In Space Propellant Depot
Roadmap Overview
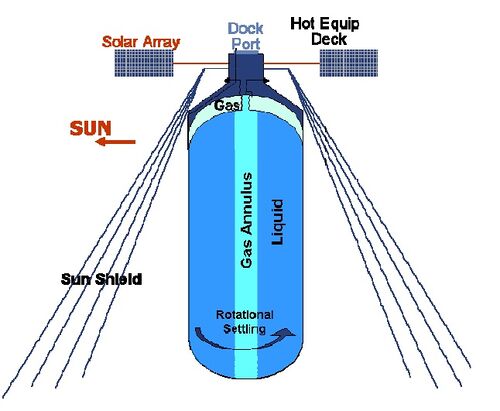
In the late 1800s James Dewar became famous for his study in the liquefaction of gases such as hydrogen and oxygen. Current Cryogenic storage containers are referred to as dewars. In the 1959 both LOX and LH2 were used to propel the second and third stages of the Saturn rocket. In 1966 LH2 and LOX were chosen to power the Atlas-Centaur rocket. “As early as 1928, scientists studying interplanetary travel began arguing that pre-positioning propellants in orbit would be required for any sustainable large-scale travel beyond Earth.” [1]. In 2007 Boeing addressed the value of creating propellant depots to increase the payload one could carry to future moon missions [2]. This idea was also brought up to Masten space systems in 2008[3]. In 2010 ULA (United Launch Alliance), began to develop ACES (Advanced Cryogenic Evolved Stage) which was a high-performance upper stage rocket with the ability to store and transfer propellant to later missions. ULA also was working on creating CRYOTE (Cryogenic Orbital Testbed) to demonstrate the feasibility of cryogenic fluid management in micro and zero gravity [5]. In 2015 NASA was able to maintain zero boil off on an earth-based test bed using LOX for 19 days [6]. In 2018 Vice President Pence at the 34th Space Symposium outlined the plan to have NASA return to the moon with the eventual use of a space depot. [6]. To date though there has been no space tested propellant depot.
<ref>Goff Ja et al. “Realistic Near-Term Propellant Depots: Implementation of a Critical Spacefaring Capability” p 2 </ref>
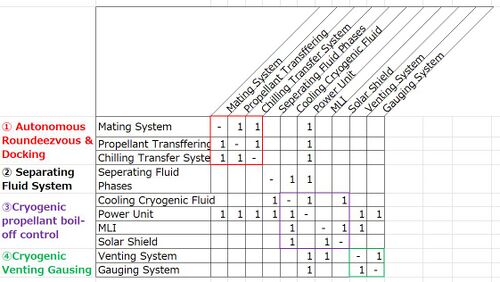
Design Structure Matrix
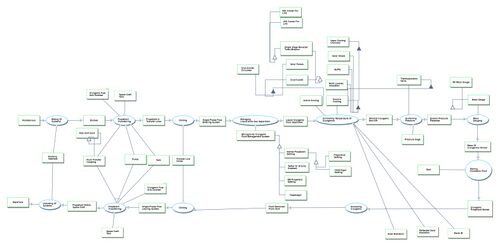
Object Process Diagram
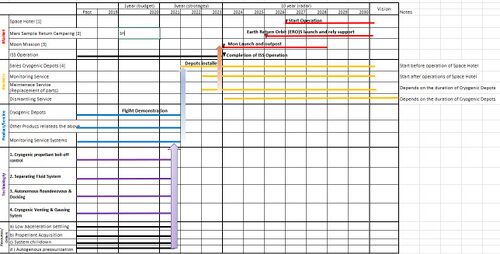
Technology Roadmap
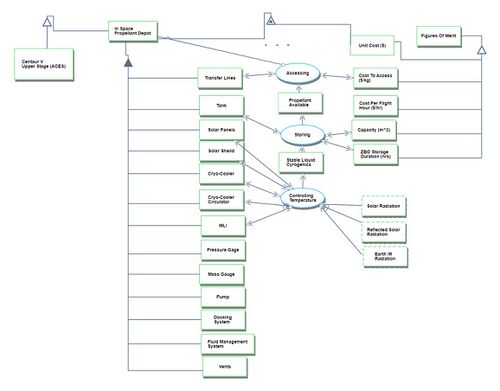
Figures of Merit
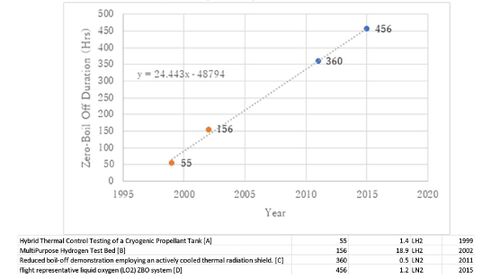
The FOMs are following:
● Duration of ZBO storage [days]
● Maximum Capacity [m^3]
● Unit Cost [$]
● Cost per hour(operational and maintenance [$/hr]
● Cost to attain per weight [$/kg]