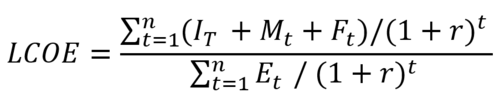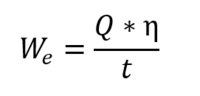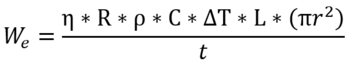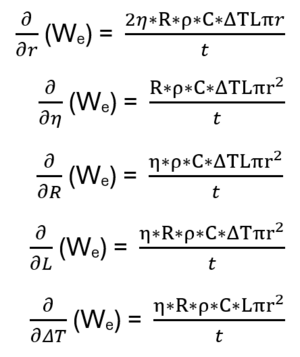Difference between revisions of "Geothermal Power Plant"
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
The key observations from the competitor analysis include the higher CAPEX required for AGS systems compared to EGS systems, a lower overall LCOE for AGS systems, and the differences in expected energy output and operational period between AGS and EGS. The two projects utilizing AGS technology include the GreenFire Energy Coso Project and the SAGE Geosystems Project, both located in the United States. The higher CAPEX for the AGS projects indicated the higher cost of implementing closed-loop systems. A higher CAPEX would usually lead to a higher project LCOE, but that is not true for the AGS projects. Both AGS projects have a lower expected LCOE than the EGS projects. The average power output for each AGS project is not significantly higher than that of the EGS projects, but the expected operation periods are longer. Therefore, companies utilizing AGS technology focus on lower and more consistent energy output over longer periods of time, whereas EGS technology will focus on more rapid utilization of a geothermal reservoir. | The key observations from the competitor analysis include the higher CAPEX required for AGS systems compared to EGS systems, a lower overall LCOE for AGS systems, and the differences in expected energy output and operational period between AGS and EGS. The two projects utilizing AGS technology include the GreenFire Energy Coso Project and the SAGE Geosystems Project, both