User talk:SAF Brazil
Roadmap Creators: Gabriel Ruscalleda, Emilia Ospina Arango and Dawit Dagnaw
Time Stamp: Updated 10 October 2024
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
Our technology roadmap identifier is shown as:
- 2BSSAF - Brazil Solution - Sustainable Aviation Fuel
This indicates that we are dealing with a “level 2” roadmap at the product level, where “level 1” would indicate a market level roadmap, "level 2" would indicate our SAF Production and “level 3” or “level 4” would indicate an individual technology roadmap.
Roadmap Overview
The aviation industry, currently responsible for approximately 800-850 million tons of CO2 equivalent emissions annually, faces a significant challenge as demand for air transportation services is projected to double in the coming decades. [1] Despite the inherent difficulties of decarbonizing its fossil-fuel-dependent business model, the global airline industry has committed to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. [1] The primary source of these emissions is the combustion of Conventional Aviation Fuel (CAF), also known as Jet Fuel, which powers aircraft engines. In response to this challenge, Sustainable Aviation Fuels (SAFs) have emerged as a crucial milestone in the sector's decarbonization path. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, low-carbon alternative fuels derived from sustainable feedstocks and production processes could potentially reduce emissions by up to 94% compared to CAF, which has an emission factor of 89 gCO2e/MJ.[6] The potential impact of SAFs is substantial, with estimates suggesting they could contribute up to 65% of industry-wide emission reduction targets, [1] making them a key component in the aviation sector's efforts to achieve sustainability and meet its ambitious climate goals.
Brazil's abundant natural resources position it as a key player in the future global sustainable fuel economy, particularly in Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) production. [] The country's strengths align with multiple decarbonization levers,[3] including:
- Nature Based Solutions in reforestation of vast degraded/deforested lands to produce 1st or 3rd generation feedstock
- Sustainable Agriculture for production of 1st and 3rd generation feedstock using Regenerative Agriculture practices
- Renewable Energies to power production with clean energy matrix, offering SAF with higher emission reduction potential
Global SAF production is expected to reach 1.9 billion liters in 2024, three times the production capacity of 2023 estimated at ~500,000 liters per year. [] In a decade, this is forecasted to evolve so that Brazil and US produce equal amounts of SAF (50 B L/year each). [7] While Brazil's domestic SAF demand is estimated at 8 billion liters per year, the US is expected to require 120 billion liters annually, positioning Brazil in a unique position to become a supplier for the global market with its substantial production surplus[7]
Considering Brazil's agricultural strengths and competitive advantages, [3] the most promising short-term SAF production pathways are HEFA and ATJ, leveraging well-established ethanol infrastructure, while long-term prospects (subject to technological progress) include hydrogen and e-fuels produced with renewable energy. The development of Brazil's SAF ecosystem will largely depend on public policy, with positive signals from Brazil’s government through the approval of "Lei do Combustível do Futuro," which mandates increased use of biofuels and aims for a 10% reduction in airline emissions by 2037. [4]
This roadmap explores the dilemma of SAF scalability in Brazil, focusing on two critical aspects: availability and affordability. The feedstock supply and production capacity are analyzed within the country, and innovative strategies are proposed to enhance scalability. Additionally, economic competitiveness of SAF will be evaluated and compared to conventional jet fuel, considering factors such as production costs, market incentives, and policy support in Brazil.
