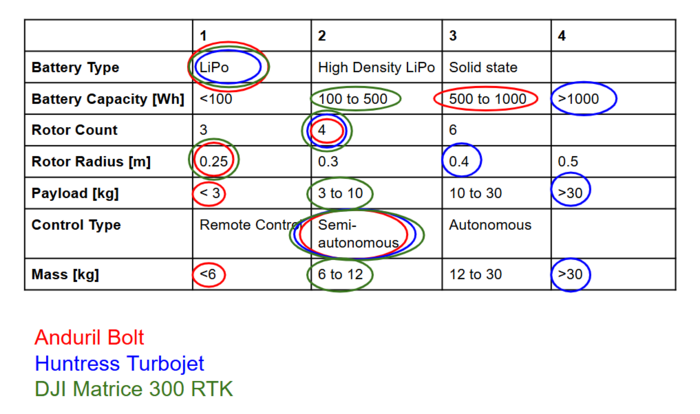
Analyzing the morphological matrix of the drones at the pareto frontier, we see design convergence with regard to battery type, rotor count and control type. The differences that contribute to variations in the endurance and range FOMs are mainly determined by battery capacity, mass and payload. The DJI Matrice does well with its relatively smaller battery capacity yet still having an endurance limit on the pareto front. | |||
[[File:MorphoADS.PNG|700px]] | [[File:MorphoADS.PNG|700px]] | ||
=== Governing Equations === | |||
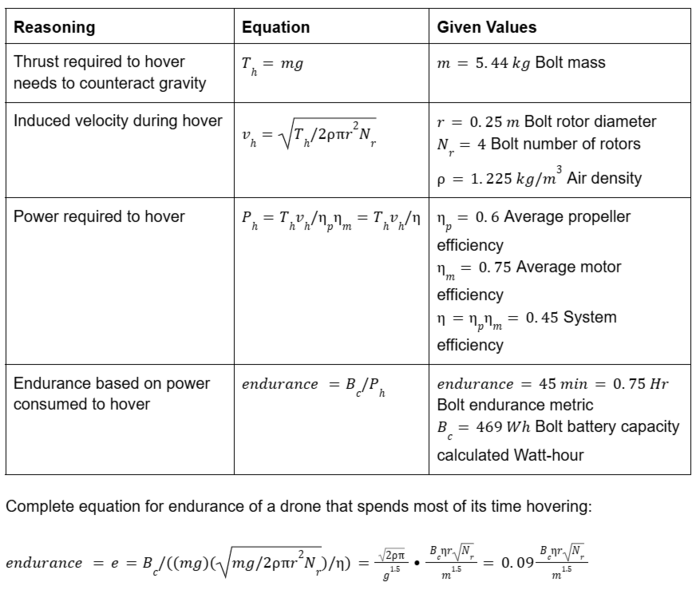
For the purpose of this technical analysis, we will look at the governing equations of a multi-rotor drone swarm doing surveillance. Since the analysis for each drone in the swarm would be similar, we will specifically analyze the equations related to the hovering characteristics of these drones using an Anduril Bolt military drone as a reference point. | The key FOMs affected by the technical model of the drone are endurance and range. For the purpose of this technical analysis, we will look at the governing equations of a multi-rotor drone swarm doing surveillance. Since the analysis for each drone in the swarm would be similar, we will specifically analyze the equations related to the hovering characteristics of these drones using an Anduril Bolt military drone as a reference point. | ||
[[File:tech-specs.PNG|700px]] | [[File:tech-specs.PNG|700px]] | ||
| Line 171: | Line 258: | ||
Notably, the rotor parameters disappear from the range calculations because the optimal velocity is being fixed for the analysis based on empirical results. | Notably, the rotor parameters disappear from the range calculations because the optimal velocity is being fixed for the analysis based on empirical results. | ||
== | ==Financial Model== | ||
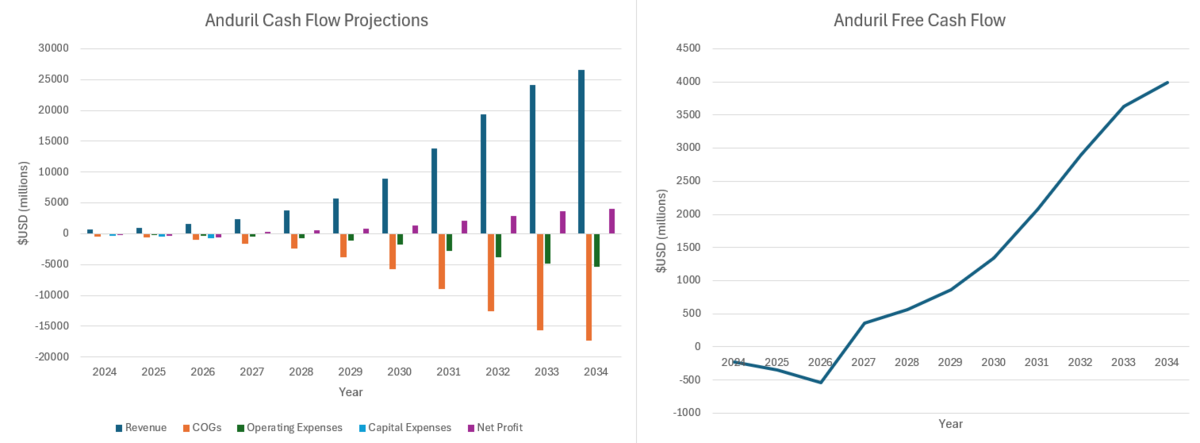
Anduril is one of the companies at the forefront of drone swarm development. Their Lattice software allows different drones and other autonomous agents to communicate and operate together to perform a military task. This technology as a whole has the potential to generate lots of positive free cash flow since the operating model of drone swarms allows it to have different business model dynamics than the traditional cost plus model of defense companies. For example, the cost of goods sold (65%) is lower for military drone swarms since drones are made from commodity materials. Drones being unmanned also reduces complexity. Since autonomous software is a major component of this business, in the long run, the operating costs will be similar to those of a software-as-a-service company (20%). The defense spending is expected to continue increasing at 3.5% annually which will become the perpetual free cash flow growth rate for Anduril. To accelerate growth, the company plans to invest over $1.5 billion by 2026. Based on these projections, the company has a net present value of roughly $14 billion which aligns with its current valuation. | |||
Givens: | |||
* COGs is 65% of sales | |||
* Operating Expenses is 20% of sales in long run | |||
* Military budget increases at 3.5% annually | |||
* Capital Expenses will be an additional $1.5 billion by 2026 | |||
* R&D Expenses are captured into COGs and CapEx and prorated to each unit sold | |||
* Discount rate of 15% | |||
[[File:Fin-model-drone.PNG|1200px]] | |||
==R&D Projects == | |||
The projects of interest were selected based on their contribution to moving FOMs such as cost and endurance, and advancing foundational technologies such as swarm algorithms. These projects exist at a variety of phases and budgets showing the level of continues investment going into 2ADS. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ Project Details | |||
! Project !! Phase !! Description !! Figures of Metrit (FOM) !! Budget !! Timeline | |||
|- | |||