located in the United States. The higher CAPEX for the AGS projects indicated the higher cost of implementing closed-loop systems. A higher CAPEX would usually lead to a higher project LCOE, but that is not true for the AGS projects. Both AGS projects have a lower expected LCOE than the EGS projects. The average power output for each AGS project is not significantly higher than that of the EGS projects, but the expected operation periods are longer. Therefore, companies utilizing AGS technology focus on lower and more consistent energy output over longer periods of time, whereas EGS technology will focus on more rapid utilization of a geothermal reservoir. | ||
[[File:Geothermal_Competition_Table_1.png]] | |||
==Technical Model== | ==Technical Model== | ||
Revision as of 16:49, 5 November 2024
Technology Roadmap
Roadmap Overview
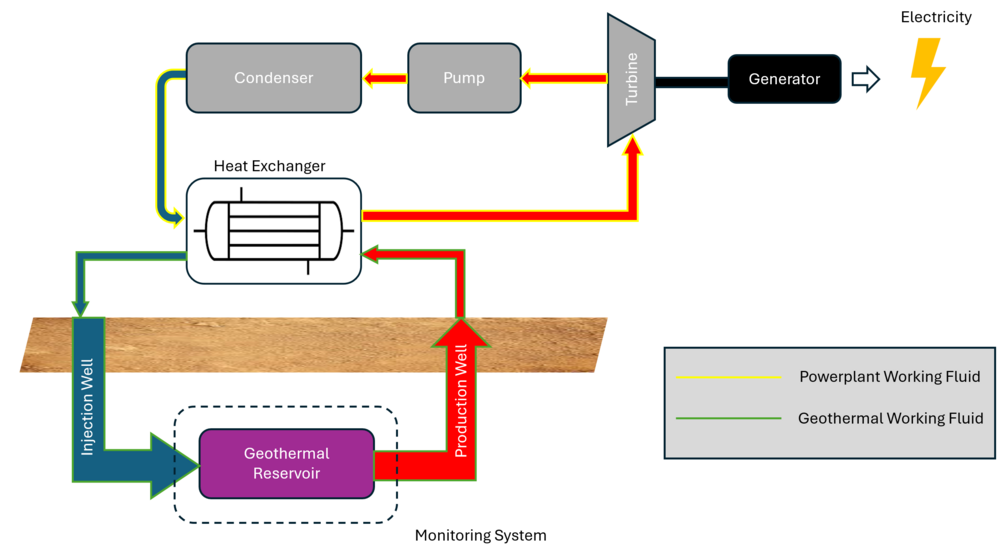
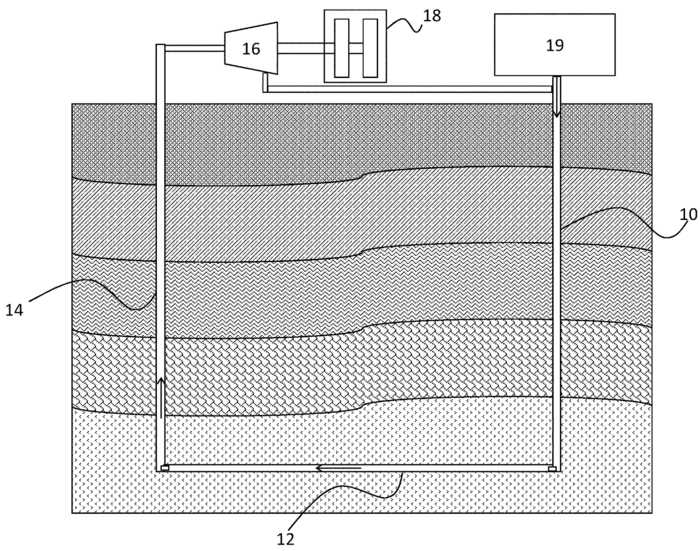
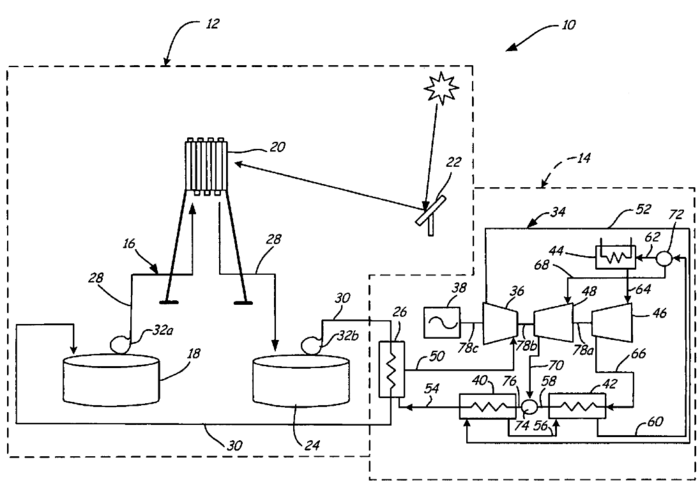
Technology Description: Geothermal power plants generate electricity by harnessing geothermal energy through a series of steps. First, geothermal fluid is heated by accessing the geothermal reservoir, either by injecting it directly into the reservoir (Enhanced Geothermal System) or using pipes that pass through the reservoir (Closed Loop). The heated fluid is then brought to the surface and passed through a heat exchanger, transferring its heat to a working fluid. This working fluid, now heated, drives a turbine, which powers a generator to produce electricity. Afterward, the working fluid is cooled and condensed back into a liquid form before being recirculated through the heat exchanger to repeat the process.
