Difference between revisions of "On Demand Spare Manufacturing"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Feature Size || The smallest detail that can be reproduced || μm | | Feature Size || The smallest detail that can be reproduced || μm | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Lifespan || Replacement part lifespan || year | | Lifespan || Replacement part lifespan || year | ||
Revision as of 04:45, 10 October 2024
Overview
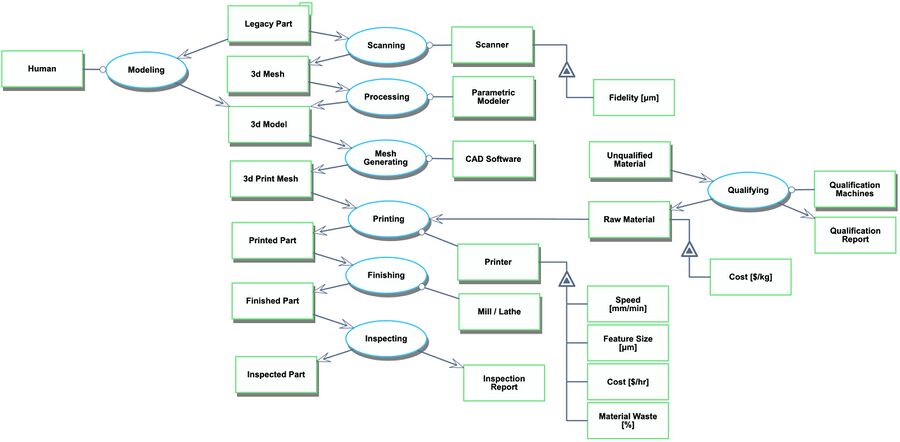
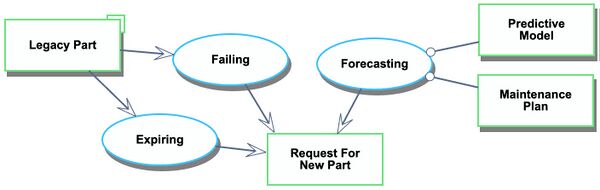
On Demand Spare Manufacturing is the manufacturing of spare parts as-needed as opposed to a traditional stockpiling approach. It leverages digital manufacturing technologies such as additive manufacturing, 3D scanning, optimization algorithms, and supply chain logistics. On Demand Spare Manufacturing requires identifying the need for a spare, transporting materials for manufacturing, scanning, processing, mesh generating, manufacturing the spare part, finishing, inspecting, transporting the spare part to the system, and installing the replacement part.
Design Structure Matrix
Roadmap Model using Object-Process-Methodology (OPM)
Figures of Merit
| FOM | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Turn-Around-Time | Time from need identified to need met | hr |
| Cost | Total replacement part cost | $ |
| Feature Size | The smallest detail that can be reproduced | μm |
| Lifespan | Replacement part lifespan | year |
| Material Cost | Raw material cost | $/kg |
| Production Cost | Aggregate cost of labor, machine time, etc... | $/hr |
| Material Waste | Excess material utilized in the production process | % |
| Defect Rate | The fraction of parts that are not suitable for use | % |