Difference between revisions of "Hypersonic Transport Vehicles"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[File:Hypersonic_DSM_Hierarchy.png|600px|center]] | [[File:Hypersonic_DSM_Hierarchy.png|600px|center]] | ||
Note Note XX | |||
[[File:Hypersonic_DSM.PNG|600px|center]] | [[File:Hypersonic_DSM.PNG|600px|center]] | ||
Revision as of 18:11, 8 October 2023
System Overview
Hypersonic transport vehicles are a type of aircraft from the wider group of hypersonic systems. Hypersonic systems are all vehicles that operate in the flight regime where aerodynamic heating becomes significant, typically thought of as flight faster than Mach 5. Such systems include most atmospheric entry vehicles, some orbital launch vehicles, and several types of ballistic or maneuvering missiles. Hypersonic transport vehicles aim to move personnel and cargo from place to place much faster than traditional transonic or even supersonic aircraft. With a commercial application, this would be accomplished with the aim of generating profit for the company providing the transport service.
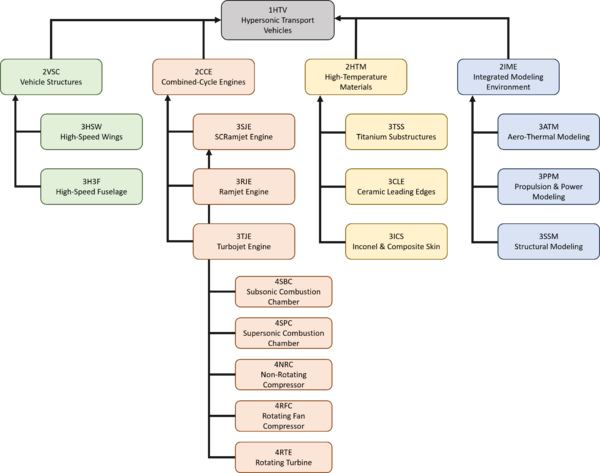
Roadmap Hierarchy
In Progress
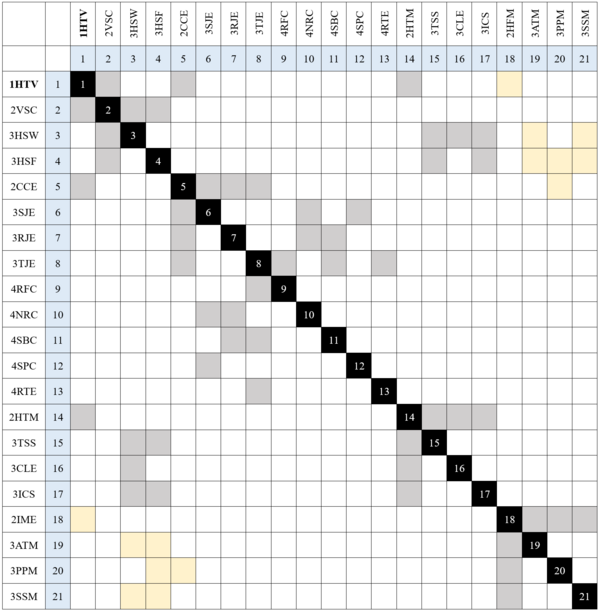
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
In Progress
Note Note XX
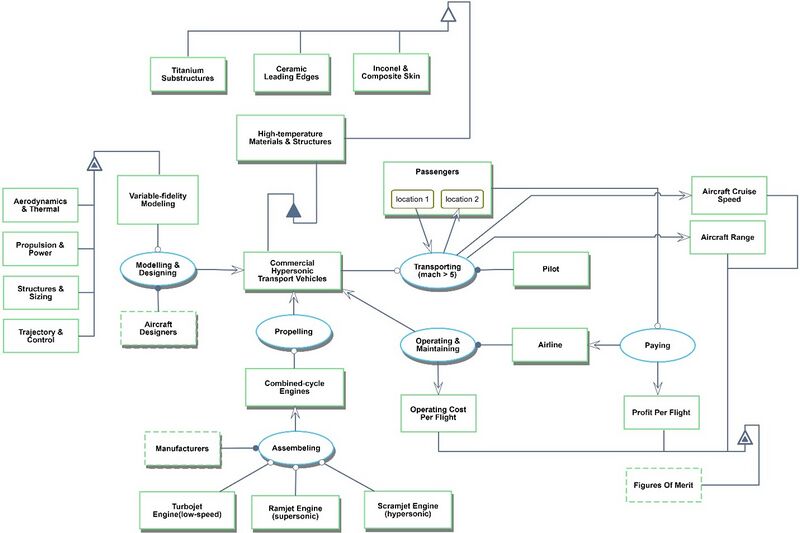
Roadmap Model Using Object-Process Methodology (OPM)
An OPM diagram showing a sample of the processes required for the creation and operation of commercial hypersonic transport vehicles is shown below. Note that the technology of interest (hypersonic transport vehicle) is shown near the center of the figures. The hypersonic transport vehicle serves to transport passengers from one location to another (also indicated near the center of the diagram). FOMs are shown towards the bottom right, with connections to relevant processes. It is noted that the sub-technologies shown in the diagram (high-temperature materials and structures, variable fidelity modeling, and combined-cycle engines) are discussed in detail by Bowcutt in [5].
Figures of Merit
The figures of merit (FOMs) relevant to commercial hypersonic transports include the distance covered per time (speed, v), aircraft range R, operating cost per flight C_O, and the aircraft profit per flight p. The profit p generated by the airline may be the single most important figure of merit, as it is the ultimate driver for the existence of commercial hypersonic vehicles (without profit, airlines will not offer such a service). These FOMs are described mathematically with nominal values in the table below.
| Figure of Merit (FOM) | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Speed | [m/s] | XXX |
| Aircraft Range | [m] | XXX |
| Operating Cost | [$] | XXXX |
| Profit per Flight | [$] | XXXX |
| Allowed Flights per Aircraft | [n] | XXXX |