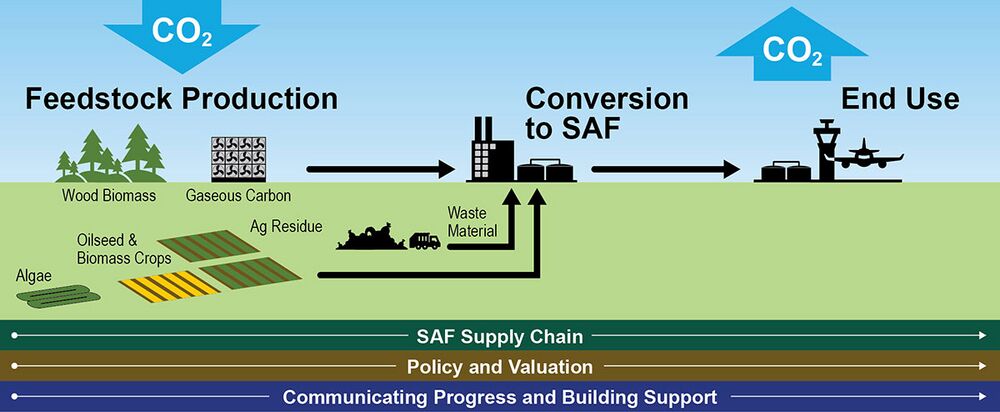
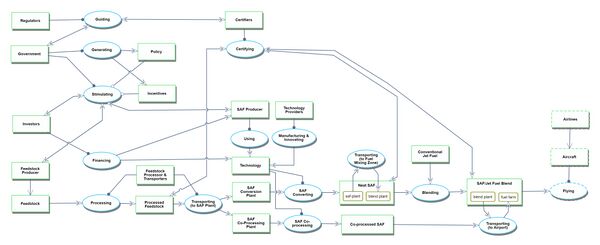
The figure below contains graphic representation of the SAF supply chain from the SAF Grand Challenge Roadmap
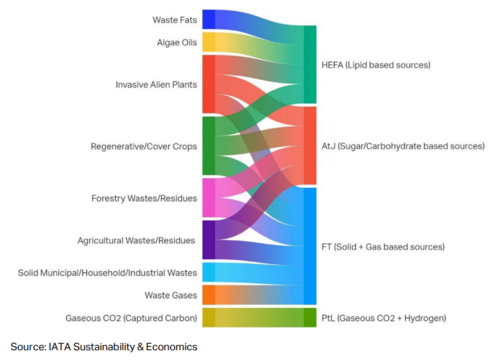
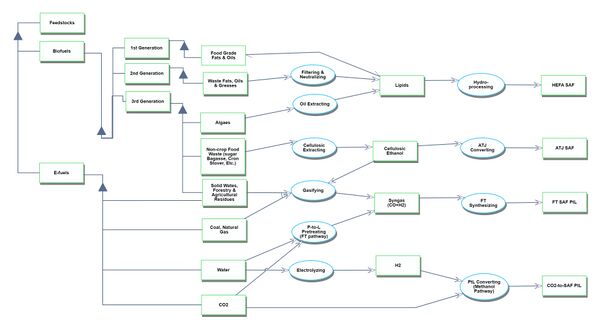
Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) can be produced through various technological pathways using diverse feedstock combinations, resulting in different types of SAF. Currently, more than 11 production pathways and multiple feedstocks are under active research, with new methods and potential materials expected to emerge in the coming years. Several pathways have successfully produced drop-in fuels that meet quality standards and are compatible with existing aircraft, airplane systems, and pipeline infrastructure. Although successful test flights have been conducted using 100% SAF (neat SAF), current usage primarily involves blending SAF with conventional jet fuel in varying proportions, partly due to supply constraints. The aviation industry continues to explore and refine SAF production methods, focusing on expanding viable feedstocks, improving production efficiency, and increasing SAF yield and quality. For a comprehensive understanding of feedstocks and their associated pathways, refer to the illustration provided below.
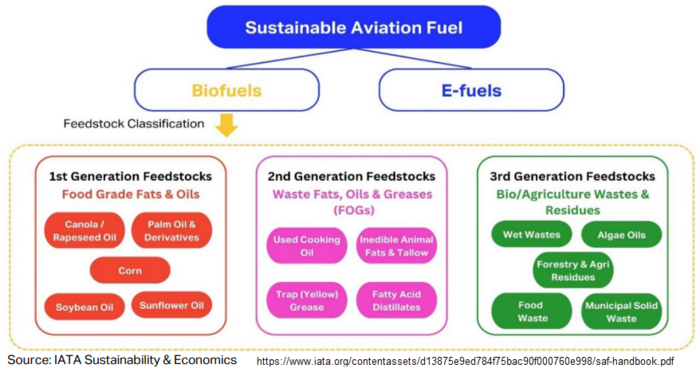
Three generations of feedstocks are defined on the IATA SAF Handbook based on their usage chronology, emission reduction potential, sustainability criteria, environmental impact, and availability:
1.First Generation (1G): Includes food-grade fats and oils like canola, palm, and soybean. While technologically mature and commercially scalable, they pose sustainability issues such as competing with food supply and high land usage.
