Difference between revisions of "Autonomous Underwater Vehicle"
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
==Key Publications and Patents== | ==Key Publications and Patents== | ||
In the inspection of Oil & Gas offshore platforms, AUV moves slowly near the facilities such as pipelines on the seabed, and AUV checks the facilities by using nondestructive inspection methods. The key factors of inspection AUVs are | In the inspection of Oil & Gas offshore platforms, AUV moves slowly near the facilities such as pipelines on the seabed, and AUV checks the facilities by using nondestructive inspection methods. The key factors of inspection AUVs are "navigation”, “energy supply", "safety”, and “inspection method", so we select the related key publication and patent as below. | ||
===Publications=== | ===Publications=== | ||
Revision as of 03:35, 29 October 2020
Roadmap Overview
Throughout history, the ocean has been a vital source of sustenance, transport, commerce, growth, and inspiration. Yet for all of our reliance on the ocean, more than eighty percent of this vast, underwater realm remains unmapped, unobserved, and unexplored. AUVs provide great opportunities for exploring our oceans. An autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) is a robot that travels underwater without requiring input from an operator.
Image source: Naval Technology
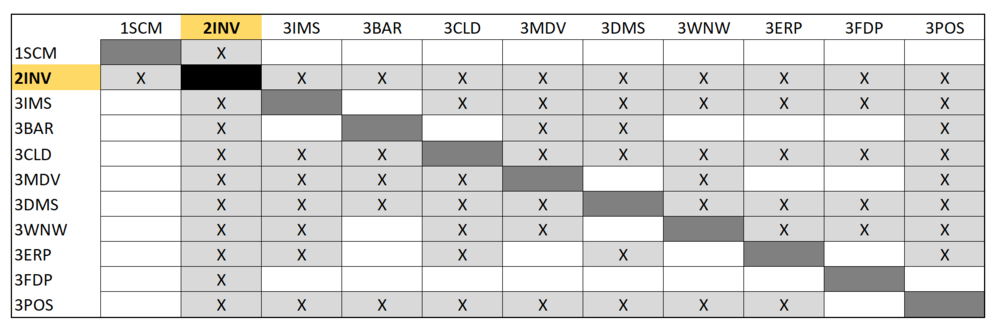
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
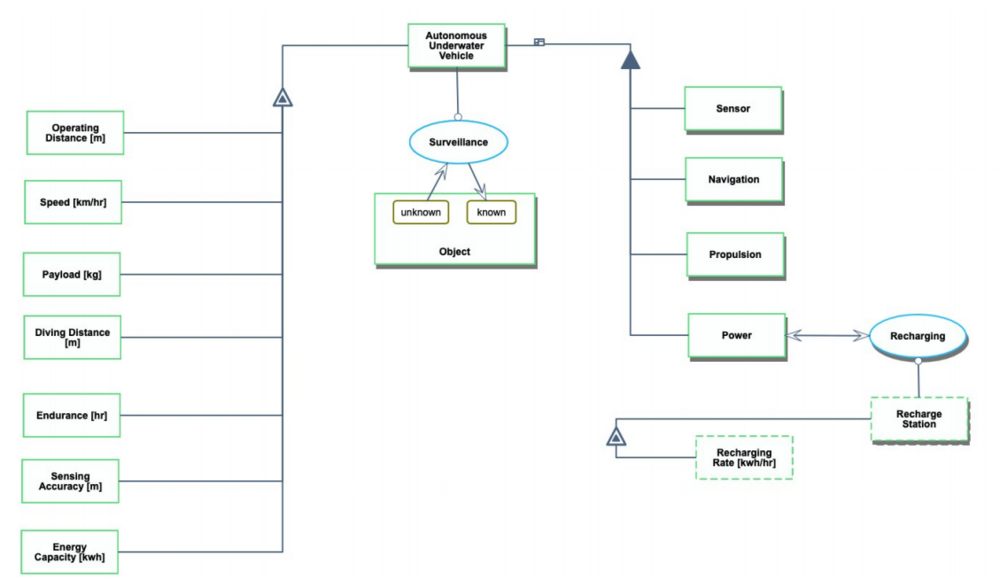
Roadmap Model using OPM
This diagram captures the main object of the roadmap (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle), its various instances including its decomposition into subsystems (Sensors, Navigation, propulsion, Battery, etc…), its characterization by Figures of Merit (FOMs) as well as the main processes (Surveying, Recharging, etc).
An Object-Process-Language (OPL) description of the roadmap scope is auto-generated and given below. It reflects the same content as the previous figure, but in a formal natural language.