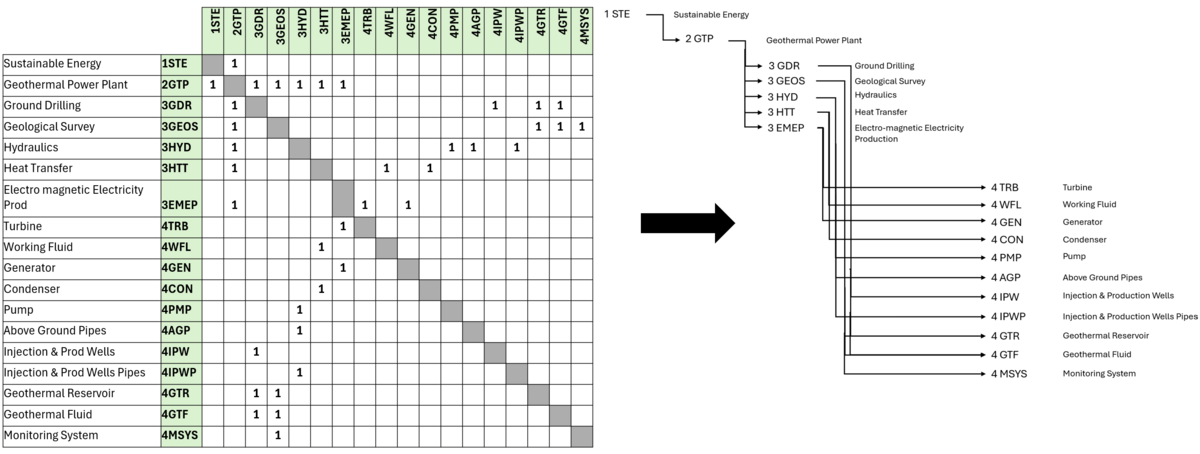
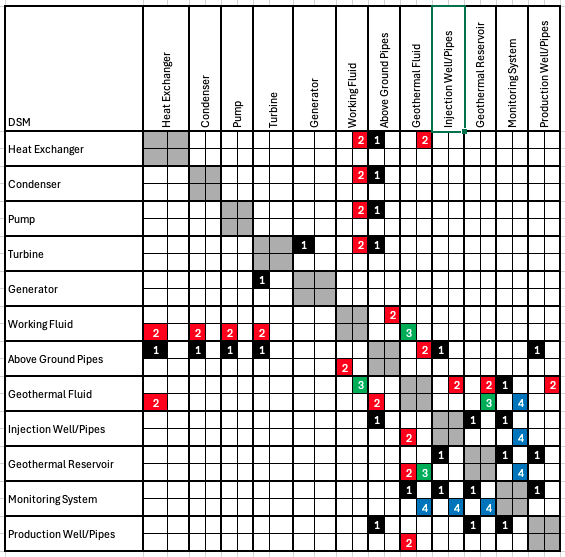
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
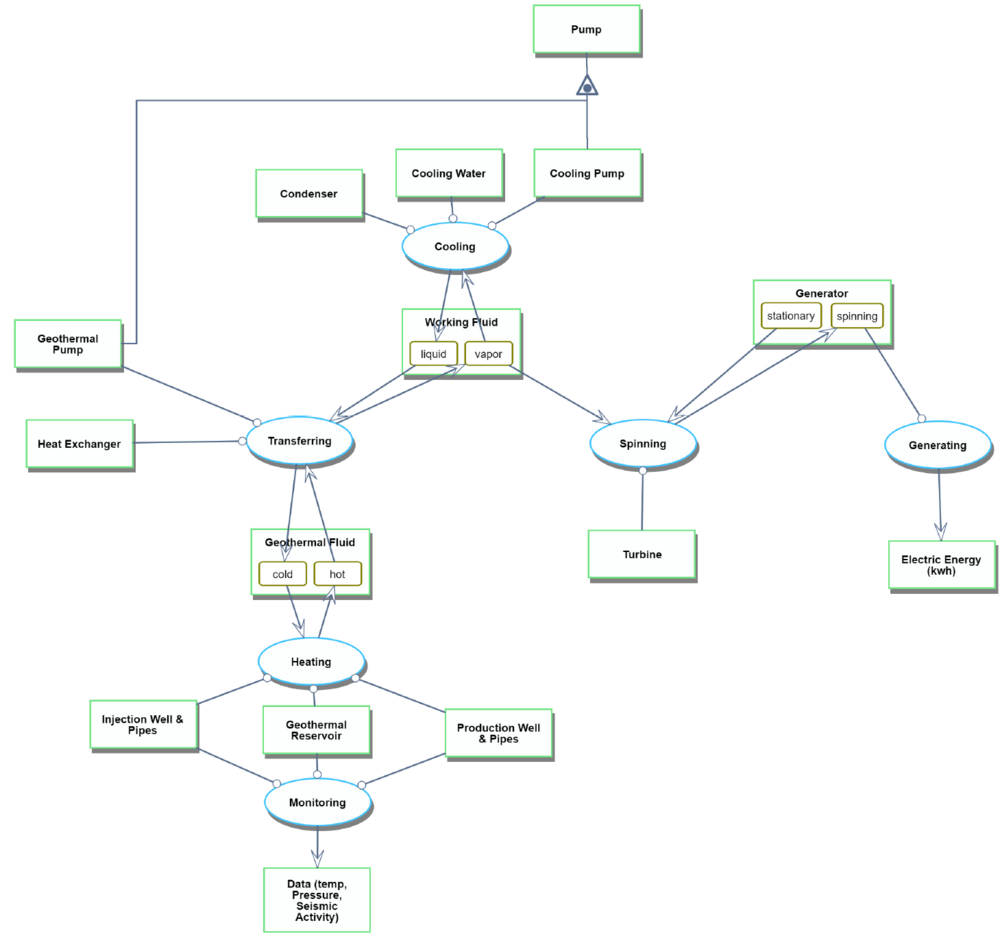
Roadmap Model using OPM
Figures of Merit
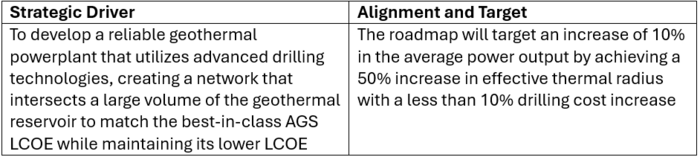
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
As a new company in the geothermal power production market, the effective thermal radius is the most sensitive design parameter that would allow us to make significant gains in the energy extracted. To increase this thermal radius, significant R&D will have to be invested in drilling technologies to enable the drilling of several web-like, closed-loop structures at the geothermal reservoir in order to maximize the heat extracted. Advancements in these drilling technologies will allow us to keep the cost low and maintain the current industry LCOE for AGS systems.