| '''Restricted Environment Swarming''' - Quantum Systems & Airbus || Demonstration || Demonstrating autonomous swarm operations in control-denied environments<br>- AI reinforcement learning algorithms<br>- Mixed drone types<br>- Improve reliability and coordination algorithms || Reliability, coordination algorithms || $10M+ || 2023 to present | |||
|- | |||
| '''Hive System''' - Red Cat Holdings & Sentien Robotics || R&T || Creating robotic systems to manage drone deployment and recapture<br>- Improve cost model by removing the need for human operators<br>- Demonstrations in 2024 || Cost model improvement || $25M+ || 2016 to present | |||
|- | |||
| '''Cohesion Demonstrator''' - Thales || Demonstration || Defining unified AI Swarm Architecture<br>- Sharing of environmental information and data fusion<br>- Collaborative tactics for resilience<br>- Improve Swarm size || Swarm size, data sharing, resilience || $50M+ || 2017 to present | |||
|- | |||
| '''Bolt''' - Anduril || R&D || Creating drones that are more disposable and cheaper<br>- Modular design for quick use and increased reliability<br>- Improve costs, endurance, and range || Costs, endurance, range || $10M+ || Ongoing | |||
|- | |||
| '''Lattice''' - Anduril || R&D || General-purpose control and command interface for different autonomous assets<br>- Open architecture interface<br>- Integrated planning and optimized distributed computing across assets and base<br>- Improve Swarm size || Swarm size, interface capabilities || $1B+ || Ongoing | |||
|- | |||
| '''Solid State Batteries''' - CATL || R&T || Developing more energy-dense batteries<br>- Improve endurance and range || Endurance, range || $100M+ || 2022 to present | |||
|- | |||
| '''Lithium Sulfur Batteries''' - Li-S Energy || R&T || Developing lighter batteries for transport<br>- Using Boron Nitride Nanotubes to improve battery life cycles and performance over time<br>- Improve endurance and range || Endurance, range || $2M+ || 2021 to present | |||
|} | |||
GANTT Chart | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! Time | |||
! Budget | |||
! Project | |||
|- | |||
| 2025 | |||
| $10M | |||
| Drone Swarming | |||
|- | |||
| 2026 | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
|- | |||
| 2027 | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
|- | |||
| 2028 | |||
| $100M | |||
| CATL SS Batteries | |||
|- | |||
| 2029 | |||
| $25M | |||
| Hive System | |||
|- | |||
| 2030 | |||
| $1B | |||
| Anduril Military Drone Swarms | |||
|} | |||
==Patents and Publications== | |||
===Publications=== | |||
First we look at the following three key publications that have played very important roles in setting up the foundation of both research and product development for 2ADS: | |||
'''Paper 1''': Vásárhelyi, Gábor, et al. "Optimized flocking of autonomous drones in confined environments." Science Robotics 3.20 (2018). | |||
This paper is focused on enabling large swarms of autonomous drones to navigate complex environments without colliding with obstacles or each other. Its key research contribution is the development of a decentralized navigation algorithm called "GLAS" (Global-to-Local Autonomy Synthesis) that allows each drone to make independent decisions while maintaining swarm cohesion. The system successfully demonstrated the coordination of 10 autonomous quadrotor drones navigating through cluttered environments and narrow passages without central control, representing a significant advancement in scalable swarm robotics. The novelty of their approach is in combining global motion planning with local collision avoidance while being computationally efficient to be run on-device on individual drones in real-time. | |||
'''Paper 2''': Meier, Lorenz, et al. "Pixhawk: A system for autonomous flight using onboard computer vision." 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. IEEE, 2011. | |||
