Difference between revisions of "Variable Emissivity Materials For Spacecraft"
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
Note the DSM identifies the launch vehicle interface as a critical external dependency. While this is not in the scope of this roadmap, the availability and ultimately cost ($/kg) to launch the satellite to orbit is critical to the 2SDC roadmap and its profitability. Please reference [[Orbital_Launch_Vehicles_Roadmap|Orbital Launch Vehicle Roadmap]] for more on that roadmap. | Note the DSM identifies the launch vehicle interface as a critical external dependency. While this is not in the scope of this roadmap, the availability and ultimately cost ($/kg) to launch the satellite to orbit is critical to the 2SDC roadmap and its profitability. Please reference [[Orbital_Launch_Vehicles_Roadmap|Orbital Launch Vehicle Roadmap]] for more on that roadmap. | ||
==Sources== | |||
Birgisdottir, Rolf Frischknecht, Guillaume Habert, Thomas Lützkendorf, Alexander Passer, | |||
Embodied GHG emissions of buildings – The hidden challenge for effective climate change mitigation, | |||
Applied Energy, | |||
Volume 258, | |||
2020, | |||
114107, | |||
ISSN 0306-2619, | |||
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114107. | |||
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261919317945) | |||
Revision as of 00:37, 10 October 2024
Technology Roadmap Sections and Deliverables
- 2SDC - Satellite Data Communication
This technology is described a the level 2 level as it is a delivered service. While the service could be split across many markets (e.g. selling bandwidth and owning satellite only), for the purposes of this roadmap, 2SDC includes the ground segment, space segment, and user equipment to enable Satellite Data Communications.
Roadmap Overview
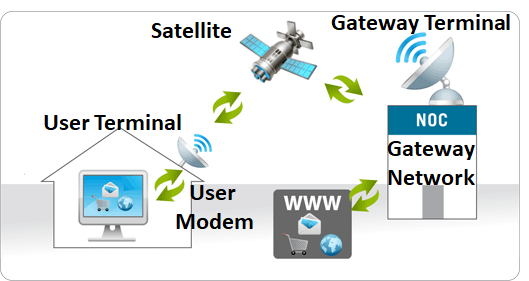
The working principle and architecture of satellite data communication is depicted in the below.
Satellite-based internet/voice access is enabled by satellites, which provide relay to extend communication beyond traditional (terrestrial) line of site of the network and users. Data encoded in radio waves is sent from the ground station, relayed via the satellite, to the user’s location. Advances in technology include High Throughput Satellites (HTS) and some next-generation satellite systems may follow low-earth orbit rather than geosynchronous orbits, which would reduce latency dramatically.
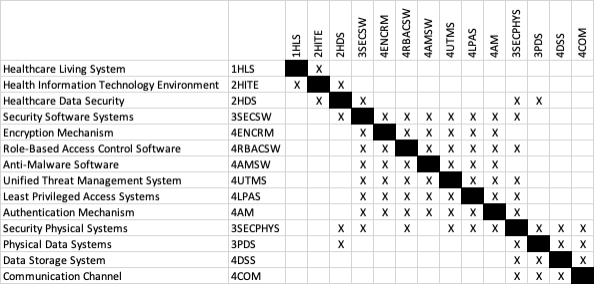
Design Structure Matrix (DSM) Allocation
The 2-SDC tree that we can extract from the DSM above shows us that Satellite Data Communication (2SDC) is part of a larger abstraction of wireless duplex communication (1WDC), and that it requires the following key enabling technologies at the system level:
- 3SCP Satellite Communication Payload
- 3SGT Satellite Gateway Terminal
- 3USM User Satellite Modem
- 3UST User Satellite Terminal
In turn these require enabling technologies at level 4, the technology subsystem level:
- 4SRA Satellite Receive Antenna
- 4STA Satellite Transmit Antenna
- 4SCE Satellite Communication Electronics
- 4SGA Satellite Gateway Aperture
- 4GTE Gateway Transmit Electronics
- 4GRE Gateway Receive Electronics
- 4UMM User Modem Modulator
- 4UMD User Modem Demodulator
- 4USA User Satellite Aperture
- 4TSC Transmit Signal Conditioners
- 4RSC Receive Signal Conditioners
Note the DSM identifies the launch vehicle interface as a critical external dependency. While this is not in the scope of this roadmap, the availability and ultimately cost ($/kg) to launch the satellite to orbit is critical to the 2SDC roadmap and its profitability. Please reference Orbital Launch Vehicle Roadmap for more on that roadmap.
Sources
Birgisdottir, Rolf Frischknecht, Guillaume Habert, Thomas Lützkendorf, Alexander Passer, Embodied GHG emissions of buildings – The hidden challenge for effective climate change mitigation, Applied Energy, Volume 258, 2020, 114107, ISSN 0306-2619, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114107. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306261919317945)