Alignment with company strategic drivers
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
The key observations from the competitor analysis include the higher CAPEX required for AGS systems compared to EGS systems, a lower overall LCOE for AGS systems, and the differences in expected energy output and operational period between AGS and EGS. The two projects utilizing AGS technology include the GreenFire Energy Coso Project and the SAGE Geosystems Project, both located in the United States. The higher CAPEX for the AGS projects indicated the higher cost of implementing closed-loop systems. A higher CAPEX would usually lead to a higher project LCOE, but that is not true for the AGS projects. Both AGS projects have a lower expected LCOE than the EGS projects. The average power output for each AGS project is not significantly higher than that of the EGS projects, but the expected operation periods are longer. Therefore, companies utilizing AGS technology focus on lower and more consistent energy output over longer periods of time, whereas EGS technology will focus on more rapid utilization of a geothermal reservoir.
File:Geothermal Competition Table 1.png
Technical Model
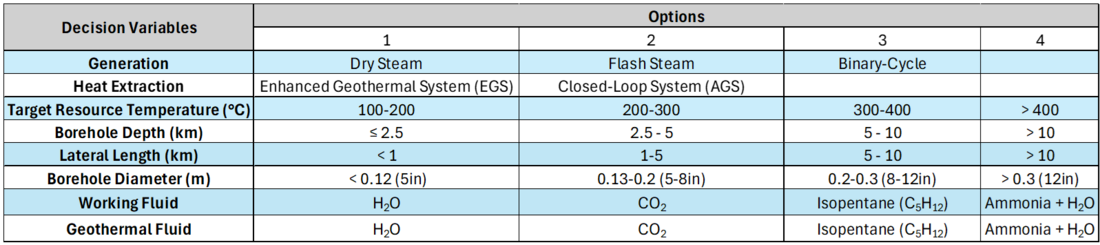
Morphological Matrix
A morphological matrix is used to determine the potential design vectors for the development of a technical model for the geothermal power plant.
Model Structure
The Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE) is a significant figure of merit when comparing these design vectors. The LCOE provides a metric in $/kWh that can be compared across all electricity generation systems.
This equation includes the lifetime costs of the system in the numerator and the lifetime energy produced in the denominator. The costs are determined by the type of geothermal power plant used and the process used to extract heat from the Earth. The energy produced is determined by understanding how much heat is available in a finite volume of the Earth, how much can be extracted, and how efficiently the chosen geothermal power plant system can convert that heat into usable energy.Due to the complexity of the energy generation model and the differences in technical heat extraction principles with varying design vectors, we chose to first focus on the first-order energy production equation, utilizing the theoretical potential equation. We then use this energy generation equation and estimated costs to determine the LCOE.
A single general equation for electricity generation from these systems is desirable to generate a tradespace of advanced geothermal concepts, including both enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) and closed loop systems (AGS). One approach to accomplish this is to use a volume-based estimation of recoverable heat with input variables that apply to both systems.
In this equation, Q is the product of a dimensionless recovery factor (R), the density of the rock (ρ), the heat capacity of the rock (C), the rock volume (V), and the temperature drop over the life of the system (ΔT)
Here, the average electrical power output (We) over the lifetime of a geothermal system could be expressed as the recoverable heat (Q), multiplied by a conversion efficiency factor (η), divided by the life of the plant (t) (or the life of a geothermal well) which we will assume to be 30 years.