2.Second Generation (2G): Comprises waste fats, oils, and greases (FOGs) like used cooking oil and inedible animal fats. These are more sustainable than 1G due to higher emission reduction and no additional land usage, but are more expensive due to limited supply.
3.Third Generation (3G): Encompasses biological/agricultural wastes and energy crops from degraded land, including municipal solid waste, forestry residues, and algae oils. They offer the most positive environmental impact and cost benefits but require advanced processing technologies.
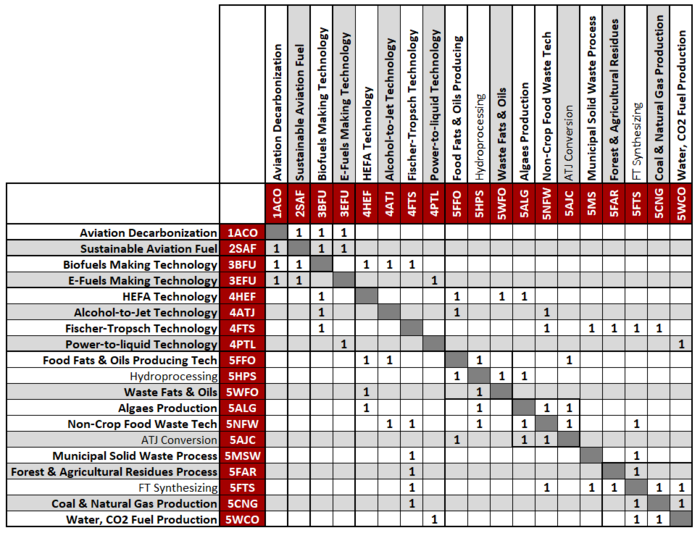
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
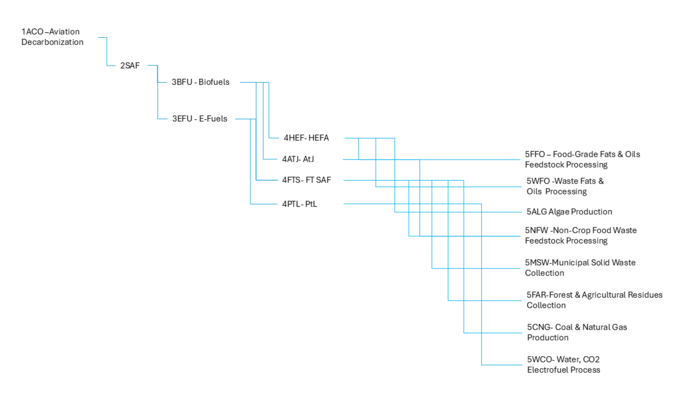
The tree below shows the relationship between other technologies related to the SAF. It is focus on the enabling technologies to SAF, considering key feedstocks and processes. Starting from our main goal to decarbonize aviation (1ACO), 2SAF plays an important role and can be decomposed in multiple technologies. Focusing on feedstock classification, SAF can be made out of two main technologies including Biofuels (3BFU) making technologies and e-fuels (3FU) making technologies such as 4HEF, 4ATJ, 4FTS and 4PTL. These technologies possess a dependency with specific feedstock technologies and processes such as 5FFO, 5HPS, 5WFO, 5ALG, 5NFW, 5AJC, 5MSW, 5FAR, 5CNG and 5WCO.
The DSM below shows the connections of SAF to Level 3, 4 and 5 technologies. These connections will be presented in more detailed in the next section using Object-Process-Model (OPM).
Roadmap Model using OPM
The Object-Process-Model (OPM) of the 2BSSAF - Brazil Solution - Sustainable Aviation Fuel roadmap is presented in the figures with the Object-Process-Language (OPL) below. The OPM was divided in two OPMs: Level 1 and Level 2. Level 1 focuses on the main stakeholders including the Feedstock Producer, Fuel Producers, Government (policy, guidelines, sponsorship), Regulators and Certifiers while Level 2 focuses on the feedstocks and SAF making technologies.
