Difference between revisions of "Electric Aircraft Propulsion Architectures"
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
reference existing roadmaps: [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/Sample_Technology_Roadmap_-_Solar_Electric_Aircraft 2SEA]] [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/Solar-Powered_HALE_Aircraft,_by_Naoki_Kobayashi,_Alex_Kunycky,_Yuya_Makino 2SPA]] ] [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/WorldWide_eVTOL 2EVL ]] [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/Energy_Storage_via_Battery 3ESB]] | reference existing roadmaps: [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/Sample_Technology_Roadmap_-_Solar_Electric_Aircraft 2SEA]] [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/Solar-Powered_HALE_Aircraft,_by_Naoki_Kobayashi,_Alex_Kunycky,_Yuya_Makino 2SPA]] ] [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/WorldWide_eVTOL 2EVL ]] [[https://roadmaps.mit.edu/index.php/Energy_Storage_via_Battery 3ESB]] | ||
[[File:DSM EAPATree.JPG]] | [[File:DSM EAPATree.JPG]](1) | ||
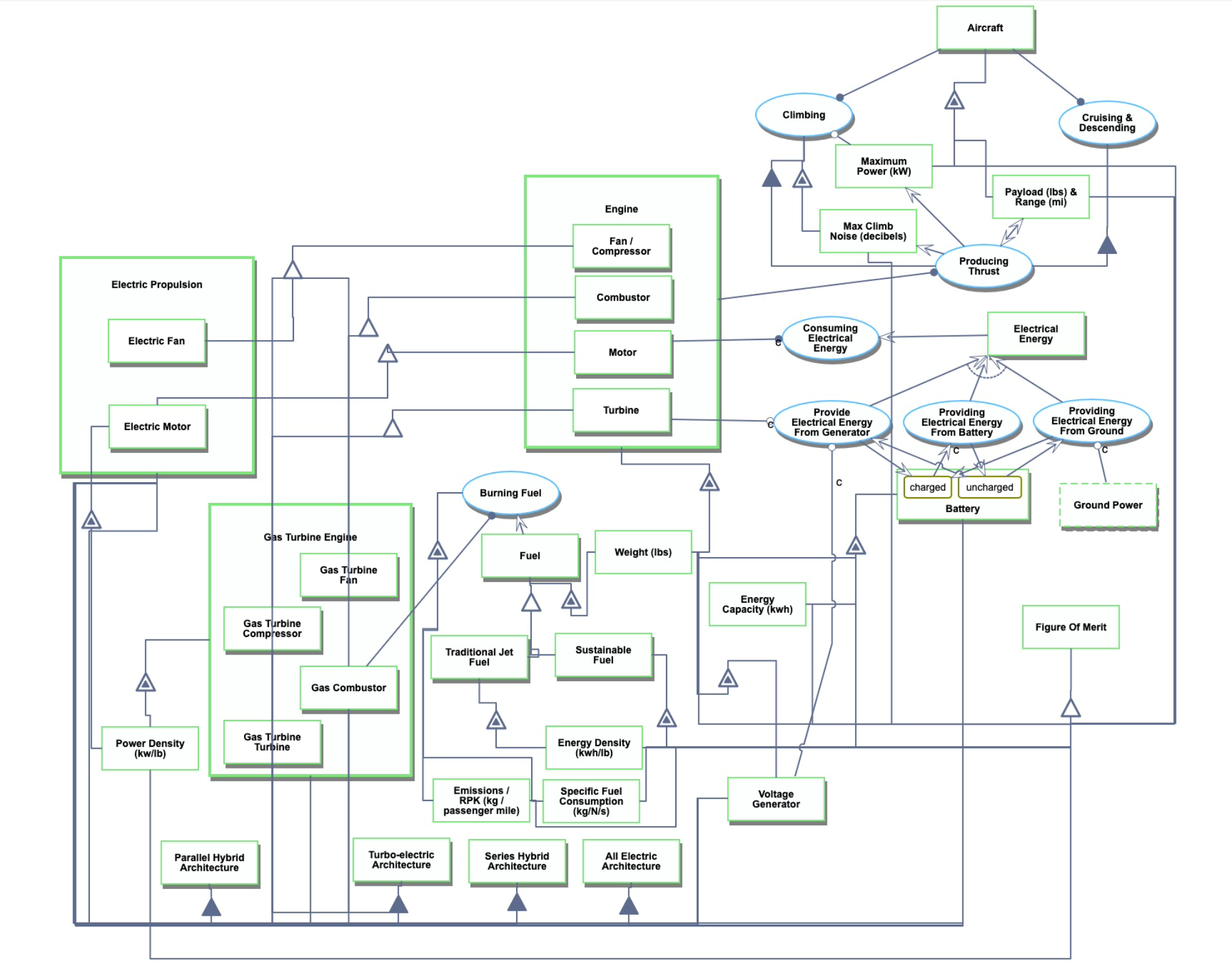
==Roadmap Model using OPM== | ==Roadmap Model using OPM== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
==Technology Strategy Statement== | ==Technology Strategy Statement== | ||
TBD | TBD | ||
==Resources== | |||
(1) https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20180004252/downloads/20180004252.pdf | |||
Revision as of 22:19, 10 October 2021
Team members: Josh Weisburg, Scarlett Koller, Jennifer Pandolf
