Electric Vehicle Charging Technologies
EV Charging Technology Roadmap
- 2EVCT - Electric Vehicle Charging Technology
This is a Level 2 roadmap. Level 1 would be the technologies enabling zero-emission transport while Level 3 and 4 would include technologies enabling the charging of electric vehicles.
Roadmap Overview
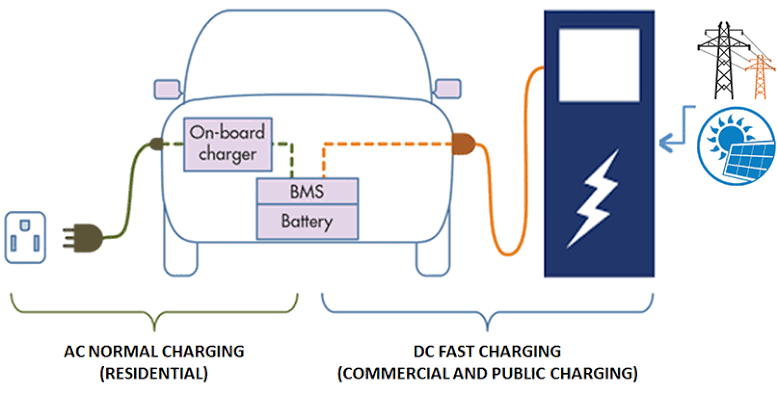
Our chosen technology is that of charging energy storage devices using power from the grid. With the current technology, electric vehicles can be charged using a standard 120V outlet or a 240V industrial outlet. An electric vehicle usually has an onboard charger unit (OBC) which converts AC power into DC to store it in the high voltage battery. The vehicle accepts charge via a charge port where the user can insert the charging plug. The charging plug is a part of a wall-mounted (off-board) unit which is connected to the grid and supplies AC power to the vehicle when the vehicle is ready to accept charge. The user is usually responsible for initiating charging by connecting the vehicle to the off-board unit (EVSE) and optionally keying in a unique id to “unlock” the unit to provide charge.
*image-source - https://www.verdemobility.com/charge.html
With today’s technology long-range EVs (200+ mile range) could take as high as 12+ hours to fully charge the battery pack using a regular home outlet. Fast charging technologies have also been developed which can bring the charge time down to a few hours (~2 hours), but these times are still significantly higher than the time needed to fill a fuel tank in a gasoline/ diesel vehicle and also warrant better cooling technologies to keep optimal battery thermal performance. With the battery cost ($ per KWh or $ per mile) decreasing, we could see a trend of bigger batteries / higher range vehicles being deployed, which would further increase the charging time. Hence, we feel the current technology would have to be advanced to be able to charge as fast as possible, thus reducing range anxiety.