This is a particularly influential early work in autonomous drone swarms. The paper addresses the fundamental challenge of controlling multiple “micro aerial vehicles” (MAVs) in GPS-denied environments, particularly indoor spaces where traditional navigation methods are ineffective. They have developed a system that enables small flying robots to achieve stable autonomous flight and coordinated swarm behavior using only onboard sensors and processors, particularly through computer vision, without relying on external positioning systems. This technical advancement has significant implications for real-world applications of autonomous drone swarms, such as indoor search and rescue operations, surveillance, and infrastructure inspection. | |||
'''Paper 3''': Alyassi, Rashid, et al. "Autonomous recharging and flight mission planning for battery-operated autonomous drones." IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 20.2 (2022): 1034-1046. | |||
The paper represents a more recent direction of research in autonomous drone swarm control and introduces a distributed formation control framework that merges sliding mode control with neural networks. The authors' primary contribution lies in developing a robust control strategy that can effectively handle both model uncertainties and external disturbances while maintaining precise formations. Through the integration of an adaptive mechanism, the system demonstrates ability to compensate for unknown dynamics and environmental factors that typically disrupt swarm coordination. Further, they provide rigorous mathematical proofs of stability and convergence, supported by numerical simulations to validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. | |||
===Patents=== | |||
Next, we look at three key patents in this space: | |||
'''Patent 1''': Pillai, Unnikrishna Sreedharan, and Alain Anthony Mangiat. "Method and apparatus for dynamic swarming of airborne drones for a reconfigurable array." U.S. Patent No. 9,488,981. 8 Nov. 2016. | '''Patent 1''': Pillai, Unnikrishna Sreedharan, and Alain Anthony Mangiat. "Method and apparatus for dynamic swarming of airborne drones for a reconfigurable array." U.S. Patent No. 9,488,981. 8 Nov. 2016. | ||
| Line 199: | Line 374: | ||
*G08G 5: For air traffic control systems associated with autonomous drones and drone swarms | *G08G 5: For air traffic control systems associated with autonomous drones and drone swarms | ||
== | ==Technology & Strategy Statement== | ||
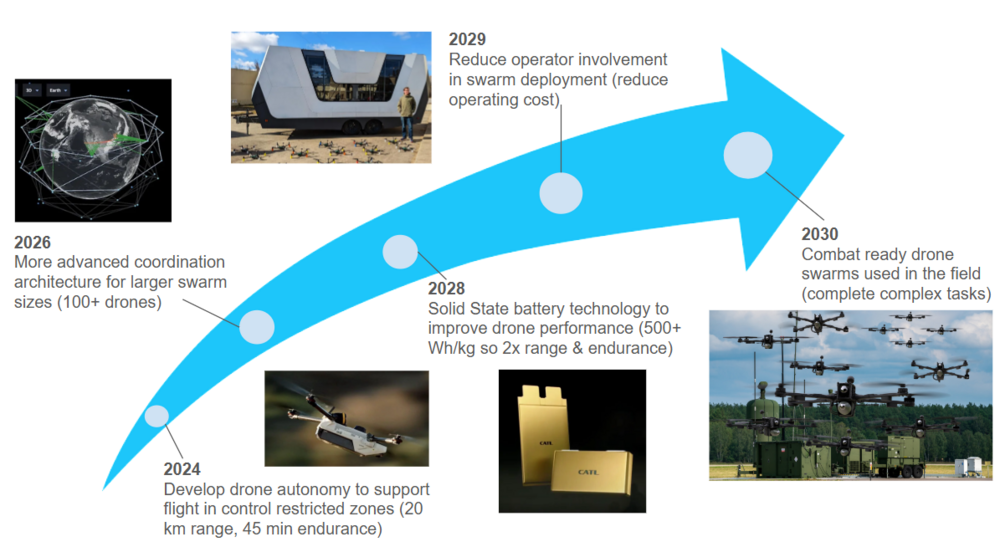
The target is to develop autonomous drone swarm systems capable of accomplishing complex military operations by 2030. In order to accomplish this goal, there needs to be key advances in autonomous navigation and control systems, swarm architectures and improvements in drone performance metrics. The first technology to invest in is Anduril's Lattice to enable the control of more than 100 drones by 2026. CATL's Solid state batteries will also get investment to double the drone endurance for the same weight class by 2028. Finally, investments into drone infrastructure to reduce operational costs will pay off in 2029. These investments will enable drone swarms to accomplish complex tasks by 2030. | |||
[[File:Swoosh-drone.PNG|1000px]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:30, 3 December 2024
Authors: Abinaya Rajesh, Joe Mattekatt, Madhav Datt
Autonomous Drone Swarms
Roadmap Overview
Autonomous drone swarms are a collection of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) that collaborate to perform a task with minimal human intervention. These drones take some information from a ground control station to outline the task but mainly rely on their own autonomous decision making to perform that task and synchronize with other drones in the swarm. Swarms can range from a few to thousands of drones depending on the application and the maturity of the technology used in these drones.