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
The unique identifier for this roadmap is:
- 3EAPA - Electric Aircraft Propulsion Architectures
This indicates that we are dealing with a “level 3” roadmap at the subsystem level, where "level 1" would indicate a market level roadmap (airline industry), “level 2” would indicate a product level roadmap (aircraft) and “level 4” would indicate an individual technology roadmap (propulsion subsystem components). We are considering this roadmap of propulsion architectures as "level 3" because it is being developed specifically for commercial aircraft applications (only one relevant "level 2" roadmap).
Roadmap Overview
Modern aircraft burn hydrocarbon fuels to create thrust, but electric power from renewable sources is an opportunity to reduce operating cost & emissions. Electric propulsion requires extremely dense (by weight) energy storage and motor power, which is not yet sufficient for commercial aircraft travel. To utilize electric power in the meantime, hybrid architectures utilize electric motors either alongside gas turbine engines (Parallel Hybrid), or to apply the power of a gas turbine engine to create thrust (Turbo & Series).
To summarize the 4 key electric propulsion architecture options:
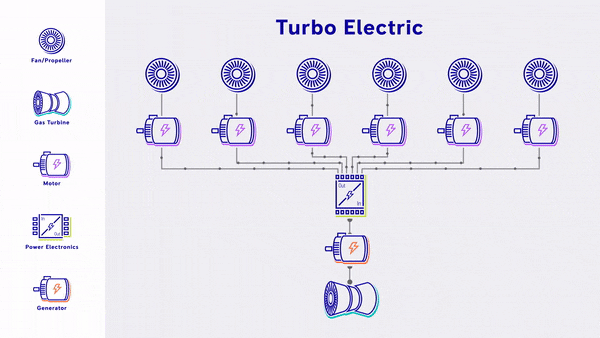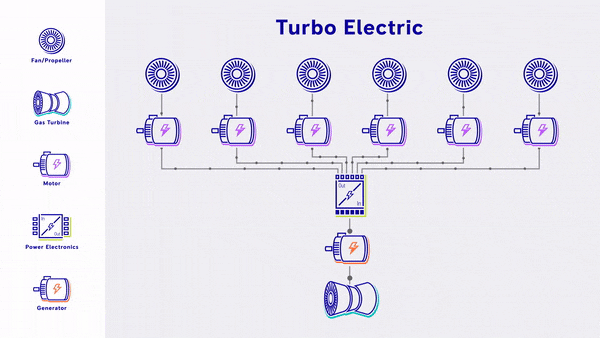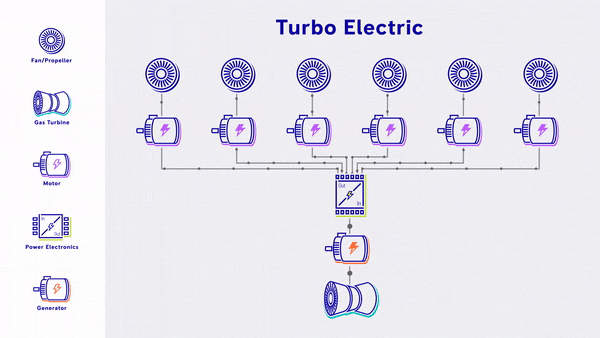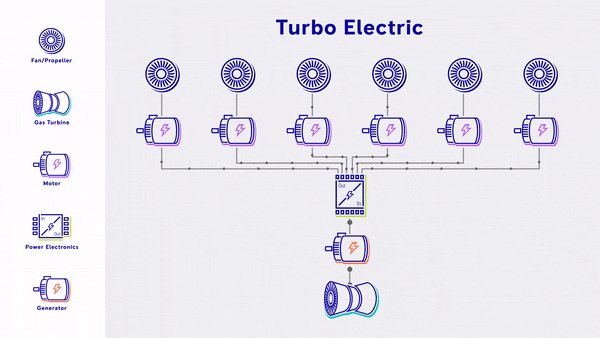
- Turbo-Electric - Uses a gas turbine to generate electricity, which is fed straight into electric based propulsion, without any energy storage.
