Difference between revisions of "Bioelectronic Devices for Electrical Stimulation"
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[1] Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research. (2023, September 18). Retrieved from: https://feinstein.northwell.edu/institutes-researchers/bioelectronic-medicine | [1] Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research. (2023, September 18). Retrieved from: https://feinstein.northwell.edu/institutes-researchers/bioelectronic-medicine | ||
Revision as of 03:23, 12 October 2023
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
The Bioelectronic Devices for Electrical Stimulation [3BDES] is a level 3 technology roadmap focused around electrically stimulating biological systems (e.g., muscles, nerves, cells) for clinical purposes. A roadmap will be developed to explore the current status of the technology and the potential venues of progress from both a technical and business side.
Roadmap Overview
Bioelectronic Medicine is a novel approach that combines molecular medicine, neuroscience, and bioengineering to threaten and diagnose diseases and injuries. Bioelectronic devices can read and modulate electrical activity within the body. These devices open new possibilities and alternatives to diagnose and treat real-time diseases by using electrical pulses to restore health instead of chemical and biological drugs. In the literature, Bioelectronic Medicine can be found as neuromodulation, biostimulation, or electroceuticals. <ref> Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research. (2023, September 18). Retrieved from: https://feinstein.northwell.edu/institutes-researchers/bioelectronic-medicine </ref> [2] [3]
The bioelectronic devices that delivers electrical stimulation and dominate the market are:
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators (ICD)
- Cardiac Pacemakers (CP)
- Cochlear Implants (CI)
- Spinal Cord Stimulators (SCS)
- Deep Brain Stimulators (DBS)
- Sacral Nerve Stimulators (SNS)
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulators (TENS)
- Vagus Nerve Stimulators
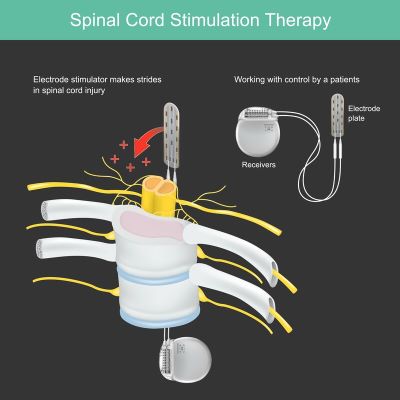
Below is an example use case of a stimulator used for the spinal cord:
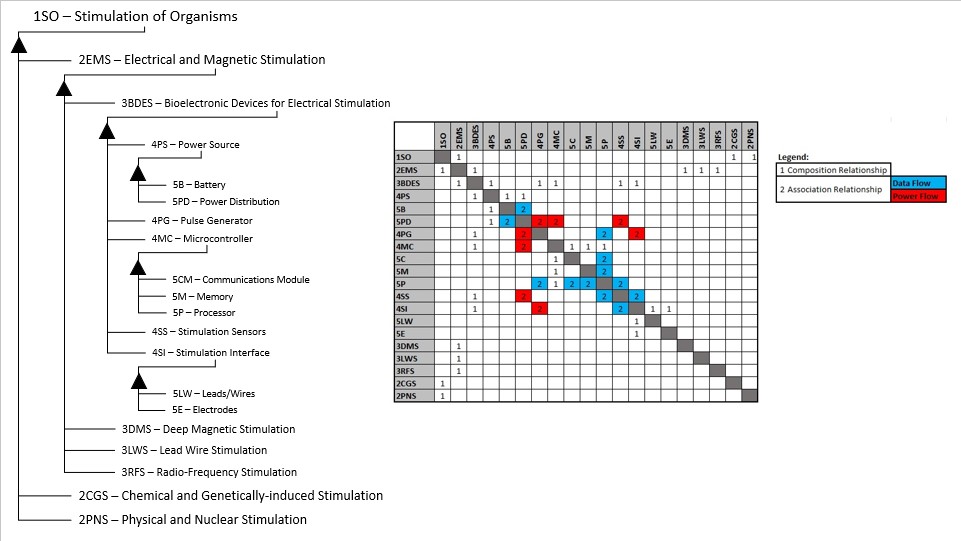
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
The above breakdown of the technology shows different potential roadmaps of consideration within the wider Organism Stimulation level 1 roadmap. Since the technology that was selected is generic in nature (i.e. no particular target organism for stimulation), alternative venues of implementation such as chemical stimulation can be compared in the future. The enabling technologies are listed under the roadmap of interest (3BDES): Power Source (4PS: to power the electronic components), Pulse Generator (4PG: to emit the electric signals), Microcontroller (4MC: to receive, analyze, control the pulse generator, and communicate with an external device), Stimulation Sensors (4SS: to sense feedback signals from the target organism), and Stimulation Interfaces (4SI: to interface directly with the organism). The level 4 and 5 technologies within the 3BDES roadmap are interrelated by power flows and data flows as shown.
Roadmap Model using OPM
Provided below is an OPD and OPL of the 3BDES roadmap. The OPM shows the components that make up the device, their Figures of Merit (FOMs), and the functions that take place to stimulate the bio-signal and change its states.
Figures of Merit
XXX
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
XXX
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
XXX
Technical Model
XXX
Financial Model
References
[1] Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research. (2023, September 18). Retrieved from: https://feinstein.northwell.edu/institutes-researchers/bioelectronic-medicine
[2] PNAS. (2023, September 18). Retrieved from: https://www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/pnas.1919040116
[3] National Library of Medicine. (2023, September 18). Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6057139/