Difference between revisions of "Nuclear Fusion"
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==Figures of Merit== | ==Figures of Merit== | ||
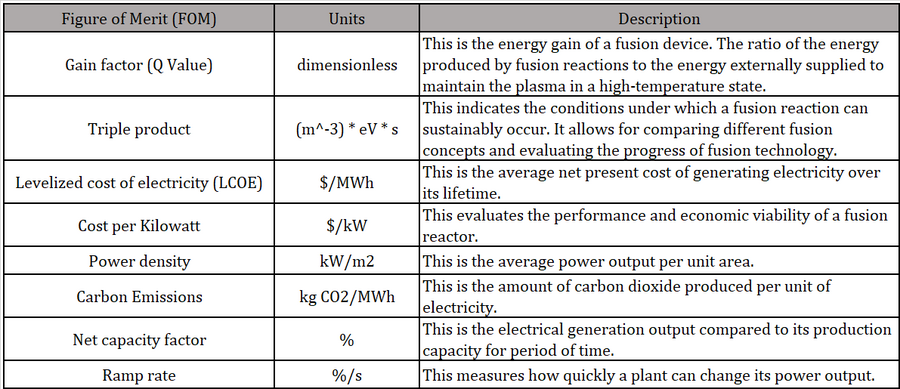
The table below shows a list of FOMs of nuclear fusion. | The table below shows a list of FOMs of nuclear fusion. | ||
[[File:team9_9.png|900px]] | |||
Gain factor(Q-Value) and Triple product is fusion-specific figures of merit. The Q-value is a crucial metric for evaluating the performance and viability of a fusion device. A device with a high Q-value suggests a significant net energy gain, increasing its potential as a practical energy source. | Gain factor(Q-Value) and Triple product is fusion-specific figures of merit. The Q-value is a crucial metric for evaluating the performance and viability of a fusion device. A device with a high Q-value suggests a significant net energy gain, increasing its potential as a practical energy source. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 45: | ||
Where Density is the number of nuclei per unit volume, Temperature is the kinetic energy of the particles in the plasma (the unit for temperature in fusion contexts is usually expressed in electron volts (eV)), and Confinement Time is the average time that a particle remains in the plasma before escaping. | Where Density is the number of nuclei per unit volume, Temperature is the kinetic energy of the particles in the plasma (the unit for temperature in fusion contexts is usually expressed in electron volts (eV)), and Confinement Time is the average time that a particle remains in the plasma before escaping. | ||
Revision as of 07:52, 12 October 2023
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
- 2NCF - Nuclear Fusion
Roadmap Overview
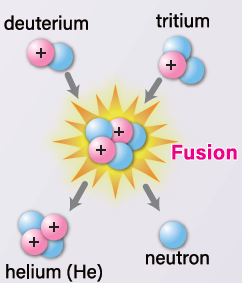
Nuclear Fusion Technology is a technology that involves the process of combining atomic nuclei to create new nuclei and generate energy in the process. It seeks to replicate the same physical process as the energy source of the Sun and other stars and is also referred to as nuclear fusion. One of the several fusion reactions is expressed as;
D+T -> 4He+n
where
- D: Deuterium
- T: Tritium
- He: Helium
- n: neutron
Fusion reactions occur when two or more nuclei come close enough to each other for a long enough time that the nuclear forces attracting the nuclei exceed the electrostatic forces pulling them apart, fusing them into a heavier nucleus. To realize nuclear fusion for energy generation, there are technical challenges, such as plasma control and energy supply, to create and maintain high temperatures and high pressure.