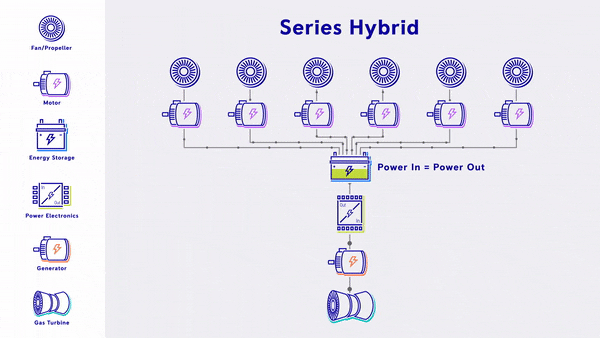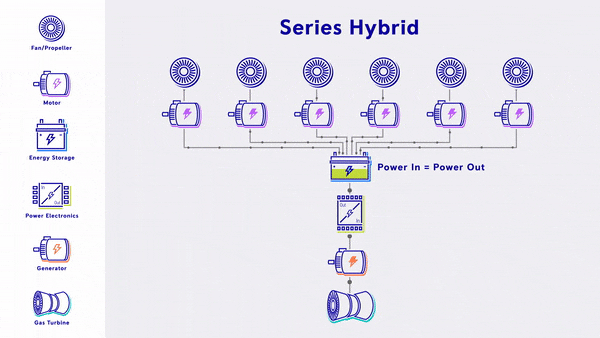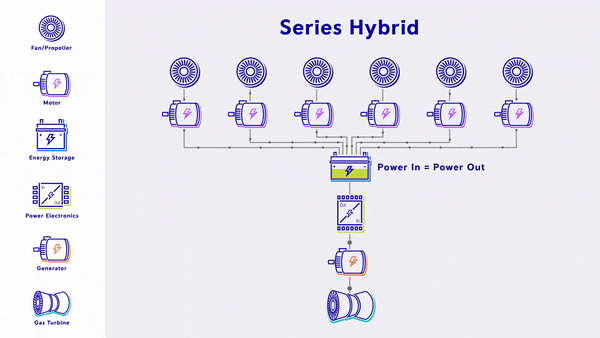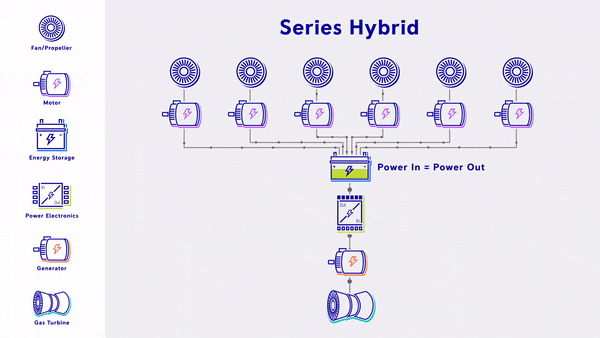
- Series Hybrid - Uses a gas turbine to generate electricity, which is fed into electric based propulsion through a battery that provides energy storage.