In this equation, Q is the product of a dimensionless recovery factor (R), the density of the rock (ρ), the heat capacity of the rock (C), the rock volume (V), and the temperature drop over the life of the system (ΔT) (Augustine, 2011). In practice, there is a limit to the allowable temperature drop over the power plant's life imposed by the plant design; an average value of ΔT = 10°C has been suggested as a practical constraint (Augustine, 2011). This is somewhat counterintuitive as it results in the recoverable heat not being a function of reservoir temperature. We have chosen a more optimistic characterization of recoverable heat using a ΔT of 10% of the initial reservoir temperature. This more optimistic assumption could be justified by infill drilling. As the reservoir is thermally depleted, the well's flow rate must be reduced if we want to maintain the same temperature. Hence, we can still produce fluid at the required temperature at lower rates. It is reasonable to assume that it is desirable to extend the life of a plant with infill drilling. This allows us to extract more heat and value from each well. The impact of the reservoir temperature is accounted for in the conversion efficiency factor. A conservative recovery factor of 20% was suggested by Augustine 2011. The reservoir rock volume from which we extract heat is perhaps the most important and also one of the most difficult to constrain variables (as is the case in analogous systems of unconventional oil and gas reservoirs). Assuming a horizontal geothermal well, the thermally depleted rock volume could be approximated by the product of the lateral length of the well and pi multiplied by an effective radius of thermal depletion squared. This effective radius (r) is the main difference between EGS and closed-loop systems. For closed-loop systems (unless the reservoir has sufficient porosity and permeability to allow convection to occur), the effective radius of thermal depletion can be derived as a function of time and thermal diffusivity (α) of the reservoir. Assuming a well life of 30 years and a diffusivity of 1.57 E-6 (Toews & Holmes, 2021), this results in an effective radius of depletion of ~ 60 meters for closed-loop systems. The estimation of effective radius for EGS systems has higher uncertainty due to the complexity of the stimulated rock volume (SRV) created via hydraulic fracturing. A reasonable estimate of ~ 150 meters for the effective radius is supported by microseismic studies conducted at the DOE FORGE site in Utah (Finnila et al., 2023) and is also consistent with the average well spacing employed by Fervo at their Cape project (Fercho et al., 2024). This is a gross oversimplification of the physics, as, in reality, EGS entails an injector well and a producer linked via the hydraulically stimulated fracture network. Hence, in a closed loop where we have a temperature transient that reaches the full effective radius towards the end of the 30-year well life, in EGS, we immediately begin to sweep the reservoir volume between the wells. The model proposed here employs a binary value for effective radius, assuming a radius of 60 meters for closed-loop systems and a radius of 150 meters for EGS systems. The dimensionless efficiency factor (η) is characterized in our model as a function of temperature based on a linear fit to reported model results by Augustine 2011.
Combining these equations, we obtain an expression for the average electrical power output of an advanced geothermal system:
Like the overall energy production, many considerations are required to determine the overall life-cycle costs for a geothermal power plant. The system costs must be generalized to determine the first-order LCOE equation sensitivity to our design decisions. Due to the complexity of the possible design vectors, we use the system drilling costs in place of the total life-cycle costs. This allows us to compare all possible design vectors using the same cost estimation method. Also, in geothermal energy production, the drilling costs account for over 50% of the total system costs (Lowry et al.). In contrast, the stimulation and other maintenance costs can be insignificant or nearly zero based on the system's design.
There are many methods and models to estimate the drilling costs associated with geothermal energy production. Available models vary in the input parameters and consider various variables to determine the overall drilling cost. These costs are also only an estimate due to the non-homogenous nature of the subsurface. For this analysis, we used the ThermoGIS model to estimate the drilling costs for each design vector. This model uses the following equation to estimate the total cost of drilling based on the combination of well depth and total lateral drilling length (Limberger et al.).
For this cost estimate, s represents a well cost scaling factor with 1.0 or 1.5 used based on the well depth. MD represents the measured depth of the system, combining the total wellbore depth with the total drilled lateral length. Lastly, n represents the number of wells drilled. This parameter becomes important for EGS operations if energy is drawn from a reservoir faster than it can be replenished. In this case, additional wells must be drilled to stimulate the reservoir further.
