Difference between revisions of "Space-based Solar Power"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
The working principle of Space-based Solar Power is depicted in the below. | The working principle of Space-based Solar Power is depicted in the below. | ||
[[File: Space-based_solar_power_article.png | | [[File: Space-based_solar_power_article.png |700px|center]] | ||
This technology transforms solar radiation using a spacecraft with solar panels, then wirelessly transmits it. The energy is then captured by a receiver and converted to electricity before storage and/or distribution. | This technology transforms solar radiation using a spacecraft with solar panels, then wirelessly transmits it. The energy is then captured by a receiver and converted to electricity before storage and/or distribution. | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation== | ==Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation== | ||
[[File: DSM SPS.png | | [[File: DSM SPS.png |800px|center]] | ||
==Roadmap Model using OPM== | ==Roadmap Model using OPM== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Figures of Merit== | ==Figures of Merit== | ||
[[File: FOM SPS.png | | [[File: FOM SPS.png |800px|center]] | ||
Revision as of 04:39, 10 October 2024
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
- 2SSP - Space-based Solar Power
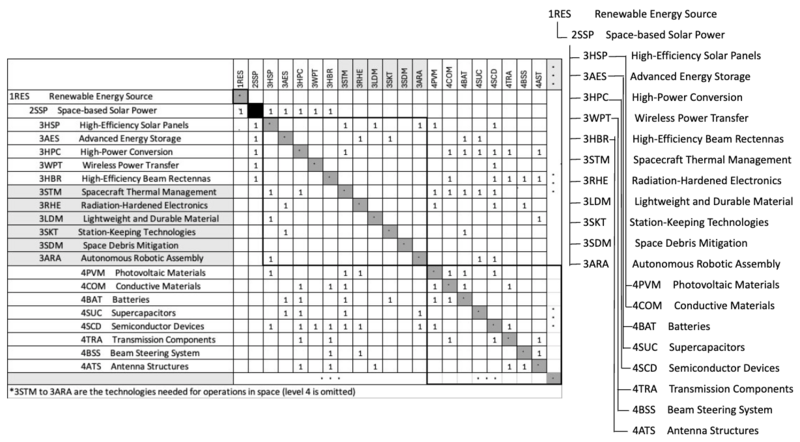
We’ve chosen the acronym 2SSP to represent our technology of Space-based Solar Power. The 2 in our acronym implies the system level, within the level 1 system of renewable energy source. Our level 2 system level can be broken down into level 3 subsystems (high-efficiency solar panels, wireless power transfer, etc.) and level 4 components (photovoltaic materials, antenna structures, etc.).
Roadmap Overview
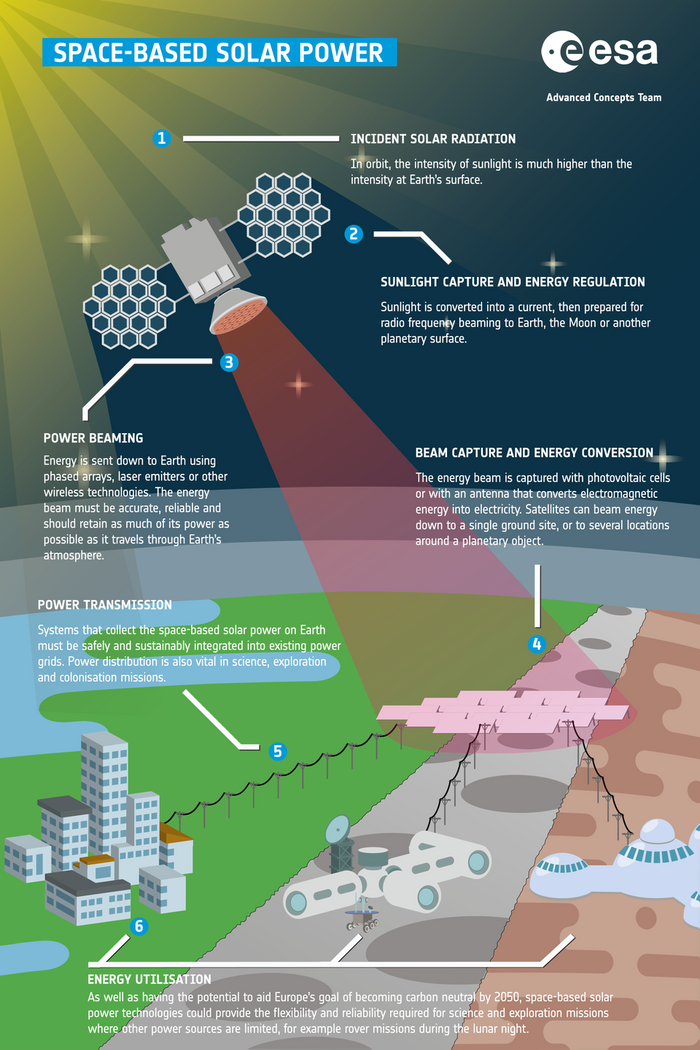
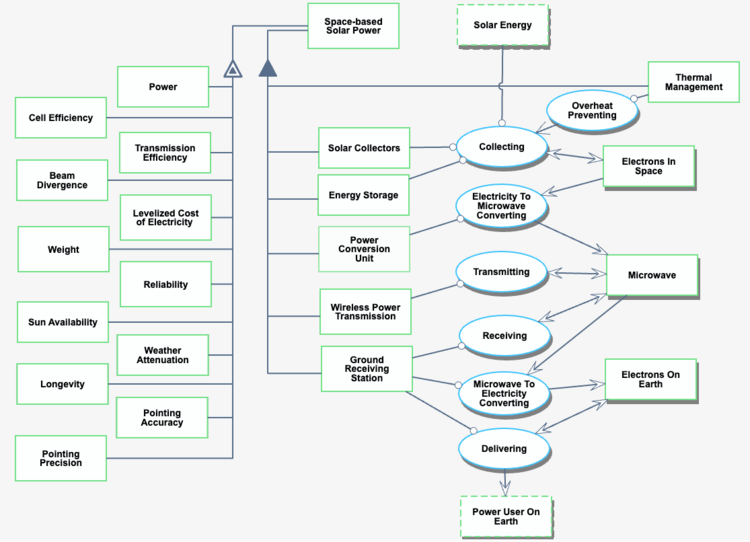
The working principle of Space-based Solar Power is depicted in the below.
This technology transforms solar radiation using a spacecraft with solar panels, then wirelessly transmits it. The energy is then captured by a receiver and converted to electricity before storage and/or distribution.
A large solar array would be used to take advantage of the higher intensity sunlight outside of a planet's atmosphere using existing solar panel technology, then the electricity would be converted to an advantageous frequency for wirelessly transmitting long distances in a focused and steerable way – a key technical challenge. Finally, it would be received and converted back to electricity at the ground station or satellite for use.