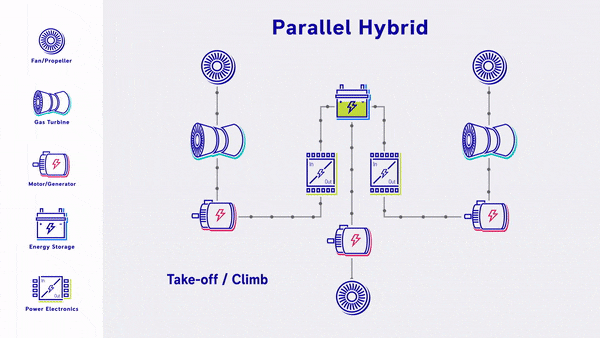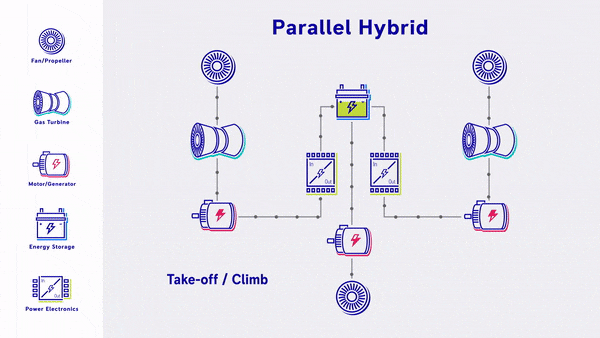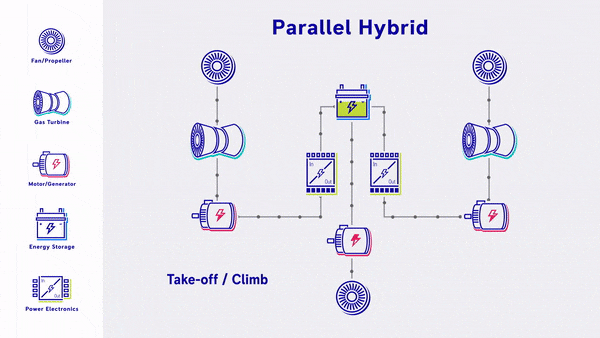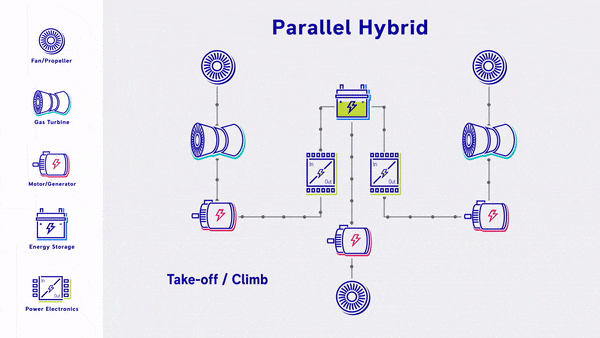
- Parallel Hybrid - Propulsive power is provided by a mix of gas turbine driven fans and electric driven fans, with energy storage. The gas turbine engines power both the fan and the electric motor & battery. The electric motors are used as supplemental power during take off & climb.
- All Electric - No gas turbines are used, the propulsive power is all electric. Batteries provide energy storage and power all of the fans.
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
reference existing roadmaps: [2SEA] [2SPA] ] [2EVL ] [3ESB]
Roadmap Model using OPM
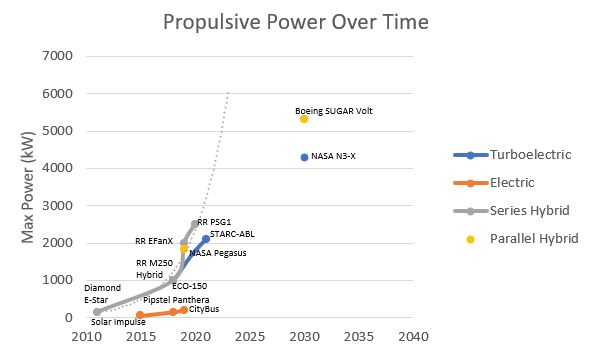
Figures of Merit
Alignment with Company Strategic Drivers
TBD - To be developed
Positioning of Company vs. Competition
TBD
Technical Model
TBD
Financial Model
TBD
Key Publications, Presentations and Patents
TBD
Technology Strategy Statement
TBD
Resources
(1) https://ntrs.nasa.gov/api/citations/20180004252/downloads/20180004252.pdf