Difference between revisions of "FSOC"
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers== | ==Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers== | ||
Free Space Optical Communication is a technology characterized by a set of goals, which can be boiled down to providing more reliable communication technology with reduced power consumption at cheaper costs to all locations. The strategic drivers in this technology space are identified below, and the alignment of this roadmap is highlighted. | |||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
==Key Publications, Presentations and Patents== | ==Key Publications, Presentations and Patents== | ||
Free-space optical communication (FSOC) terminals transmit data across a line of sight (LOS) path via light waves. The main components of the technology are the emitter laser and optics, the photodetector and receiver optics, and the steering mechanism to align both terminals relative to each other. FSOC is used for intersatellite crosslinks, downlinks to ground stations on earth, and also from earth to space. Optical communications have also been established for point to point on earth and underwater communications. The Consultative Committee for Sapce Data Systems published the “orange book” to standardize the practice of optical communications, from the coding and synchronization schemes applied at specific wavelengths, to various fine and coarse pointing acquisition and tracking techniques used to establish and maintain a link between satellites. | |||
===Patent Review=== | ===Patent Review=== | ||
Revision as of 15:40, 1 November 2024
Welcome to the Free-Space Optical Communications Technology Roadmap.
- Technology Roadmap Identified as FSOC - Free-Space Optical Communications
- This indicates a Level 2 Individual-Technology Level Roadmap. This page describes the functions, uses, history, present, and future development of Free Space Optical Communication.
Roadmap Overview
Free-space optical communication (FSOC) utilizes optical carriers in the visible and infrared (IR) spectrum to transmit information wirelessly. This combined spectrum is 2,000 times larger than that used in RF technologies. The narrow beam of the optical signal, along with FSOC's point-to-point architecture, enables energy-efficient and secure communication links. As 6G networks demand advancements in data rates, channel capacity, power efficiency, and low latency, FSOC emerges as a promising solution. This roadmap explores the implementation of coherent FSOC for next-generation wireless communications.
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
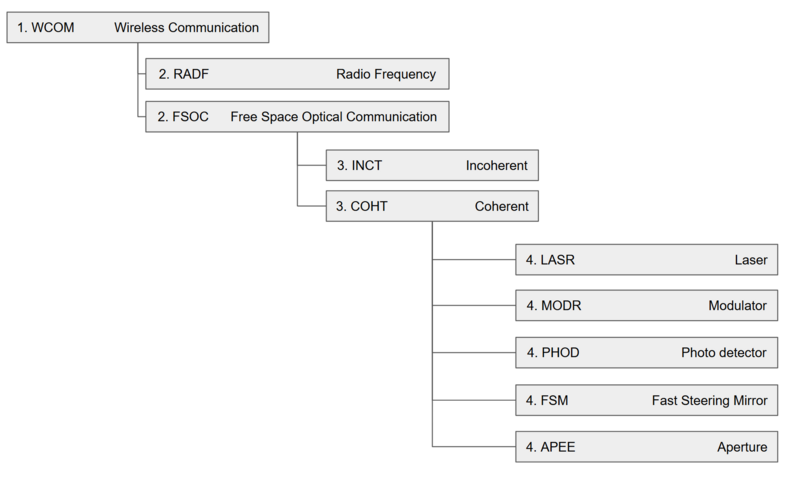
DSM Tree
This DSM tree was constructed for the FSOC technology in the context of larger wireless communication technologies.
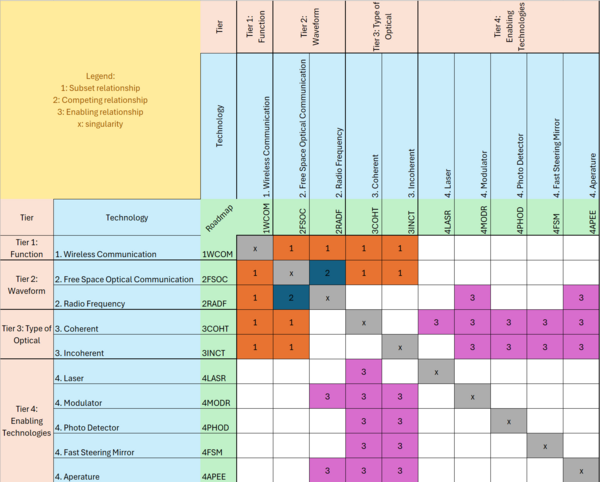
DSM Matrix
This DSM shows the relationships between FSOC and the most important technology roadmaps that are broader, competing, and enabling to FSOC.
Roadmap Model Using OPM
We use OPD to create a model of the FSOC technology, including its attributes, and the relevant processes that compose it.
Roadmap Figures of Merit
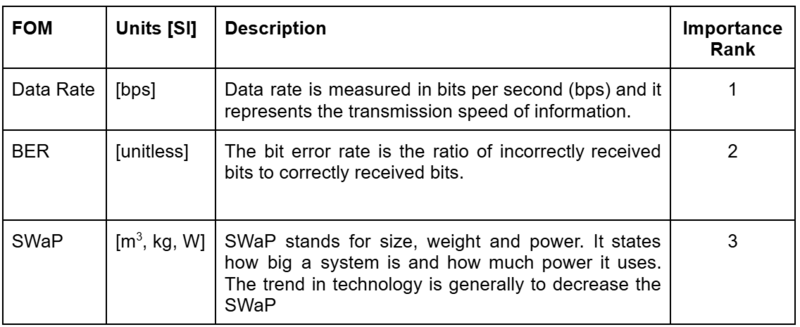
Key FOMs
This table shows the key figures of merit used to quantify the progress of this technology over time.
The following graph contains information on trends for the main figure of merit we can trace through most communication systems: Data Rate. Whereas this graph focuses on FSOC technology, the use and mention of data rate comes as a way to quantify communication technology progress over time from centuries ago.
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
Free Space Optical Communication is a technology characterized by a set of goals, which can be boiled down to providing more reliable communication technology with reduced power consumption at cheaper costs to all locations. The strategic drivers in this technology space are identified below, and the alignment of this roadmap is highlighted.
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
Vector Chart
Technical Model
Morphological Matrix
Tradespace
Sensitivity Analyses
Key Publications, Presentations and Patents
Free-space optical communication (FSOC) terminals transmit data across a line of sight (LOS) path via light waves. The main components of the technology are the emitter laser and optics, the photodetector and receiver optics, and the steering mechanism to align both terminals relative to each other. FSOC is used for intersatellite crosslinks, downlinks to ground stations on earth, and also from earth to space. Optical communications have also been established for point to point on earth and underwater communications. The Consultative Committee for Sapce Data Systems published the “orange book” to standardize the practice of optical communications, from the coding and synchronization schemes applied at specific wavelengths, to various fine and coarse pointing acquisition and tracking techniques used to establish and maintain a link between satellites.