Sensitivity Analysis
Theoretical Potential Thermal Model
The theoretical potential thermal model sensitivity analysis was done using a 200°C EGS design vector. Variables considered are effective thermal radius, efficiency, recovery factor, lateral length, and delta temperature. See partial derivatives below evaluated for the 200°C EGS design vector.
After normalization of the partial derivatives considered, we see that electricity generation is equally sensitive to η, R, ΔT, and L since these variables are all multiplicative in the numerator. The effective thermal radius is the most sensitive variable considered since it is squared.
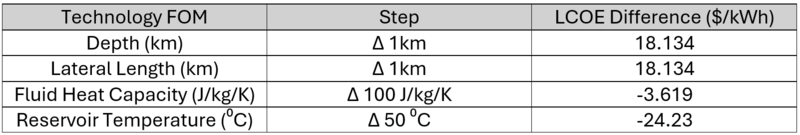
Drilling Cost Model
Using ThermoGIS drilling cost equation and the finite difference approximation method applied to a design vector representing the proposed Eavor-Loop 2.0 model design vector, we determined the incremental step changes in LCOE. The values of LCOE determined using finite difference approximation are shown in the table below.
Normalization:
Tradespace
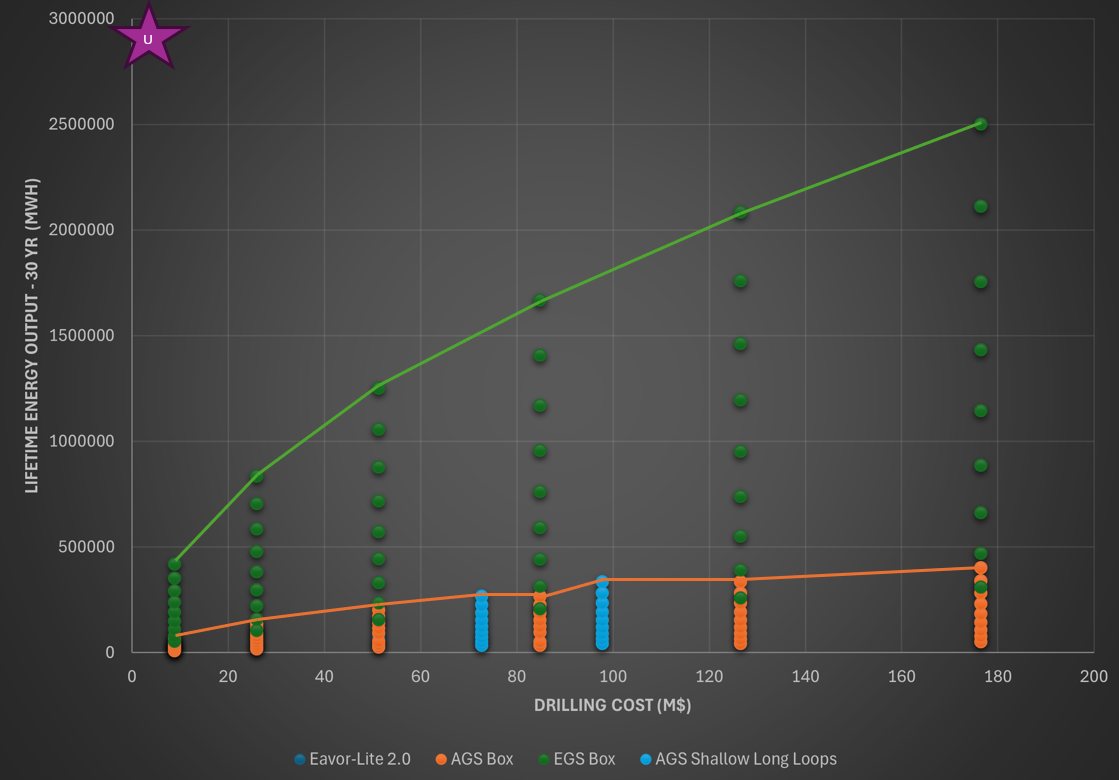
The following initial tradespace explores the relationship between a project's drilling costs, in a million USD, and the anticipated lifetime energy production over a 30-year operational timeline in MWh. The design vectors displayed identify the differences in EGS and AGS technologies. The distribution of design vectors in columns represents EGS and AGS projects with identical depths and lateral lengths but at increasing reservoir temperatures. This reservoir temperature begins at 200 degrees Celsius, increasing by 50 degrees, until reaching a maximum of 600 degrees Celsius. The green line represents the Pareto front for systems utilizing EGS technology, and the orange line is the Pareto front for systems utilizing AGS technology. Each point on the respective front represents either an EGS or AGS system with a reservoir temperature of 600 degrees Celsius. There is significant potential to shift the current Pareto front by exploring different combinations of depth and laterals lengths for each system.