The 2ADS - Autonomous Drone Swarms identifier represents a Level 2 technology roadmap that pertains to product-level aspects of Autonomous Drone Swarms.
Key features of autonomous drone swarms are as follows:
- Collective behavior: Drones in a swarm coordinate their actions, sharing data, relative locations (through GPS or other mechanisms in GPS-denied environments) and reacting to environmental stimuli in real-time.
- Distributed sensing: Swarms can cover vast areas simultaneously, gathering data from multiple sensors to enhance situational awareness and enable detailed mapping, environmental monitoring, and disaster assessment.
- High reliability: The failure of a single drone does not lead to an overall failure of the swarm due to redundancies, ensuring reliability in mission critical settings.
- Adaptability: Autonomous swarms can use artificial intelligence techniques to respond to new or unexpected situations.
Due to the above features, autonomous drone swarms have extensive high-impact use-cases such as:
- Military operations: reconnaissance, electronic warfare, payload delivery
- Disaster response: search and rescue, wildfire fighting, damage assessments
- Agriculture: crop monitoring, harvesting, pollination
- Entertainment: aerial light shows replacing fireworks
Autonomous drone swarms are disruptive innovation since they offer previously impossible capabilities such as large-scale coordinated aerial operations with minimal/no human control. Drone swarms have the potential to disrupt multiple markets simultaneously, from military operations to agriculture and entertainment. This is a broad impact across various sectors instead of focused improvements on existing markets.
Thus, the focus of this research will be the technological advancements in edge compute, drone hardware and swarm algorithms that have enabled the development of drone swarms and a prediction of where this technology will go next. We will analyze all the developments within the military application space since it is the most rapidly maturing application of drone swarms. Ultimately, drone swarms will revolutionize how we approach distributed tasks and bring us closer to emulating the swarm behaviors we see in nature.
DSM Allocation
Autonomous Drone Swarms can be broken down into the following technologies that have some inter-dependencies. Autonomous Drone Swarms at the product level relies heavily on the product roadmap of drone technology since 2ADS is a composition of multiple units of 2D. 3FCS has many inter-dependencies with 3ES since the flight control system needs the components in the electrical system.
The high levels of inter-dependencies show that while individual technologies can improve certain operating characteristics of a single drone, multiple technologies need to advance together to realize the full benefits of autonomous drone swarms. For example, better batteries, more efficient motors and advanced autonomy software can significantly improve the flight time FOM.
DSM
1SR Swarm Robotics
- 2ADS Autonomous Drone Swarms
- 2D Drones
- 3BF Body Frame
- 4CF Carbon Fiber
- 3PS Propulsion System
- 4P Propellers
- 4BM Brushless Motors
- 3FCS Flight Control System
- 4IMS Inertial Measurement Sensors
- 4GPS GPS
- 4A Autonomy
- 4SA Swarm Algorithms
- 3ES Electric System
- 4IC Integrated Circuits
- 4RTR Radio Transmitter & Receiver
- 4LIO Lithium Ion Batteries
- 3BF Body Frame
OPM
The main physical components of the drone swarm are individual drones and the control station. The drone swarm has a few key operations:
- Commanding - manages the interactions between the drones in the swarm and the control station
- Flying - translates the flight commands into physical motion of the drone
- Decision Making - assess the environment and task instructions to generate flight commands
- Charging - recharges the drone
Figures of Merit (FOM)
There are a number of FOMs applicable to the 2ADS product roadmap. Swarm size and cost are FOMs attributed to the entire drone swarm system while the remaining FOMs are for an individual drone. The most important FOM for the drone swarm is the number of drones in the swarm while the most important FOM for an individual drone is endurance. Swarm size is analyzed in more detail below the table; endurance is analyzed in the technical model section.
