Difference between revisions of "Space-Based Solar Power"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables= | =Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables= | ||
* ''' | * '''2SSP - Space-Based Solar Power''' | ||
We’ve chosen the acronym | We’ve chosen the acronym 2SSP to represent our technology of Space-Based Solar Power. The 2 in our acronym implies the system level, within the level 1 system of Renewable Energy Source. Our level 2 system level can be broken down into level 3 subsystems (High-Efficiency Solar Panels, Wireless Power Transfer, etc.) and level 4 components (Photovoltaic Materials, Antenna Structures, etc.). | ||
==Roadmap Overview== | ==Roadmap Overview== | ||
Latest revision as of 23:33, 9 October 2024
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
- 2SSP - Space-Based Solar Power
We’ve chosen the acronym 2SSP to represent our technology of Space-Based Solar Power. The 2 in our acronym implies the system level, within the level 1 system of Renewable Energy Source. Our level 2 system level can be broken down into level 3 subsystems (High-Efficiency Solar Panels, Wireless Power Transfer, etc.) and level 4 components (Photovoltaic Materials, Antenna Structures, etc.).
Roadmap Overview
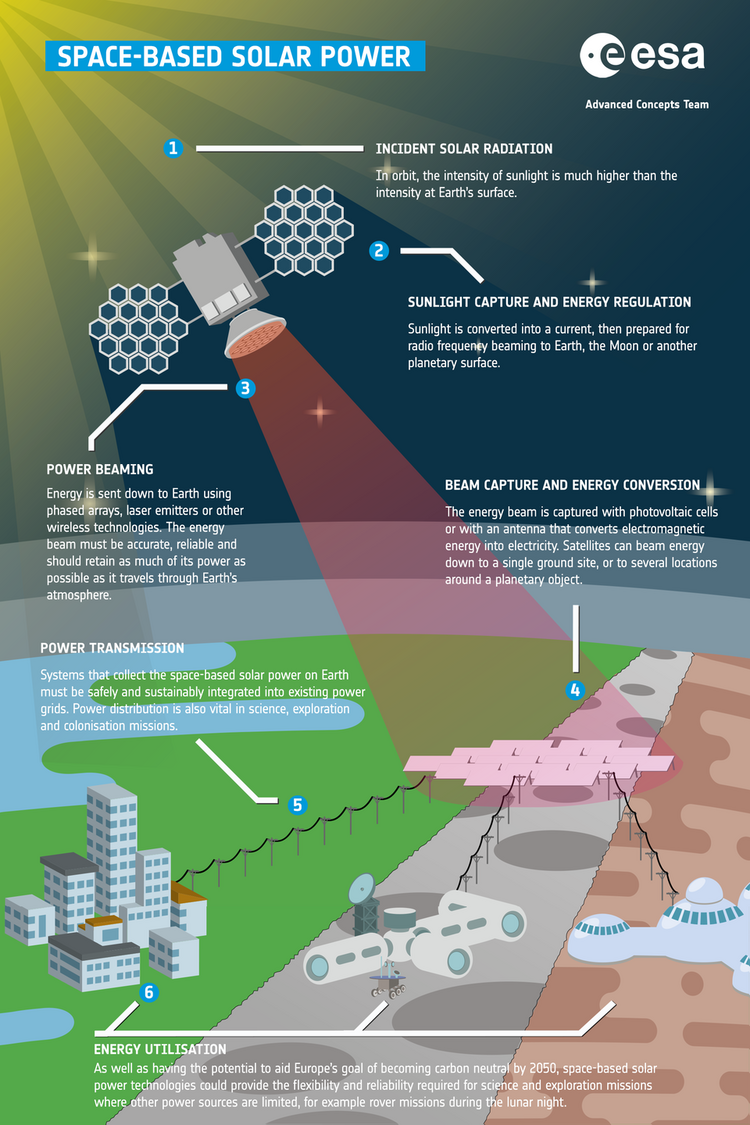
The working principle and architecture of Space-Based Solar Power is depicted in the below.
This technology transforms solar radiation using a spacecraft with solar panels, then wirelessly transmits it. The energy is then captured by a receiver and converted to electricity before storage and/or distribution.
A large solar array would be used to take advantage of the higher intensity sunlight outside of a planet's atmosphere using existing solar panel technology, then the electricity would be converted to an advantageous frequency for wirelessly transmitting long distances in a focused and steerable way – a key technical challenge. Finally, it would be received and converted back to electricity at the ground station or satellite for use.