Financial Model
List of R&T Projects and Prototypes
Key Publications and Patents
Key publications and patents pertaining to geothermal power plants incorporate various technologies and functional areas. This analysis's key publications and patents correlate to three functional areas related to geothermal power plants. These areas include drilling, subsurface resource extraction systems, and surface generation systems.
Publications
Sandia GeoVision Analysis Report - T. S. Lowry et al., “GeoVision Analysis Supporting Task Force Report: Reservoir Maintenance and Development”
The Sandia GeoVision Analysis report is widely cited as a reference for drilling considerations on all geothermal well development. This report provides a baseline for drilling costs given different borehole diameters and drilling directions. The drilling analysis includes bit design, environmental considerations, non-drilling activities, reservoir stimulation mechanisms and their associated costs, and hydraulic performance. These considerations are oriented on performance and cost, producing well cost curve scenarios for many drilling situations. This provides a significant resource in planning geothermal borehole development without requiring experience in the specific characteristics of the location or development. This report also includes maintenance and management practices to ensure enthalpy production remains within planned bounds. The combination of drilling costs tied to capital expenditure and maintenance and management costs provides a strong resource for estimating the overall costs needed for a levelized cost of electricity assessment.
Numerical Investigation of Closed-loop Geothermal Systems in Deep Geothermal Reservoirs - M. White et al., “Numerical investigation of closed-loop geothermal systems in deep geothermal reservoirs,” Geothermics, vol. 116, p. 102852, Jan. 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2023.102852.
The numerical model presented by White et al., in conjunction with multiple national labs and universities, collects data and processes from many sources and integrates them into a working web-based application. This application, called GeoCluster, provides an estimate for geothermal production and economic viability considering seven input parameters. These parameters are mass flow rate, horizontal extent, vertical drilling depth, rock geothermal gradient, borehole diameter, injection temperature, and rock thermal conductivity. To construct this model, the team integrated multiple computational models developed independently by each laboratory. These models focused on the heat recovery mechanisms of a closed-loop system in deep geothermal reservoirs. The models were integrated to incorporate advantages found in each and then validated using data from the active Utah FORGE geothermal testing site. This subsurface model becomes the Sandia HDR (hot-dry-rock) model. This model was combined with the surface generation model provided by NREL to produce the full GeoCLUSTER application. Overall, this application provides a significant asset to entities entering the geothermal power market by providing accurate cost and benefit estimates for implementing a closed-loop geothermal system considering a range of system and geological constraints.
Patents
Millimeter-Wave Drilling System:
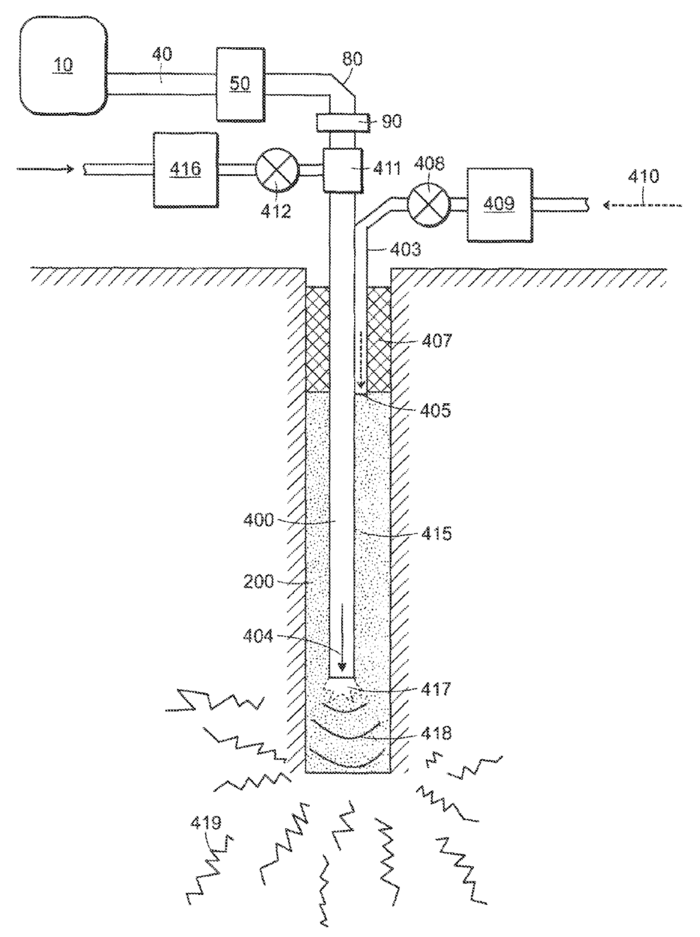