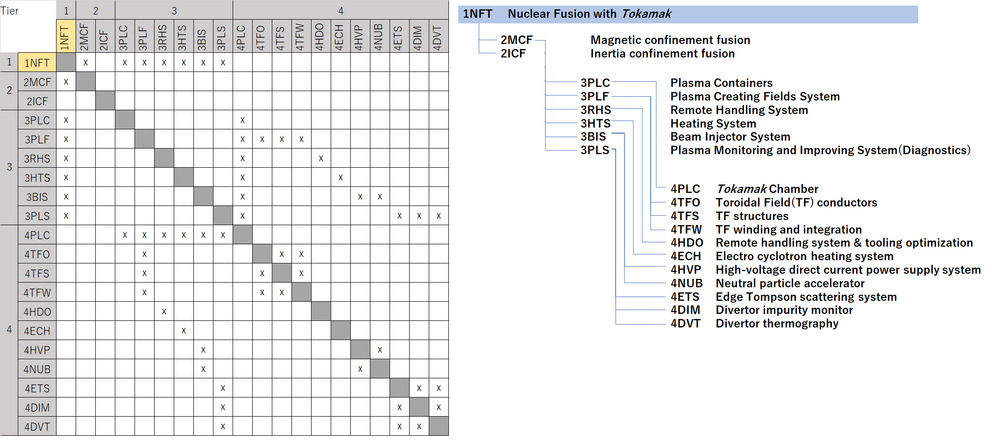
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
The 2LCNF tree shows us that Laser Confined Nuclear Fusion is part of larger global Nuclear Fusion Power initiative to harness fusion power. The DSM and tree both show that 2LCNF requires the following technologies at the subsystem level 3: 3LAS Laser, 3TAR ICF Targets, 3DIA Diagnostics, 3CTP Cryogenic Target Positioning, and 3CHB Target Chamber. Each level 3 subsystem also require enabling technologies shown as level 4 systems.
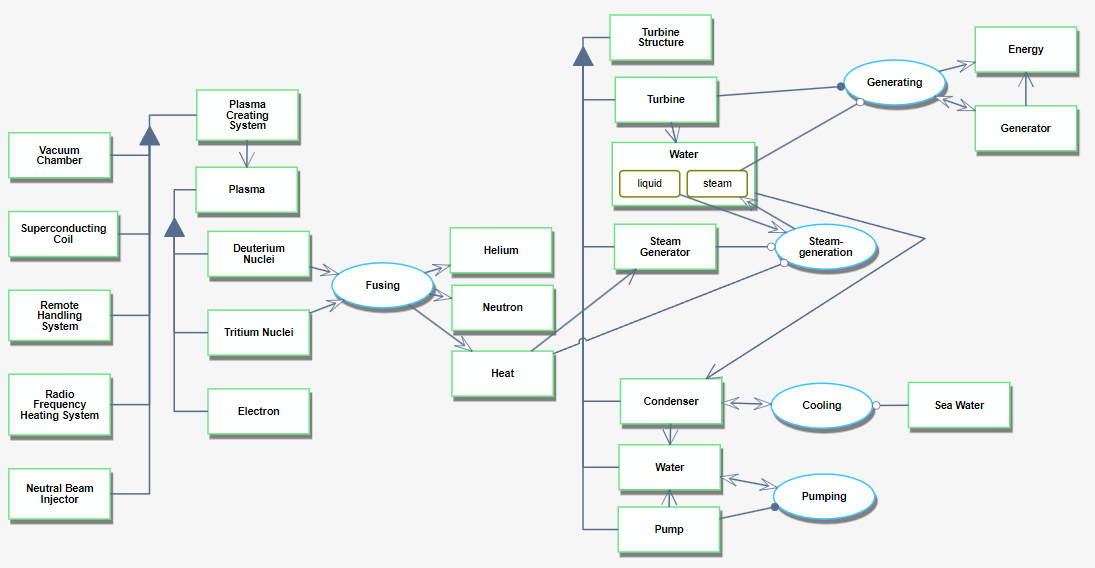
Roadmap Model using OPM
The OPM and OPL of one possible fusion technology system are depicted below. This technology assists in harnessing nuclear energy to generate power with lower risk than nuclear generation in a controlled environment and produces less radioactive waste.
Figures of Merit
The table below shows a list of FOMs of nuclear fusion.
Gain factor(Q-Value) and Triple product is fusion-specific figures of merit. The Q-value is a crucial metric for evaluating the performance and viability of a fusion device. A device with a high Q-value suggests a significant net energy gain, increasing its potential as a practical energy source.
Gain factor (Q-Value) = (Energy produced by fusion reactions) / (External energy input to the plasma)
Triple product can be used to compare performance across various approaches to fusion, such as magnetic confinement schemes, inertial confinement schemes, and magneto-inertial schemes, being independent of the scheme used to create the fusion plasma. It is defined as the product of three factors: plasma density, temperature, and confinement time. Triple produc is expressed as:
Triple product ((m^-3) * eV * s) =density(1/m^3) × temperature(eV) × confinement time (s)
Where Density is the number of nuclei per unit volume, Temperature is the kinetic energy of the particles in the plasma (the unit for temperature in fusion contexts is usually expressed in electron volts (eV)), and Confinement Time is the average time that a particle remains in the plasma before escaping.