Figures of Merit (FOMs)
The table below shows a list of FOMs by which autonomous underwater vehicle can be assessed.
| FOM name | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Operating Distance | km | Distance that can be traveled in an operation |
| Speed | km/h | Cruising speed in the water |
| Payload | kg | Useful payload that can be carried |
| Diving Depth | m | Depth that can be reached |
| Endurance | h | Hours that can be operated |
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
| # | Strategic Objective | Alignment and Targets |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | To develop batteries for AUVs that can last longer | This will enable the AUVs to dive for a longer duration of time without coming back to the docking station. This will also increase the range to which AUVs can go in one charge. |
| 2 | Better docking system for AUVs | Dockers are used to charge the battery and transfer information from AUVs. But current dockers are prone to error. So a better docking station will make the system more reliable. |
| 3 | Better sensing system for AUVs | One of the typical sensing technologies of the marine vehicle is SONAR. A more accurate SONAR system will help the AUVs to detect any defects in the pipes accurately. |
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
source: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3417/10/4/1256/pdf
Technical Model
Among many technical components of AUV, the sensor and power source are key components in order to use in the inspection field of the offshore oil & gas production facility, so we focused on these components.
Sensor
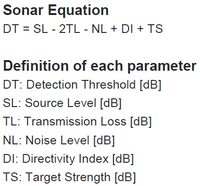
The key FOM of sonar is the “Detection Threshold (DT)”, and the technical equation of DT is as below.
Below is the normalized tornado chart that shows the sensitivity of each parameter to DT.
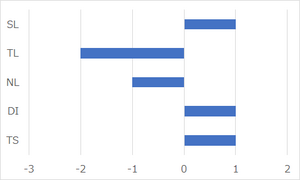
As this chart shows, TL is the most sensitive parameter. However, it is impossible to change TL and NL because these parameters are determined by the composition and depth of seawater. In addition, TS depends on the character of the inspection target, so we can’t also change this parameter. If we increase SL, DT will be improved, but it needs more energy in order to increase SL. This method may not be effective for AUV because the energy capacity of AUV is limited. On the other hand, DI can be improved by changing the directivity of the receiver, and this improvement would have minimal impact on other components of AUV, so this approach may be effective to improve DT.
Power Source
One of the expected power sources of AUV is a fuel cell. If we want to increase the energy capacity of a fuel cell, it is necessary to increase the amount of hydrogen storage. However, the space capacity of AUV is limited, so increasing the pressure of the stored hydrogen, rather than making the dimension of the hydrogen tank larger, would be effective. The relationship between the hydrogen pressure and the tank dimension is below.

If we can’t change the overall dimension of the hydrogen tank because of the AUV's size limitation, the variables that can be changed are “σ” and “t” in order to increase the hydrogen capacity. Below is the normalized tornado chart that shows the sensitivity of “σ” and “t” to the maximum hydrogen pressure.
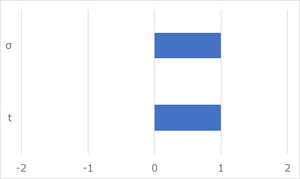
As this chart shows, “σ” and “t” have the same sensitivity for maximum hydrogen pressure. However, if we increase “t”, this directly leads to increasing the hydrogen tank weight. In order to avoid weight increase, it is effective to increase“σ”by changing the material of the hydrogen tank.
Key Publications and Patents
In the inspection of Oil & Gas offshore platforms, AUV moves slowly near the facilities such as pipelines on the seabed, and AUV checks the facilities by using nondestructive inspection methods. The key factors of inspection AUVs are "navigation”, “energy supply", "safety”, and “inspection method", so we select the related key publication and patent as below.
Publications
- Yoshiki Sato, Toshihiro Maki, Kotohiro Masuda, Takumi Matsuda, and Takashi Sakamaki, "Autonomous Docking of Hovering Type AUV to Seafloor Charging Station based on acoustic and visual sensing", IEEE Underwater Technology, 2017 Executive Summary: This report is about the automatic navigation and docking technology that use the acoustic signal and visible LED light. In addition, the author also reports the result of wireless charging to AUVs during docking.
Patents
- Byrd, et al. (2019) "Underwater vehicle for inspection of a subsea structure in a body of water and related method", United States Patent 10370074 Executive Summary: This patent is about the AUV for the inspection of undersea structures such as pipelines. The AUV has a body like a torpedo and has 2 sensors on the upper and lower side of its body. These 2 sensors enable us to detect problems such as corrosion in the pipelines non-destructively.