The Millimeter-Wave Drilling System patent (US Patent # 8,393,410 B2) is classified as E21B 7/14 in the Cooperative Patent Classification (CPC) system. In this system, E21B refers to technology related to Earth of Rock Drilling; Obtaining oil, gas, water, soluble or meltable materials or a slurry of minerals from wells and 7/14 add the modifier Drilling by use of heat; e.g. flame drilling (CPC: E21B 7/14). We identified this system during our disruptive technology analysis. The classification of this system as using “flame drilling” instead of high energy waves likely identifies the novelty of the technology in the E21B “Earth and Rock Drilling” field. The Millimeter-Wave Drilling System identified in this patent uses millimeter waves generated by a gyrotron and funneled into a borehole by a proprietary waveguide to radically heat the rock at the leading edge of the hole. This rock can be heated to temperatures sufficient to vaporize the rock. This vapor is then exfiltrated out of the borehole using a purge gas system to allow for continuous advancement. If brought into commercial operation, this technology claims to radically decrease the cost of well boring at extreme depths. This would significantly change the cost considerations when considering implementing a geothermal power system.
Geothermal Loop Energy Production System:
The Geothermal Loop Energy Production System (US Patent # 11,674,504 B2) has two classifications in the CPC system. They are F03G 7/04 and E21B 47/07. F03G 7/04 includes technology Spring, weight, inertia, or like motors; mechanical-power producing devices or mechanisms, not otherwise provided for or using pressure differences of thermal difference occurring in nature (CPC: F03G 7/04). E21B 47/07 includes a similar classification from the drilling technology but differs in purpose. This classification includes Earth or rock drilling, obtaining oil, gas, water, soluble or meltable materials, or a slurry of minerals from wells, and measuring the temperature of boreholes or wells (CPC: E21B 47/07). This technology utilizes the model principles in White et al. to generate electricity using supercritical CO2 (sCO2) in a closed-loop geothermal system. This design connects two vertical boreholes with a horizontal borehole running through a geothermal resource. The heated sCO2 is pumped through this subsurface system to a turbine to generate electricity. Once through the turbine, the sCO2 is compressed and sent back into the subsurface system to extract more heat. This closed-loop system can be implemented in a dry resource and does not require an existing or manufactured reservoir to operate. This increases the locational viability of the system to include more regions without easy access to subsurface permeable areas for heat.
Supercritical CO2 Turbine For Use In Solar Power Plants:
A significant patent related to this area is for a Supercritical CO2 Turbine for use in Solar Power Plants (US Patent # 7,685,820 B2). This system is classified as F03G 6/00 in the CPC. This classification includes Spring, weight, inertia, or like motors; mechanical-power-producing devices or mechanisms not otherwise provided for devices for producing mechanical power from solar energy (CPC: F03G 6/00). This patent may seem out of place when referring to geothermal power production, but the actual design only includes solar power plants to generate the initial heat required to run the turbine. The patent identifies that any process capable of providing heat to a heat exchanger could be an entity utilized in this design. The key piece of this design is the process of heating, compressing, and storing sCO2 as a working fluid to operate a turbine efficiently. This particular sCO2 turbine design is influential because it can utilize the working material with any significant heat resource and takes additional steps to capture unused heat energy to improve generation efficiency. This includes using three separate temperature recuperators to manage the sCO2 energy levels throughout the system. This allows the system to operate on a Brayton cycle, improving system efficiency over the Rankine cycle conversion system. This design also incorporates a heat storage system on the non-sCO2 side of the heat exchanger. This component includes nitrate salt storage tanks to store hot and cold salts during increased load demand.