Difference between revisions of "Random Forest in Data Analytics"
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Roadmap Model using OPM== | ==Roadmap Model using OPM== | ||
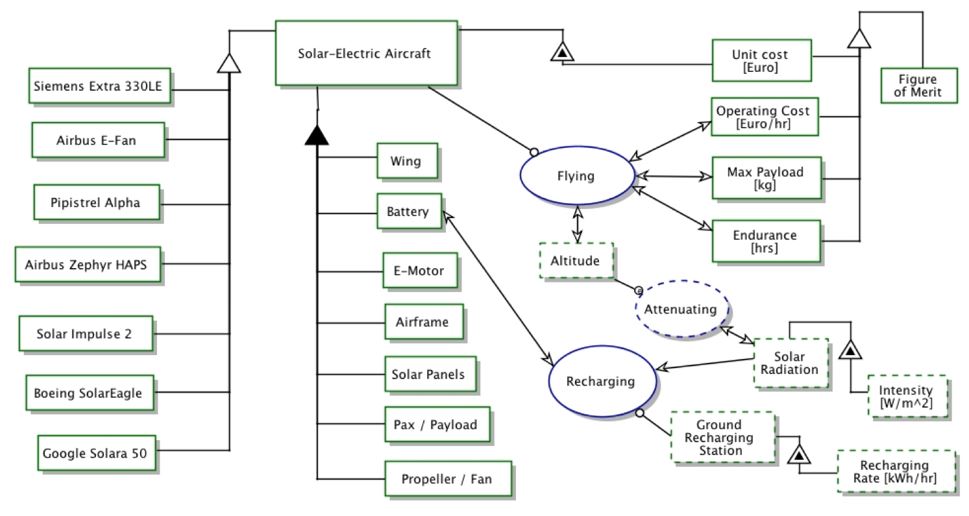
We provide an Object-Process-Diagram (OPD) of the 3RF roadmap in the figure below. This diagram captures the main object of the roadmap (Random Forest), its various instances with a variety of focus, its decomposition into subsystems (data, decision trees, votes), its characterization by Figures of Merit (FOMs) as well as the main processes (defining, predicting). | |||
[[File:Section 3.JPG]] | |||
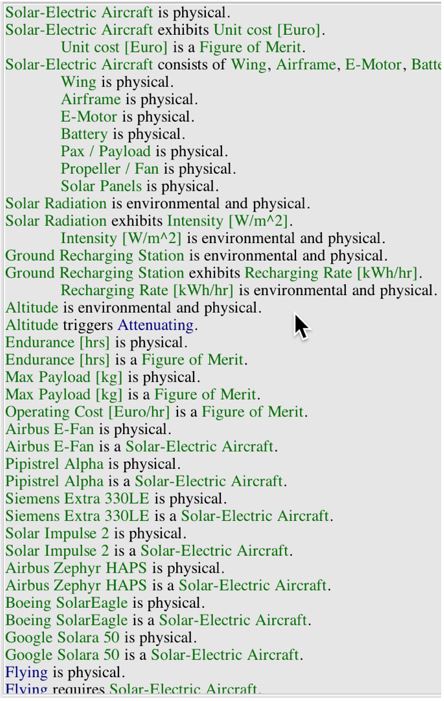
An Object-Process-Language (OPL) description of the roadmap scope is auto-generated and given below. It reflects the same content as the previous figure, but in a formal natural language. | |||
[[File:Section 3_2.JPG]] | |||
==Figures of Merit== | ==Figures of Merit== | ||
Revision as of 01:06, 8 October 2019
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
Unique identifier:
- 3RF-Random Forest
This is a “level 3” roadmap at the technology/capability level (see Fig. 8-5), where “level 1” would indicate a market level roadmap and “level 2” would indicate a product/service level technology roadmap.
Roadmap Overview
The high level workflow is depicted in the below.
Random forest is an ensemble Machine Learning technique to boost the accuracy of prediction of future, based on data from the past. “Wisdom of crowd” Building block is decision tree; a voting scheme is used to determine the final prediction Commonly used ensemble approaches are booting, bagging, and stacking
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
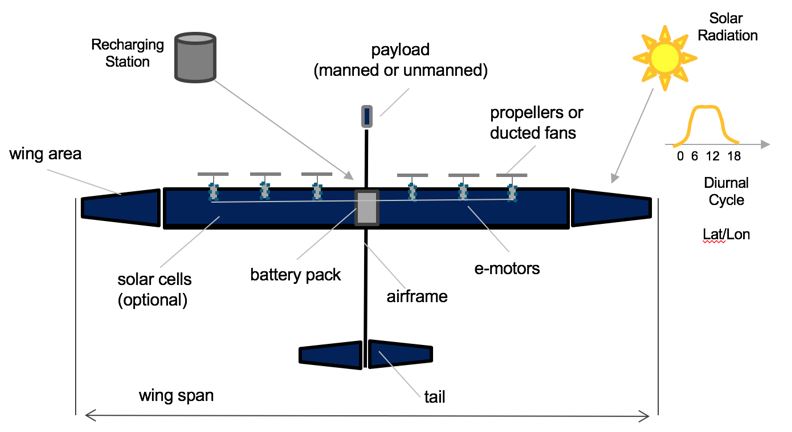
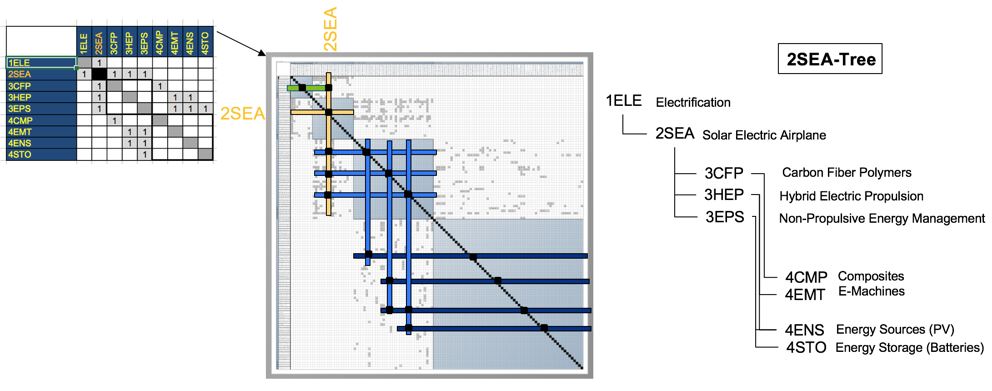
The 3-RF tree that we can extract from the DSM above shows us that the Random Forest(3RF) is part of a larger data analysis service initiative on Machine Learning (ML), and Machine Learning is also part of a major marketing initiative (here we use online advertising as an example). Random Forest requires the following key enabling technologies at the subsystem level: Bagging (4BAG), Stacking (4STK), and Boosting (4BST). These three are the most common approaches in Random Forest, and are the technologies and resources at level 4.
Roadmap Model using OPM
We provide an Object-Process-Diagram (OPD) of the 3RF roadmap in the figure below. This diagram captures the main object of the roadmap (Random Forest), its various instances with a variety of focus, its decomposition into subsystems (data, decision trees, votes), its characterization by Figures of Merit (FOMs) as well as the main processes (defining, predicting).
An Object-Process-Language (OPL) description of the roadmap scope is auto-generated and given below. It reflects the same content as the previous figure, but in a formal natural language.