| FOM | Units | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Swarm Size | [number of drones] | The number of drones in the swarm dictate the size and complexity of the light display that can be created. Larger swarms also require more sophisticated control software. |
| Endurance | [min] | The battery life of a drone determines how long an aerial show can last. |
| Speed | [miles/hour] | Determined by motor. Decides if fit for certain use cases. |
| Range | [km] | Specifies scope of operation and geographical coverage before. Computed as Flight Time * 60 * Speed. |
| Cost | [US Dollars] | Cost over overall system including per unit drone cost. |
| Latency | [ms] | How quickly a drone can respond to commands from a control center or react to signals from other drones. Lower latency systems will be safer. |
| Mass | [kg] | Overall mass of drone. Affects other FOMs such as endurance. |
Deep Dive into Swarm Size FOM
We can analyze the trends and factors affecting swarm size to attempt a quantitative model of improvement over time. The following factors affect UAV drone swarm size:
- Algorithmic complexity: Primary limit on drone swarm size is the development of algorithms and systems to coordinate drones receiving increasingly complex information
- Computing power: As computing power grows, the capacity to manage information exchanges between more drones increases
- Energy density: Ongoing research in energy density increases payload capacity and flight endurance of unmanned platforms
- Communication capabilities: Communication bandwidth and protocols are necessary for coordination among swarm members
- Cost: As swarms become more sophisticated, production costs may increase, potentially limiting strategic value
To quantitatively model the rate of improvement, we create a simple model based on Moore’s law, assuming that the key factors we have described above (particularly algorithmic complexity, computing power, communication capabilities and energy density) follow similar/comparable growth trajectories.
Thus, we define our model as:
Where:
- S(t) is the swarm size at time t
- S_0 is the initial swarm size at time t_0
- t is the current year
- t_0 is the base year
- d is the doubling period in years
Based on known swarm sizes over time, we can plot the trajectory of growth of Swarm Size as follows:
This model projects infinite exponential growth in swarm sizes over time. While there is no theoretical limit to swarm sizes, there are practical limitations which could lead to growth slowing down over time. Some of these practical considerations are as follows:
- Cost: As swarm sizes increase, the total cost may become prohibitive for many applications.
- Regulatory limits: Current regulations (including those imposed by the FAA) often restrict drone operations, which may limit practical swarm sizes in certain contexts
We estimate that this technology is in the rapid progress phase of the S-curve. This is supported by the following details:
- The technology has moved beyond the initial concept and early prototypes, and is thus past the Incubation phase. Successful demonstrations and tests with over 100 drones have been conducted.
- Significant progress in drone swarm technology in recent years. For example, Airbus and Quantum Systems successfully tested AI-driven drone swarm technology for the German Armed Forces in September 2024 [ref, ref, ref].
- Increasing Capabilities: Recent tests have demonstrated advanced features such as AI-powered coordination of mixed UAS swarms, real-time merging of reconnaissance data, and
autonomous mission execution in GPS-denied conditions
While advancing rapidly, drone swarms have not reached widespread adoption or maturity. Many applications are still in theoretical, early or test phases.
Alignment with Company Drivers
| Number | Strategic Driver | Alignment and Targets |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | To develop drones capable of operating in a swarm to accomplish field tasks that would be too challenging for individual drones to accomplish. | The 2ADS technology roadmap will target drones acting together to form swarms that can accomplish tasks. Based on the Moore’s law target set in Assignment 2, the goal is to have swarm sizes of 500 by 2028. |
| 2 | To create lower cost drones so that customers buy a larger volume of drones instead of spending more on individual drones. | The 2D technology roadmap will benefit from cost saving developments in any of the component level roadmaps. |
| 3 | To develop autonomy that will enable drones to operate in locations that are not conducive to receiving human control signals. | The 3FCS technology roadmap will target improvements in autonomy that will initially allow a human to control multiple drones (Anduril Lattice) then eventually allow the drone to operate on its own. |
| 4 | To increase endurance of drones so that they can perform more complex tasks that take longer to complete. | The 3PS and 4LIO technology roadmaps will focus on improving propulsion efficiency and battery capacity (transition to solid-state batteries) which will enable longer endurance limits. |
| 5 | To increase the payload capacity of drones so that end effectors on drones can be more robust. | Improvements made in the propulsion efficiency and battery capacity of the 3PS and 4LIO technology roadmaps will also enable the drone to carry a larger payload if the endurance is kept constant. |
Company Positioning vs. Competition
The following table summarizes the positioning of various drones manufactured by the top UAV companies. Individual drones are typically compared based on the FOMs of range and endurance. Comparing these FOMs to mass allows us to observe how these drones tradeoff between key FOMs and mass. The drones that do this most effectively will exist on the leading edge of the pareto front.
| Drone Name | Range [km] | Endurance [min] | Mass [kg] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anduril Bolt | 20 | 45 | 5.44 |
| Huntress Turbojet | 30 | 120 | 50 |
| DJI Matrice 300 RTK | 15 | 55 | 6.3 |
| Skydio X10 | 10 | 35 | 2.5 |
| Parrot ANAFI USA | 4 | 32 | 4.5 |
| Freefly Alta X | 5 | 40 | 11 |
The Parrot ANAFI, Anduril Bolt and Huntress Turbojet are some products that exist on the pareto frontier of both range and endurance. These drones also exhibit differences in use cases that make sense at their positions of the pareto front.