Level 1 OPM
Level 2 OPM
Figures of Merit
The table below shows a list of FOMs focus on productivity, scalability, accessibility & cost of pathways for evaluation of SAF’s production ecosystem.
| Category | Figure of Merit | Units | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Competitiveness | SAF unit cost | [USD/ton] | Market cost of SAF per unit of volume or energy |
| Cost per reduced ton | [USD / tCO2e] | Incremental cost per ton of carbon equivalent reduced vs CAF | |
| Investment potential | [USD / tCO2e] | Financing opportunity per potential unit output of technology | |
| Installation cost per unit | [USD / L] | Cost of deploying SAF production infrastructure relative to capability | |
| Efficiency | Energy efficiency | [%] | Energy input to produce SAF vs energy output in SAF |
| Productivity | Feedstock crop yield | [Ton / ha] | Crop yield in volume produced per unit area |
| Feedstock availability | [Ton / year] | Crop availability in volume produced per year | |
| SAF conversion yield | [%] | SAF produced with relation to total refinery biofuel production | |
| Performance | Energy density | [MJ/L] | Energy content per unit volume of fuel |
| Blend ratio of pathway/feedstock | [%] | Volume SAF relative to total volume of fuel after blend | |
| Sustainability | Carbon savings potential | [tCO2e / L] | Potential reduction in emissions for use of SAF vs CAF as baseline |
| Carbon emissions | [gCO2e / MJ] | Life-cycle carbon equivalent emissions to generate unit of fuel |
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
Article 2. Techno-economic and environmental assessment of renewable jet fuel production in integrated Brazilian sugarcane biorefineries
Citation: Klein, Bruno Colling, Mateus Ferreira Chagas, Tassia Lopes Junqueira, Mylene Cristina Alves Ferreira Rezende, Terezinha de Fátima Cardoso, Otavio Cavalett, and Antonio Bonomi. “Techno-Economic and Environmental Assessment of Renewable Jet Fuel Production in Integrated Brazilian Sugarcane Biorefineries.” Applied Energy 209 (January 1, 2018): 290–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.10.079.
Highlights: • Study sponsored by Embraer, The Boeing Company and CTBE compares routes for SAF production in integrated sugarcane biorefineries in Brazil, from an economic and environmental performance. • All biorefineries are assumed to be self-sufficient with no reliance on external energy sources and benchmarked against a base case that comprises an ethanol distillery operating during sugarcane season • 8 scenarios with sugarcane mills are annexed to 3 ASTM approved SAF technologies are evaluated for a series of elegible feedstock in the Brazilian context: o HEFA • Palm Oil • Macauba Oil • Soybean Oil o FT Gasification • Sugarcane straw and bagasse • Eucalyptus lignocellulosic material o ATJ • Ehtanol 1G • Ethanol 2G • Isobutanol • Main conclusions:
o HEFA based biorefineries yielded highest production capacity of SAF (267 M L/y) o FT produced SAF at the most competitive cost however with low levels of output and heavily dependent of feedstock and process configuration o All routes enable an overall positive climate change impact of ~70% when compared to conventional Jet Fuel
Detailed overview:
The study considers a "self-sufficient" biorefinery that operates out of a variety of biomass feedstock and does not require external supply of electricity, natural gas or others for operations. Energetic requirements of plant are met by burning bagasse and straw (occasionally) in Cogeneration of Heat and Power units to produce steam and electricity, where excess electricity is sold to the grid
Sugarcane production in Brazil follows one of three plant configurations: • Autonomous Ethanol Distillery: Y: 100% Ethanol • Sugar factory: 100% Sugar • Sugar factory with annexed ethanol distillery: Both Ethanol and Sugar
Study focuses on Autonomous Ethanol Distillery as host plants for production of SAF. • Main output: hydrous ethanol (93% w/w) • Differentiating factor: Use of 50% of recovered straw through second-pass straw harvesting process increases power output vs mills that dont
Conventional way of addressing and studying SAF's impact and feasibility often center in standalone production plants. The article explores the potential for risk-mitigation and reduction of the MJSP as a result of establishing an integrated biorefinery configuration. Though some previous studies have evaluated similar hypothesis for ATJ, the research extends the hypothesis to also cover FT and HEFA pathways in the Brazilian context.
