Blockchain As A For Service Supply Chain
Technology Roadmap
Roadmap Overview
Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) will be used to enhance data traceability and integrity in the supply chain by utilizing blockchain using Hyperledger Fabric, which is an open-source modular blockchain framework that has “permissioned” networks.
The supply chain data (events, transactions, technical information) is stored in hashed smart contracts (blockchain) to have transparent and traceable records. If there is a request (such as a recall), the supply chain information of the product can be retracted to inform the stakeholders. Data integrity is achieved through a consensus protocol of nodes on the blockchain.
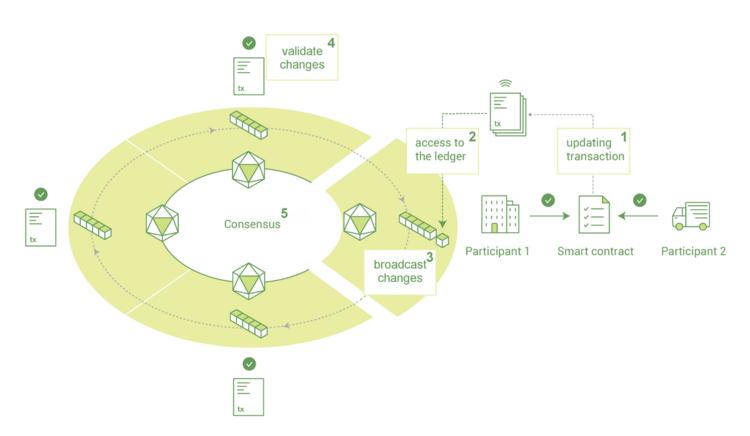
Image from https://blog.codecentric.de/en/2018/04/blockchain-application-fabric-composer/
Supported by the cloud infrastructure [3CIS], Blockchain-as-a-Service [2BAS] would have upload tools, analytical tools, and read tools. Upload tools [4US] would generate digital data [5DD] into smart contracts [5SC] and blockchain product ID [5BPID]. Analytics tools [4AT] would organize the encrypted data [5OED]. Read tools [4RT] would generate data traced reports [5DTR].
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
Object Process Model (OPM)
Figures of Merit (FOM)
We have gathered FOM of maximum transactions per second for different blockchain technologies against the released year of each technology to understand the rate of improvement:
8 https://www.ibm.com/blogs/research/2018/02/architecture-hyperledger-fabric/
9 https://mg.co.za/special-reports/2021-09-21-binance-coin-a-top-performing-cryptocurrency/
10 https://mg.co.za/special-reports/2021-09-07-why-solana-is-the-top-performing-cryptocurrency-of-2021/
This yielded a rough exponential graph with an equation 3.08E-184e^0.214x:
Referring to Figure 4-15 in Chapter 4, we concluded that blockchain technology is still early and considered to be in its Takeoff and not yet slowing nor in stagnation. The theoretical limit of blockchain would be bound to a practical number of servers and the performance of the servers. Just like any other distributed system, blockchain can scale both vertically (with the enhancement of performance of machines) and horizontally (with the additional number of servers); and thus, it is very early to find the theoretical limit at this moment even if it exists.