- Parrot ANAFI is light and ideal for short distances, hence it is used primarily for photography
- Huntress Turbojet is heavy and built for long distance travel, hence it is used for payload transfer
- Anduril Bolt has average mass and range, hence it is used for both reconnaissance and payload transfer
In order to move the pareto front higher, technological improvements need to be made on battery capacity and efficiency of the overall drone system. Currently, the existing companies are trying to get to the existing pareto front taking on a fast follower strategy. A hypothetical company attempting to move this front would be an attacker in this space. A hypothetical company could also find a niche by providing the best-in-class drone for a specific application which could have a more nuanced pareto front.
Technical Model
Morphological Matrix
Analyzing the morphological matrix of the drones at the pareto frontier, we see design convergence with regard to battery type, rotor count and control type. The differences that contribute to variations in the endurance and range FOMs are mainly determined by battery capacity, mass and payload. The DJI Matrice does well with its relatively smaller battery capacity yet still having an endurance limit on the pareto front.
Governing Equations
The key FOMs affected by the technical model of the drone are endurance and range. For the purpose of this technical analysis, we will look at the governing equations of a multi-rotor drone swarm doing surveillance. Since the analysis for each drone in the swarm would be similar, we will specifically analyze the equations related to the hovering characteristics of these drones using an Anduril Bolt military drone as a reference point.
We can observe that the endurance is affected by the battery capacity, efficiency, rotor radius, number of rotors and mass of the drone.
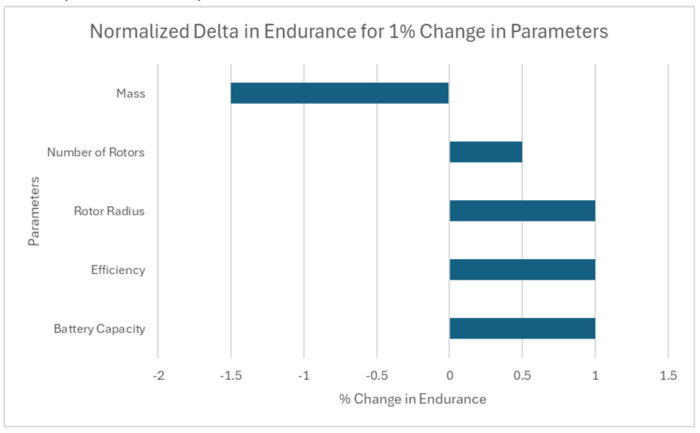
Given the design vector of the Anduril Bolt Drone, here are the ways to increase endurance of the drone based on the magnitudes on the normalized tornado plot:
- Making a 1% decrease in the mass will have the greatest effect in increasing endurance by 1.5%.
- Making a 1% increase in the rotor radius, efficiency or battery capacity will increase endurance by 1% however if this increases the mass of the drone, some negative effects will be encountered.
- Making a 1% increase in Number of Rotors will increase the endurance by 0.5% however, this sort of change needs to be in whole rotor increments.
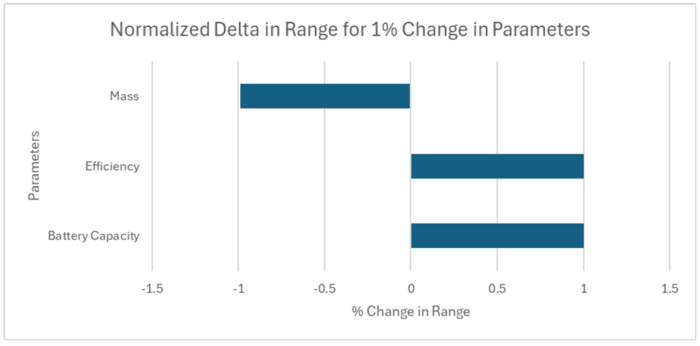
Given the design vector of the Anduril Bolt Drone, here are the ways to increase range of the drone based on the magnitudes on the normalized tornado plot:
- Making a 1% increase in the efficiency or battery capacity will increase range by 1% however if this increases the mass of the drone, some negative effects will be encountered.
- Making a 1% decrease in the mass will increase endurance by 0.99%.
Notably, the rotor parameters disappear from the range calculations because the optimal velocity is being fixed for the analysis based on empirical results.