(PASTE PHOTO)XXXXXXX
HEFA Route: • Explored 3 types of vegetable oils through the process illustrated in Fig 1.a. to evaluate their hydrocarbon production potential. This is mainly determined by the degree of unsaturation of fatty acids which has a direct effect on the amount of hydrogen needed for the conversion into liquid hydrocarbon. • Consumption was found to be most efficient for Palm Oil (31.7 kg H2/ton Oil) followed by Macauba Oil (33.3 kg H2/ton Oil) and finally Soybean Oil (37.7 kg H2/ton Oil) • Plant capacity is determined by surplus electricity as limiting factor for H2 production, as supplied from annexed sugar cane mill
FT Route: • Explores lignocellulosic material from two sources: sugarcane and Eucalyptus. Both biomass have a similar chemical composition and are of significant importance in Brazil's energy sources • Output of FT process is heavily reliant on scale of plant, process configuration and feedstock type/composition • Given the sensibility of the process to the initial state of the biomass, development of efficient pretreatment options is a key factor in allowing for a financially viable scaling • Process has a series of byproducts including large volumes of Green Naphtha and energy, in the form of steam from high-temperature process in the thermochemical plant that can act as energy sources for annexed sugarcane mill • Plant capacity is determined by amount of biomass produced, considering seasonality and availability of feedstock
ATJ: • Explores 1G and 2G Ethanol with the hope of leveraging existing ethanol-producing infrastructure in Brazil as well as Isobutanol as a result of fermentation of sugarcane juice • Process has a series of byproducts including Green Naptha and Green Diesel • Plant capacity is determined by alcohol availability as produced by sugarcane mill, reserving a proportion of it to continue operating the plant in off-season
Both HEFA and ATJ routes require hydrogen as an input for SAF production. Considering the self-sufficiency aspect of the biorefinery in question, multiple methods for its in-situ synthesis are mentioned, ultimately postulating Water Electrolysis as the most adequate in the context of Brazilian sugarcane mills. Other methods such as methanol/ethanol steam reforming exhibited short comings such as excessive reliance on fossil fuels, low cost-efficiency or required proximity to the natural gas grid. The authors highlight further the attractiveness of the Water Electrolysis process when considering the generation of ethanol as byproduct and its importance for the Brazilian biofuel economy.
Technoeconomic assessment: • Production costs of the different biomasses are contemplated, leveraging information from comprehensive databases of agricultural production • Minimum selling prices of oil are determined considering all the revenues of coproducts from processing and extraction of grains/seeds/fruits into oil under a predetermined IRR for the plant, as well as including capital and transportation costs. • Similarly, green Diesel produced as byproduct is assumed to be recirculated to meet demands from agricultural production process, estimated at 4L diesel/ton of sugarcane, helping lower overall biomass production costs and lowering associated environmental impacts. • HEFA and FT biorefineries replace 100% of the fossil fuels required as input with green diesel byproduct, ATJ still requires external fuel to some extent • Liquid hydrocarbon output increases when biorefinery operates with multiple types of biomass and larger volumes, rather than off a single one • Land use and direct occupation of agricultural land are also evaluated, concluding that ATJ requires the least extension, followed by Macauba and Palm HEFA routes which produce higher volumes of SAF with less area than their Soybean counterpart.
The main inputs and outputs of the technoeconomic assessment for the 8 pathways are described below in Table 4. The series on underlying assumptions are discussed in detail in the article:
(PASTE PHOTO)XXXXXXX
Environmental assessment:
• All SAFs routes explored offer a reduction to global environmental impact of across 70% when compared to alternative conventional jet fuels. Specific reduction is heavily dependent on specific production path, as presented in Table 9 below. • However, at a local scale they have adverse impacts, particularly related to toxicity, acidification of land and land occupation inherently related with agricultural production chain of feedstock. • Between the 8 scenarios analyzed, FT routes exhibit best environmental performance, followed by ATJ's performance which is heavily impacted by low conversion yields and fewer coproducts to share the environmental impact. Lastly, HEFA exhibits the least favorable scenario due to the large volume of input required and the heavy use of fertilizers associated to them.
