Difference between revisions of "Sample Technology Roadmap - Solar Electric Aircraft"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
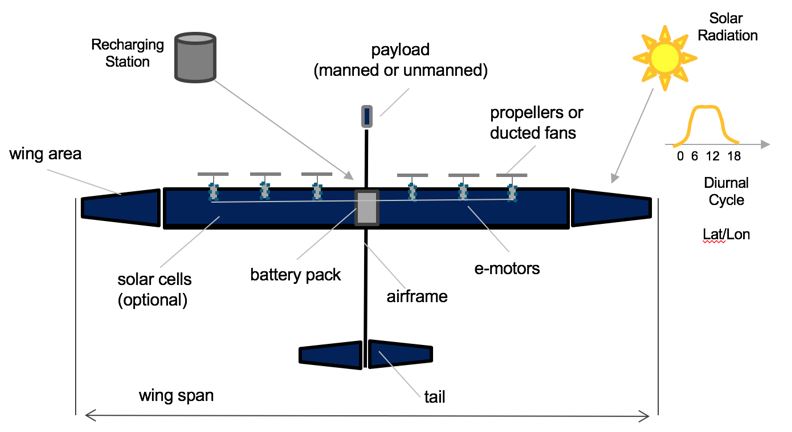
The working principle and architecture of solar-electric aircraft is depicted in the below. | The working principle and architecture of solar-electric aircraft is depicted in the below. | ||
[[File:Section 1.JPG|Figure 8- | [[File:Section 1.JPG|Figure 8-8 in text]] | ||
Solar-electric aircraft are built from light-weight materials such as wood or carbon-fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) and harvest solar energy through the photoelectric effect by bonding thin film solar cells to the surface of the main wings, and potentially the fuselage and empennage as well. The electrical energy harvested during the day is then stored in on-board chemical batteries (e.g. Lithium-Ion, Lithium-Sulfur etc…) and used for propelling the aircraft at all times, including at night. For the system to work there needs to be an overproduction of energy during the day, so that the aircraft can use the stored energy to stay aloft at night. The flight altitude of about 60,000-70,000 feet is critical to stay above the clouds and not to interfere with commercial air traffic. Depending on the length of day, i.e. the diurnal cycle which determines the number of sunshine hours per day, which itself depends on the latitude and time-of-year (seasonality) the problem is easier or harder. The reference case in the technology roadmap is an equatorial mission (latitude = zero) with 12 hours of day and 12 hours of night. | Solar-electric aircraft are built from light-weight materials such as wood or carbon-fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) and harvest solar energy through the photoelectric effect by bonding thin film solar cells to the surface of the main wings, and potentially the fuselage and empennage as well. The electrical energy harvested during the day is then stored in on-board chemical batteries (e.g. Lithium-Ion, Lithium-Sulfur etc…) and used for propelling the aircraft at all times, including at night. For the system to work there needs to be an overproduction of energy during the day, so that the aircraft can use the stored energy to stay aloft at night. The flight altitude of about 60,000-70,000 feet is critical to stay above the clouds and not to interfere with commercial air traffic. Depending on the length of day, i.e. the diurnal cycle which determines the number of sunshine hours per day, which itself depends on the latitude and time-of-year (seasonality) the problem is easier or harder. The reference case in the technology roadmap is an equatorial mission (latitude = zero) with 12 hours of day and 12 hours of night. | ||
Revision as of 02:52, 24 September 2019
We provide a notional technology roadmap for solar-electric aircraft as a potential new business category. The potential market and business applications for this type of aircraft, also known as High-Altitude-Pseudo-Satellites (HAPS) includes military surveillance, civilian research and observation, and radio communications relays, amongst others. The first point is that each technology roadmap should have a clear and unique identifier:
- 2SEA - Solar Electric Aircraft
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
Roadmap Overview
The working principle and architecture of solar-electric aircraft is depicted in the below.
Solar-electric aircraft are built from light-weight materials such as wood or carbon-fiber reinforced polymers (CFRP) and harvest solar energy through the photoelectric effect by bonding thin film solar cells to the surface of the main wings, and potentially the fuselage and empennage as well. The electrical energy harvested during the day is then stored in on-board chemical batteries (e.g. Lithium-Ion, Lithium-Sulfur etc…) and used for propelling the aircraft at all times, including at night. For the system to work there needs to be an overproduction of energy during the day, so that the aircraft can use the stored energy to stay aloft at night. The flight altitude of about 60,000-70,000 feet is critical to stay above the clouds and not to interfere with commercial air traffic. Depending on the length of day, i.e. the diurnal cycle which determines the number of sunshine hours per day, which itself depends on the latitude and time-of-year (seasonality) the problem is easier or harder. The reference case in the technology roadmap is an equatorial mission (latitude = zero) with 12 hours of day and 12 hours of night.
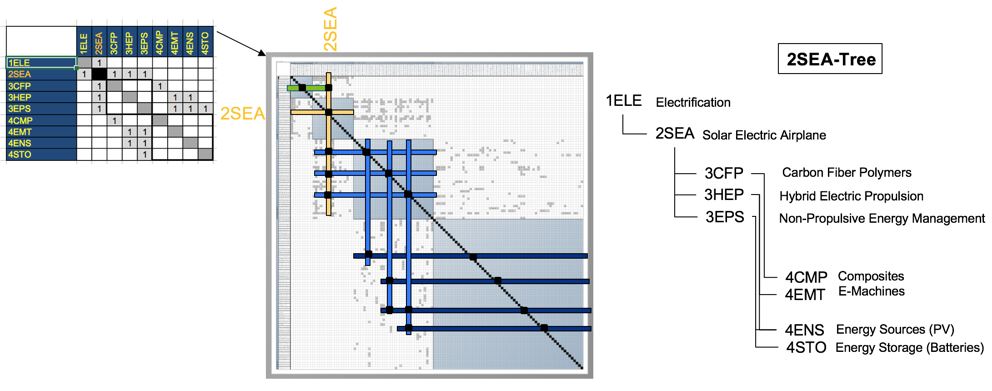
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
The 2-SEA tree that we can extract from the DSM (Fig. 8-8 right) shows us that the Solar-Electric Aircraft (2SEA) is part of a larger company-wide initiative on electrification of flight (1ELE), and that it requires the following key enabling technologies at the subsystem level: 3CFP Carbon Fiber Polymers, 3HEP Hybrid Electric Propulsion and 3EPS Non-Propulsive Energy Management (e.g. this includes the management of the charge-discharge cycle of the batteries during the day-night cycle). In turn these require enabling technologies at level 4, the technology component level: 4CMP components made from CFRP (spars, wing box, fairings …), 4EMT electric machines (motors and generators), 4ENS energy sources (such as thin film photovoltaics bonded to flight surfaces) and 4STO (energy storage in the form of lithium-type batteries).
Roadmap Model using OPM
INCLUDE LINK TO ISO 19450