Financial Model
Anduril is one of the companies at the forefront of drone swarm development. Their Lattice software allows different drones and other autonomous agents to communicate and operate together to perform a military task. This technology as a whole has the potential to generate lots of positive free cash flow since the operating model of drone swarms allows it to have different business model dynamics than the traditional cost plus model of defense companies. For example, the cost of goods sold (65%) is lower for military drone swarms since drones are made from commodity materials. Drones being unmanned also reduces complexity. Since autonomous software is a major component of this business, in the long run, the operating costs will be similar to those of a software-as-a-service company (20%). The defense spending is expected to continue increasing at 3.5% annually which will become the perpetual free cash flow growth rate for Anduril. To accelerate growth, the company plans to invest over $1.5 billion by 2026. Based on these projections, the company has a net present value of roughly $14 billion which aligns with its current valuation.
Givens:
- COGs is 65% of sales
- Operating Expenses is 20% of sales in long run
- Military budget increases at 3.5% annually
- Capital Expenses will be an additional $1.5 billion by 2026
- R&D Expenses are captured into COGs and CapEx and prorated to each unit sold
- Discount rate of 15%
R&D Projects
The projects of interest were selected based on their contribution to moving FOMs such as cost and endurance, and advancing foundational technologies such as swarm algorithms. These projects exist at a variety of phases and budgets showing the level of continues investment going into 2ADS.
| Project | Phase | Description | Figures of Metrit (FOM) | Budget | Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Restricted Environment Swarming - Quantum Systems & Airbus | Demonstration | Demonstrating autonomous swarm operations in control-denied environments - AI reinforcement learning algorithms - Mixed drone types - Improve reliability and coordination algorithms |
Reliability, coordination algorithms | $10M+ | 2023 to present |
| Hive System - Red Cat Holdings & Sentien Robotics | R&T | Creating robotic systems to manage drone deployment and recapture - Improve cost model by removing the need for human operators - Demonstrations in 2024 |
Cost model improvement | $25M+ | 2016 to present |
| Cohesion Demonstrator - Thales | Demonstration | Defining unified AI Swarm Architecture - Sharing of environmental information and data fusion - Collaborative tactics for resilience - Improve Swarm size |
Swarm size, data sharing, resilience | $50M+ | 2017 to present |
| Bolt - Anduril | R&D | Creating drones that are more disposable and cheaper - Modular design for quick use and increased reliability - Improve costs, endurance, and range |
Costs, endurance, range | $10M+ | Ongoing |
| Lattice - Anduril | R&D | General-purpose control and command interface for different autonomous assets - Open architecture interface - Integrated planning and optimized distributed computing across assets and base - Improve Swarm size |
Swarm size, interface capabilities | $1B+ | Ongoing |
| Solid State Batteries - CATL | R&T | Developing more energy-dense batteries - Improve endurance and range |
Endurance, range | $100M+ | 2022 to present |
| Lithium Sulfur Batteries - Li-S Energy | R&T | Developing lighter batteries for transport - Using Boron Nitride Nanotubes to improve battery life cycles and performance over time - Improve endurance and range |
Endurance, range | $2M+ | 2021 to present |
GANTT Chart
| Time | Budget | Project |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | $10M | Drone Swarming |
| 2026 | - | - |
| 2027 | - | - |
| 2028 | $100M | CATL SS Batteries |
| 2029 | $25M | Hive System |
| 2030 | $1B | Anduril Military Drone Swarms |
Patents and Publications
Publications
First we look at the following three key publications that have played very important roles in setting up the foundation of both research and product development for 2ADS:
Paper 1: Vásárhelyi, Gábor, et al. "Optimized flocking of autonomous drones in confined environments." Science Robotics 3.20 (2018).
This paper is focused on enabling large swarms of autonomous drones to navigate complex environments without colliding with obstacles or each other. Its key research contribution is the development of a decentralized navigation algorithm called "GLAS" (Global-to-Local Autonomy Synthesis) that allows each drone to make independent decisions while maintaining swarm cohesion. The system successfully demonstrated the coordination of 10 autonomous quadrotor drones navigating through cluttered environments and narrow passages without central control, representing a significant advancement in scalable swarm robotics. The novelty of their approach is in combining global motion planning with local collision avoidance while being computationally efficient to be run on-device on individual drones in real-time.
Paper 2: Meier, Lorenz, et al. "Pixhawk: A system for autonomous flight using onboard computer vision." 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. IEEE, 2011.
This is a particularly influential early work in autonomous drone swarms. The paper addresses the fundamental challenge of controlling multiple “micro aerial vehicles” (MAVs) in GPS-denied environments, particularly indoor spaces where traditional navigation methods are ineffective. They have developed a system that enables small flying robots to achieve stable autonomous flight and coordinated swarm behavior using only onboard sensors and processors, particularly through computer vision, without relying on external positioning systems. This technical advancement has significant implications for real-world applications of autonomous drone swarms, such as indoor search and rescue operations, surveillance, and infrastructure inspection.