(PASTE PHOTO)XXXXXXX
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
Technical Model
DESCRIPTION OF THE TABLE & MODEL (XXXXX)
| Decision Variable | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feedstock Detail | FFO - Food-grade Fats & Oils | WFO - Waste Fats & Oil | ALG - Algae Oil | NFW - Non-Crop Food Waste | MSW - Municipal Solid Waste | FAR - Forest & Agricultural Residues | CNG - Coal, Natural Gas, Biomass | WCO - CO₂ & H₂O |
| Feedstock Generation | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 3rd | 3rd | 3rd | 3rd | 3rd |
| Feedstock Type | Bio-Fuels | Bio-Fuels | Bio-Fuels | Bio-Fuels | Bio-Fuels | Bio-Fuels | Bio-Fuels | E-fuels |
| Process | Coprocessing | Coprocessing | Coprocessing | Processing | Processing | Processing | Processing | Processing |
| Pathways | HEFA | HEFA | HEFA, AtJ, FT | HEFA, AtJ, FT | FT | AtJ & FT | FT | PtL |
| Carbon Intensity (g CO₂/MJ) | 15-30 | 10-20 | 0-15 | 15-30 | 10-30 | 5-20 | 70-90 | 0 |
| Energy Density (MJ/kg) | ~37 | ~37 | ~35 | ~37 | ~36 | ~37 | ~38 | ~40 |
| Production Cost ($/L) | $1.0 - 1.5 | $0.7 - 1.2 | $2.0 - 3.5 | $1.5 - 2.5 | $1.0 - 2.0 | $1.2 - 2.0 | $0.8 - 1.5 | $3.0+ |
| Blending Ratio | Up to 50% | Up to 50% | Up to 100% | Up to 50% | Up to 50% | Up to 50% | Up to 50% | Up to 100% |
| Production Scalability | Small to Medium | Medium | Small | Medium | Medium to Large | Medium to Large | Large | Small |
Financial Model
List of R&D Projects
Key Publications, Presentations and Patents
Technology Strategy Statement
References
[1] “Developing Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF).” Accessed October 6, 2024. https://www.iata.org/en/programs/sustainability/sustainable-aviation-fuels/
[2] IATA, “SAF Handbook”, May 2024. https://www.iata.org/contentassets/d13875e9ed784f75bac90f000760e998/saf-handbook.pdf
[3] BCG, “Brazil Climate Report 2024”, September 2024. https://web-assets.bcg.com/60/86/f21ad8b64238aac139c9c95624e3/brazil-climate-summit-2024.pdf
[4] Portal da Câmara dos Deputados. “Entra em vigor a ‘Lei do Combustível do Futuro’ - Notícias.” Accessed October 9, 2024. https://www.camara.leg.br/noticias/1101627-entra-em-vigor-a-lei-do-combustivel-do-futuro/.
[5] U.S. Department of Energy, U.S. Department of Transportation, U.S. Department of Agriculture, and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. 2022. SAF Grand Challenge Roadmap: Flight Plan for Sustainable Aviation Fuel. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Department of Energy. https://www.energy.gov/sites/default/files/2022-09/beto-saf-gc-roadmap-report-sept-2022.pdf
[6] Litoral Press. “El Mercurio,” April 18, 2024. https://www.litoralpress.cl/sitio/Prensa_Detalles.cshtml?LPKey=NIKYMS2WMDPQQYZFDBKTCTO4BRTUQCQSU6C2XUEHIL5WPDACR6LQA6OINT3J5EFUEQBSBYX4DNSIA.
[7] “Brasil Pode Ser a ‘Arábia Saudita Do SAF’, Prevê CEO Da Airbus - AgFeed.” Accessed October 7, 2024. https://agfeed.com.br/negocios/brasil-pode-ser-a-arabia-saudita-do-saf-preve-ceo-da-airbus/#.