Difference between revisions of "Continuous Security Monitoring"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
=== Roadmap Overview === | === Roadmap Overview === | ||
A continuous security monitoring (CSM) tool is critical to provide near-real-time surveillance and analysis of an environment to flag potential security threats. The automation of the | A continuous security monitoring (CSM) tool is critical to provide near-real-time surveillance and analysis of an environment to flag potential security threats. | ||
A CSM tool is an integral part of any modern cybersecurity framework. The technology affords automation as central to its operation, ensuring that the tool offers ongoing insights in the security posture of an environment and improves an organization's ability to manage potential risks. | |||
The technology functions with behavior analytics to track and analyze the behavior of an environment to identify potentially malicious or anomalous behavior. The future of the technology includes advanced predicted analysis using Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools where the tool can shift from reactive to proactive intelligence. In the long-term, quantum computing preparedness will be key to ensuring the tool can manage threats in a post-quantum computing world. The tool may also possess the ability to automatically repair itself, thought it currently operates in tandem with human intervention for optimal performance. | |||
Further, the increasing regulation of cyber space and introduction of cybersecurity policy suggest the CSM tool may also be a requirement for regulatory compliance, to allow environments to stay updated with evolving cybersecurity laws and regulations. | |||
[[File:Screen Shot 2023-10-12 at 1.05.40 AM.png]] | [[File:Screen Shot 2023-10-12 at 1.05.40 AM.png]] | ||
Revision as of 18:19, 12 October 2023
Continuous Security Monitoring
Roadmap Overview
A continuous security monitoring (CSM) tool is critical to provide near-real-time surveillance and analysis of an environment to flag potential security threats.
A CSM tool is an integral part of any modern cybersecurity framework. The technology affords automation as central to its operation, ensuring that the tool offers ongoing insights in the security posture of an environment and improves an organization's ability to manage potential risks.
The technology functions with behavior analytics to track and analyze the behavior of an environment to identify potentially malicious or anomalous behavior. The future of the technology includes advanced predicted analysis using Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools where the tool can shift from reactive to proactive intelligence. In the long-term, quantum computing preparedness will be key to ensuring the tool can manage threats in a post-quantum computing world. The tool may also possess the ability to automatically repair itself, thought it currently operates in tandem with human intervention for optimal performance.
Further, the increasing regulation of cyber space and introduction of cybersecurity policy suggest the CSM tool may also be a requirement for regulatory compliance, to allow environments to stay updated with evolving cybersecurity laws and regulations.
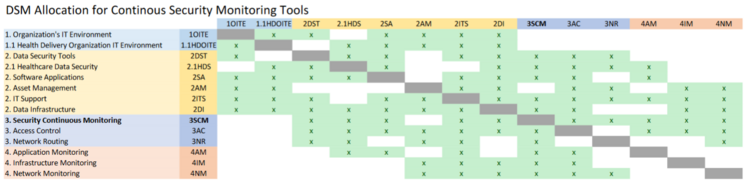
DSM Allocation
The most inter-dependencies are with the Healthcare Data Security (2HDS) roadmap. The Healthcare Data Security roadmap is narrowed in to a specific industry whereas we are focused on the more generalized industrial application but a deeper technical level of data security, Continuous Security Monitoring. The higher levels are essentially the same across roadmaps, but industry specific vs generalized. As such, we’ve marked the Healthcare specific roadmap items as subcategories underneath the non-industry specific version. We decided to omit the industry specific items, such as Medical Device Protection, from our DSM.
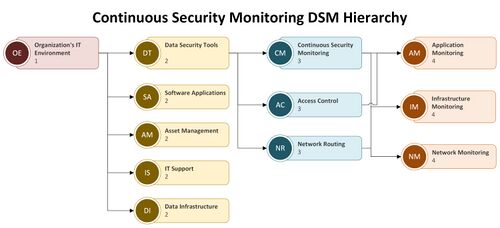
A more detailed view of the levels for the roadmap interactions is provided in hierarchy form.