Paper 3: Alyassi, Rashid, et al. "Autonomous recharging and flight mission planning for battery-operated autonomous drones." IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 20.2 (2022): 1034-1046.
The paper represents a more recent direction of research in autonomous drone swarm control and introduces a distributed formation control framework that merges sliding mode control with neural networks. The authors' primary contribution lies in developing a robust control strategy that can effectively handle both model uncertainties and external disturbances while maintaining precise formations. Through the integration of an adaptive mechanism, the system demonstrates ability to compensate for unknown dynamics and environmental factors that typically disrupt swarm coordination. Further, they provide rigorous mathematical proofs of stability and convergence, supported by numerical simulations to validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
Patents
Next, we look at three key patents in this space:
Patent 1: Pillai, Unnikrishna Sreedharan, and Alain Anthony Mangiat. "Method and apparatus for dynamic swarming of airborne drones for a reconfigurable array." U.S. Patent No. 9,488,981. 8 Nov. 2016.
This patent introduces a novel method for controlling drone swarms using a hierarchical control system combining ground-based mission planning with autonomous drone coordination. The key innovation lies in its dual virtual region approach - each drone creates an inner "bubble" region (5-15x drone size) and a larger communication sphere (several hundred times larger) around itself. The system uses a unique centroid-based control mechanism where the swarm must maintain its calculated center point (centroid) within a defined sphere while individual drones have flexibility to move.
Relevant primary CPC classification: G05D1/0027 Control of position, course, altitude or attitude of land, water, air or space vehicles, e.g. using automatic pilots associated with a remote control arrangement involving a plurality of vehicles, e.g. fleet or convoy traveling
Patent 2: Husain, Syed Mohammad Amir, and John Rutherford Allen. "Stackable unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) system and portable hangar system therefor." U.S. Patent No. 10,322,820. 18 Jun. 2019.
This Boeing patent presents an autonomous aerial refueling system for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). The system utilizes an optical positioning mechanism that combines laser beams and retroreflectors to execute mid-air refueling operations. The technology enables automated guidance of multiple receiver UAVs through refueling procedures using laser beams from the tanker aircraft that interface with retroreflective markers on receiving vehicles. This system removes manual operation requirements while maintaining positioning accuracy during refueling maneuvers. The implementation incorporates computer vision algorithms, boom control systems, and retroreflective markers to facilitate positioning and fuel transfer between aircraft. The patent demonstrates advancement in autonomous aerial operations, with applications in UAV swarm refueling scenarios.
Relevant primary CPC classification: B64F1/222 Ground or aircraft-carrier-deck installations for handling aircraft for storing aircraft, e.g. in hangars
Patent 3: Steele, Daniel W., and Joseph R. Chovan. "Unmanned air vehicle, integrated weapon platform, avionics system and control method." U.S. Patent No. 7,542,828. 2 Jun. 2009.
This patent introduces a novel design methodology for an interceptor unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) that integrates weapons capabilities with autonomous control systems. The key innovation lies in the design approach of building the UAV airframe around a weapon platform, specifically aligning the weapon's aiming axis with the aircraft's flight vector axis, essentially creating a "self-aiming winged weapon". The system incorporates a unique spherically-organized situational awareness database that processes sensor data in its native angular format, avoiding the computational complexity of Cartesian coordinate transformations. This vehicle-centric, attitude-invariant database enables parallel processing of target tracking and obstacle avoidance through independent "windowing" of the spherical data structure. The design also features innovative integration of major torque-inducing components (weapon, engine, wings) near the center of gravity, along with symmetric aerodynamic design using forward canards, which together enhance maneuverability and weapon accuracy while minimizing discharge-induced flight disturbances.
Relevant primary CPC classification: B64U2101/15 UAVs specially adapted for particular uses or applications for conventional or electronic warfare
Finally looking at patents in this space, we see the following CPC classifications overall for the
technology autonomous drone swarms:
- B64U: vehicles which are specially adapted for unmanned aeronautical use and the equipment therefor
- G05D 1/104: For autonomous control and navigation
- G08G 5: For air traffic control systems associated with autonomous drones and drone swarms
Technology & Strategy Statement
The target is to develop autonomous drone swarm systems capable of accomplishing complex military operations by 2030. In order to accomplish this goal, there needs to be key advances in autonomous navigation and control systems, swarm architectures and improvements in drone performance metrics. The first technology to invest in is Anduril's Lattice to enable the control of more than 100 drones by 2026. CATL's Solid state batteries will also get investment to double the drone endurance for the same weight class by 2028. Finally, investments into drone infrastructure to reduce operational costs will pay off in 2029. These investments will enable drone swarms to accomplish complex tasks by 2030.