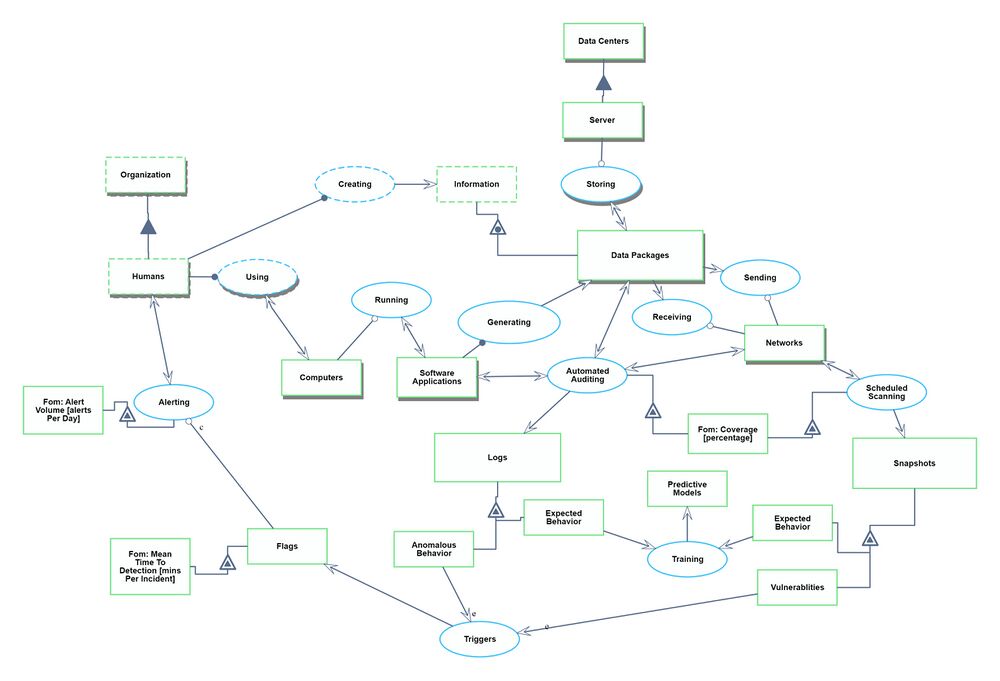
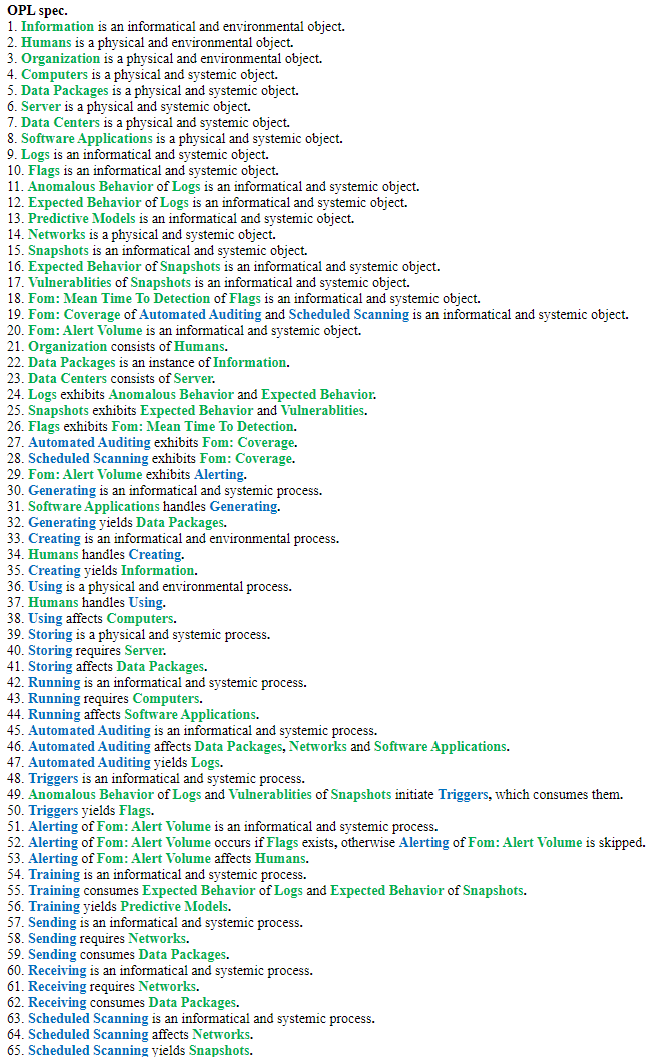
Roadmap Model using OPM (ISO 19450)
We defined a Continuous Security Monitoring Tool to sit within the environment of an organization's IT infrastructure. The system contains the IT landscape at a high level, such as software applications, data infrastructure, and network routing. We narrowed to just the monitoring and alerting functionality of a CSM tool. There could be additional functionalities within data security such as root cause analysis, remediation, and pro-active repairs, but we have excluded those from our system.
Note: Automated Auditing refers to the automatic generation of logs and monitoring of networks and applications to ensure compliance with security policies and standards.
The Object-Process Model above can be written in natural language as follows: